SET1A/COMPASS and shadow enhancers in the regulation of homeotic gene expression
- PMID: 28487406
- PMCID: PMC5435891
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.294744.116
SET1A/COMPASS and shadow enhancers in the regulation of homeotic gene expression
Abstract
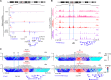
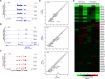
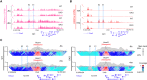
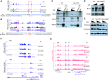
The homeotic (Hox) genes are highly conserved in metazoans, where they are required for various processes in development, and misregulation of their expression is associated with human cancer. In the developing embryo, Hox genes are activated sequentially in time and space according to their genomic position within Hox gene clusters. Accumulating evidence implicates both enhancer elements and noncoding RNAs in controlling this spatiotemporal expression of Hox genes, but disentangling their relative contributions is challenging. Here, we identify two cis-regulatory elements (E1 and E2) functioning as shadow enhancers to regulate the early expression of the HoxA genes. Simultaneous deletion of these shadow enhancers in embryonic stem cells leads to impaired activation of HoxA genes upon differentiation, while knockdown of a long noncoding RNA overlapping E1 has no detectable effect on their expression. Although MLL/COMPASS (complex of proteins associated with Set1) family of histone methyltransferases is known to activate transcription of Hox genes in other contexts, we found that individual inactivation of the MLL1-4/COMPASS family members has little effect on early Hox gene activation. Instead, we demonstrate that SET1A/COMPASS is required for full transcriptional activation of multiple Hox genes but functions independently of the E1 and E2 cis-regulatory elements. Our results reveal multiple regulatory layers for Hox genes to fine-tune transcriptional programs essential for development.
Keywords: COMPASS; Hox genes; SET1A; chromatin structure; enhancer; epigenetic marks.
© 2017 Cao et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CTCF-binding element regulates ESC differentiation via orchestrating long-range chromatin interaction between enhancers and HoxA.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100413. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100413. Epub 2021 Feb 11. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33581110 Free PMC article.
-
Histone H3K4 methylation-dependent and -independent functions of Set1A/COMPASS in embryonic stem cell self-renewal and differentiation.Genes Dev. 2017 Sep 1;31(17):1732-1737. doi: 10.1101/gad.303768.117. Epub 2017 Sep 22. Genes Dev. 2017. PMID: 28939616 Free PMC article.
-
A long noncoding RNA maintains active chromatin to coordinate homeotic gene expression.Nature. 2011 Apr 7;472(7341):120-4. doi: 10.1038/nature09819. Epub 2011 Mar 20. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21423168 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating Hox gene functions during animal body patterning.Nat Rev Genet. 2005 Dec;6(12):893-904. doi: 10.1038/nrg1726. Nat Rev Genet. 2005. PMID: 16341070 Review.
-
The MLL3/4 H3K4 methyltransferase complex in establishing an active enhancer landscape.Biochem Soc Trans. 2021 Jun 30;49(3):1041-1054. doi: 10.1042/BST20191164. Biochem Soc Trans. 2021. PMID: 34156443 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PAF1 regulation of promoter-proximal pause release via enhancer activation.Science. 2017 Sep 22;357(6357):1294-1298. doi: 10.1126/science.aan3269. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Science. 2017. PMID: 28860207 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic targeting of metabolic vulnerabilities in cancers with MLL3/4-COMPASS epigenetic regulator mutations.J Clin Invest. 2023 Jul 3;133(13):e169993. doi: 10.1172/JCI169993. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 37252797 Free PMC article.
-
CTCF-binding element regulates ESC differentiation via orchestrating long-range chromatin interaction between enhancers and HoxA.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100413. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100413. Epub 2021 Feb 11. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33581110 Free PMC article.
-
A distal enhancer maintaining Hoxa1 expression orchestrates retinoic acid-induced early ESCs differentiation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jul 26;47(13):6737-6752. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz482. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31147716 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of TWIST Transcription by Chromatin Remodeling Protein BRG1 Contributes to Liver Fibrosis in Mice.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 May 13;8:340. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00340. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32478075 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander T, Nolte C, Krumlauf R. 2009. Hox genes and segmentation of the hindbrain and axial skeleton. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 25: 431–456. - PubMed
-
- Andrey G, Montavon T, Mascrez B, Gonzalez F, Noordermeer D, Leleu M, Trono D, Spitz F, Duboule D. 2013. A switch between topological domains underlies HoxD genes collinearity in mouse limbs. Science 340: 1234167. - PubMed
-
- Bledau AS, Schmidt K, Neumann K, Hill U, Ciotta G, Gupta A, Torres DC, Fu J, Kranz A, Stewart AF, et al. 2014. The H3K4 methyltransferase Setd1a is first required at the epiblast stage, whereas Setd1b becomes essential after gastrulation. Development 141: 1022–1035. - PubMed
-
- Boyer LA, Plath K, Zeitlinger J, Brambrink T, Medeiros LA, Lee TI, Levine SS, Wernig M, Tajonar A, Ray MK, et al. 2006. Polycomb complexes repress developmental regulators in murine embryonic stem cells. Nature 441: 349–353. - PubMed
-
- Cartharius K, Frech K, Grote K, Klocke B, Haltmeier M, Klingenhoff A, Frisch M, Bayerlein M, Werner T. 2005. MatInspector and beyond: promoter analysis based on transcription factor binding sites. Bioinformatics 21: 2933–2942. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
