The mechanics of microtubule networks in cell division
- PMID: 28490474
- PMCID: PMC5461028
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201612064
The mechanics of microtubule networks in cell division
Abstract
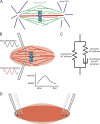
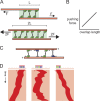
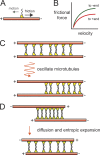
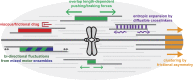
The primary goal of a dividing somatic cell is to accurately and equally segregate its genome into two new daughter cells. In eukaryotes, this process is performed by a self-organized structure called the mitotic spindle. It has long been appreciated that mechanical forces must be applied to chromosomes. At the same time, the network of microtubules in the spindle must be able to apply and sustain large forces to maintain spindle integrity. Here we consider recent efforts to measure forces generated within microtubule networks by ensembles of key proteins. New findings, such as length-dependent force generation, protein clustering by asymmetric friction, and entropic expansion forces will help advance models of force generation needed for spindle function and maintaining integrity.
© 2017 Forth and Kapoor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microtubule cytoskeleton: navigating the intracellular landscape.Curr Biol. 2003 May 27;13(11):R430-2. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00362-2. Curr Biol. 2003. PMID: 12781150 Review.
-
Mechanically Distinct Microtubule Arrays Determine the Length and Force Response of the Meiotic Spindle.Dev Cell. 2019 Apr 22;49(2):267-278.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2019.03.014. Epub 2019 Apr 11. Dev Cell. 2019. PMID: 30982663
-
Spindle pole mechanics studied in mitotic asters: dynamic distribution of spindle forces through compliant linkages.Biophys J. 2011 Apr 6;100(7):1756-64. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.02.017. Biophys J. 2011. PMID: 21463589 Free PMC article.
-
Spindle microtubules in flux.J Cell Sci. 2005 Mar 15;118(Pt 6):1105-16. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02284. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 15764594
-
Mitotic spindle assembly in animal cells: a fine balancing act.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Mar;18(3):187-201. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.162. Epub 2017 Feb 8. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28174430 Review.
Cited by
-
High-quality frozen extracts of Xenopus laevis eggs reveal size-dependent control of metaphase spindle micromechanics.Mol Biol Cell. 2017 Aug 1;28(16):2170-2177. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E17-03-0174. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28592634 Free PMC article.
-
Active Bending of Disordered Microtubule Bundles by Kinesin Motors.ACS Omega. 2022 Nov 18;7(48):43820-43828. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c04958. eCollection 2022 Dec 6. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36506136 Free PMC article.
-
Seaweed Secondary Metabolites In Vitro and In Vivo Anticancer Activity.Mar Drugs. 2018 Oct 26;16(11):410. doi: 10.3390/md16110410. Mar Drugs. 2018. PMID: 30373208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell cycle transcriptomics of Capsaspora provides insights into the evolution of cyclin-CDK machinery.PLoS Genet. 2020 Mar 16;16(3):e1008584. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008584. eCollection 2020 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32176685 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional organization of the cytoskeleton: A cryo-electron tomography perspective.Protein Sci. 2020 Jun;29(6):1302-1320. doi: 10.1002/pro.3858. Protein Sci. 2020. PMID: 32216120 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

