The extracellular matrix in myocardial injury, repair, and remodeling
- PMID: 28459429
- PMCID: PMC5409799
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI87491
The extracellular matrix in myocardial injury, repair, and remodeling
Abstract
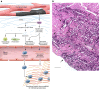
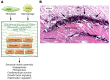
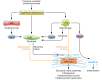
The cardiac extracellular matrix (ECM) not only provides mechanical support, but also transduces essential molecular signals in health and disease. Following myocardial infarction, dynamic ECM changes drive inflammation and repair. Early generation of bioactive matrix fragments activates proinflammatory signaling. The formation of a highly plastic provisional matrix facilitates leukocyte infiltration and activates infarct myofibroblasts. Deposition of matricellular proteins modulates growth factor signaling and contributes to the spatial and temporal regulation of the reparative response. Mechanical stress due to pressure and volume overload and metabolic dysfunction also induce profound changes in ECM composition that contribute to the pathogenesis of heart failure. This manuscript reviews the role of the ECM in cardiac repair and remodeling and discusses matrix-based therapies that may attenuate remodeling while promoting repair and regeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fibroblasts in myocardial infarction: a role in inflammation and repair.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014 May;70:74-82. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.11.015. Epub 2013 Dec 7. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24321195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Extracellular Matrix in Ischemic and Nonischemic Heart Failure.Circ Res. 2019 Jun 21;125(1):117-146. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.311148. Epub 2019 Jun 20. Circ Res. 2019. PMID: 31219741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The extracellular matrix modulates fibroblast phenotype and function in the infarcted myocardium.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2012 Dec;5(6):837-47. doi: 10.1007/s12265-012-9406-3. Epub 2012 Sep 7. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2012. PMID: 22956156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thrombospondins in the transition from myocardial infarction to heart failure.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016 Jan;90:102-10. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2015.12.009. Epub 2015 Dec 10. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 26686988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myofibroblasts and the extracellular matrix network in post-myocardial infarction cardiac remodeling.Pflugers Arch. 2014 Jun;466(6):1113-27. doi: 10.1007/s00424-014-1463-9. Epub 2014 Feb 13. Pflugers Arch. 2014. PMID: 24519465 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of HMGB1, TGF-β1, BIRC3, ADAM17, CDKN1A, and FTO in Relation to Left Ventricular Remodeling in Patients Six Months after the First Myocardial Infarction: A Prospective Study.Genes (Basel). 2024 Oct 2;15(10):1296. doi: 10.3390/genes15101296. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457420 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial Recovery versus Myocardial Regeneration: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Modulation.Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 2024 Aug 20;20(4):31-41. doi: 10.14797/mdcvj.1400. eCollection 2024. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 2024. PMID: 39184159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Infarct Collagen Topography Regulates Fibroblast Fate via p38-Yes-Associated Protein Transcriptional Enhanced Associate Domain Signals.Circ Res. 2020 Oct 23;127(10):1306-1322. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.316162. Epub 2020 Sep 4. Circ Res. 2020. PMID: 32883176 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiomyogenesis Modeling Using Pluripotent Stem Cells: The Role of Microenvironmental Signaling.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Aug 9;7:164. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00164. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31448277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond cardiomyocytes: Cellular diversity in the heart's response to exercise.J Sport Health Sci. 2023 Jul;12(4):423-437. doi: 10.1016/j.jshs.2022.12.011. Epub 2022 Dec 19. J Sport Health Sci. 2023. PMID: 36549585 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

