TRAF2 and OTUD7B govern a ubiquitin-dependent switch that regulates mTORC2 signalling
- PMID: 28489822
- PMCID: PMC5695540
- DOI: 10.1038/nature22344
TRAF2 and OTUD7B govern a ubiquitin-dependent switch that regulates mTORC2 signalling
Abstract
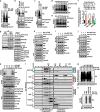
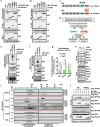
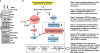
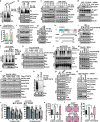
The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) has a key role in the integration of various physiological stimuli to regulate several cell growth and metabolic pathways. mTOR primarily functions as a catalytic subunit in two structurally related but functionally distinct multi-component kinase complexes, mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) and mTORC2 (refs 1, 2). Dysregulation of mTOR signalling is associated with a variety of human diseases, including metabolic disorders and cancer. Thus, both mTORC1 and mTORC2 kinase activity is tightly controlled in cells. mTORC1 is activated by both nutrients and growth factors, whereas mTORC2 responds primarily to extracellular cues such as growth-factor-triggered activation of PI3K signalling. Although both mTOR and GβL (also known as MLST8) assemble into mTORC1 and mTORC2 (refs 11, 12, 13, 14, 15), it remains largely unclear what drives the dynamic assembly of these two functionally distinct complexes. Here we show, in humans and mice, that the K63-linked polyubiquitination status of GβL dictates the homeostasis of mTORC2 formation and activation. Mechanistically, the TRAF2 E3 ubiquitin ligase promotes K63-linked polyubiquitination of GβL, which disrupts its interaction with the unique mTORC2 component SIN1 (refs 12, 13, 14) to favour mTORC1 formation. By contrast, the OTUD7B deubiquitinase removes polyubiquitin chains from GβL to promote GβL interaction with SIN1, facilitating mTORC2 formation in response to various growth signals. Moreover, loss of critical ubiquitination residues in GβL, by either K305R/K313R mutations or a melanoma-associated GβL(ΔW297) truncation, leads to elevated mTORC2 formation, which facilitates tumorigenesis, in part by activating AKT oncogenic signalling. In support of a physiologically pivotal role for OTUD7B in the activation of mTORC2/AKT signalling, genetic deletion of Otud7b in mice suppresses Akt activation and Kras-driven lung tumorigenesis in vivo. Collectively, our study reveals a GβL-ubiquitination-dependent switch that fine-tunes the dynamic organization and activation of the mTORC2 kinase under both physiological and pathological conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests. Readers are welcome to comment on the online version of the paper.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Dynamic modelling of the PI3K/MTOR signalling network uncovers biphasic dependence of mTORC1 activity on the mTORC2 subunit SIN1.PLoS Comput Biol. 2021 Sep 16;17(9):e1008513. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008513. eCollection 2021 Sep. PLoS Comput Biol. 2021. PMID: 34529665 Free PMC article.
-
Sin1 phosphorylation impairs mTORC2 complex integrity and inhibits downstream Akt signalling to suppress tumorigenesis.Nat Cell Biol. 2013 Nov;15(11):1340-50. doi: 10.1038/ncb2860. Epub 2013 Oct 27. Nat Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 24161930 Free PMC article.
-
Alkaline intracellular pH (pHi) increases PI3K activity to promote mTORC1 and mTORC2 signaling and function during growth factor limitation.J Biol Chem. 2023 Sep;299(9):105097. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105097. Epub 2023 Jul 26. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37507012 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Inhibition of Rictor/mTORC2 in Cancer Treatment: A New Era after Rapamycin.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2016;16(4):288-304. doi: 10.2174/1568009616666151113120830. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2016. PMID: 26563881 Review.
-
Disentangling the signaling pathways of mTOR complexes, mTORC1 and mTORC2, as a therapeutic target in glioblastoma.Adv Biol Regul. 2022 Jan;83:100854. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2021.100854. Epub 2021 Dec 6. Adv Biol Regul. 2022. PMID: 34996736 Review.
Cited by
-
OTUD7B knockdown inhibits proliferation and autophagy through AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in human prostate cancer cell.Discov Oncol. 2024 Jun 27;15(1):247. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01073-2. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38935308 Free PMC article.
-
SPOP and OTUD7A Control EWS-FLI1 Protein Stability to Govern Ewing Sarcoma Growth.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Jul;8(14):e2004846. doi: 10.1002/advs.202004846. Epub 2021 Jun 1. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34060252 Free PMC article.
-
K63-linked ubiquitination of DYRK1A by TRAF2 alleviates Sprouty 2-mediated degradation of EGFR.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Jun 11;12(6):608. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03887-2. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34117217 Free PMC article.
-
TBKBP1 and TBK1 form a growth factor signalling axis mediating immunosuppression and tumourigenesis.Nat Cell Biol. 2019 Dec;21(12):1604-1614. doi: 10.1038/s41556-019-0429-8. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Nat Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31792381 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Alterations of TRAF Proteins in Human Cancers.Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 20;9:2111. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02111. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30294322 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aylett CH, et al. Architecture of human mTOR complex 1. Science. 2016;351:48–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

