Inhibition of lung cancer growth by HangAmDan-B is mediated by macrophage activation to M1 subtype
- PMID: 28454399
- PMCID: PMC5403442
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2017.5730
Inhibition of lung cancer growth by HangAmDan-B is mediated by macrophage activation to M1 subtype
Abstract
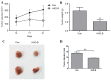
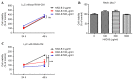
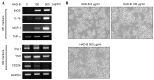
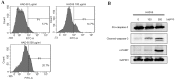
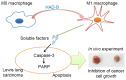
Re-education of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) toward antitumor effectors may be a promising therapeutic strategy for the successful treatment of cancer. HangAmDan-B (HAD-B), a herbal formula, has been used for stimulating immune function and activation of vital energy to cancer patients in traditional Korean Medicine. Previous studies have reported the anti-angiogenic and anti-metastatic effects of HAD-B; however, evidence on the immunomodulatory action of HAD-B was not demonstrated. In the present study, immunocompetent mice were used to demonstrate the suppression of the in vivo growth of allograft Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) cells, by HAD-B. In addition, HAD-B inhibited the in vitro growth of LLC cells by driving macrophages toward M1 polarization, but not through direct inhibition of tumor cell growth. Furthermore, culture media transfer of HAD-B-treated macrophages induced apoptosis of LLC cells. Results of the present study suggest that the antitumor effect of HAD-B may be explained by stimulating the antitumor function of macrophages. Considering the importance of re-educating TAMs in the regulation of the tumor microenvironment, the present study may confer another option for anti-cancer therapeutic strategy, using herbal medicines such as HAD-B.
Keywords: HangAmDan-B; M1; apoptosis; lung cancer; macrophage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Panax notoginseng Inhibits Tumor Growth through Activating Macrophage to M1 Polarization.Am J Chin Med. 2018;46(6):1369-1385. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X18500726. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Am J Chin Med. 2018. PMID: 30168347
-
The Ancient Chinese Decoction Yu-Ping-Feng Suppresses Orthotopic Lewis Lung Cancer Tumor Growth Through Increasing M1 Macrophage Polarization and CD4+ T Cell Cytotoxicity.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Nov 8;10:1333. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01333. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31780946 Free PMC article.
-
Lewis Lung Cancer Cells Promote SIGNR1(CD209b)-Mediated Macrophages Polarization Induced by IL-4 to Facilitate Immune Evasion.J Cell Biochem. 2016 May;117(5):1158-66. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25399. Epub 2015 Nov 2. J Cell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26447454
-
Targeting tumor-associated macrophages in the tumor microenvironment.Oncol Lett. 2020 Nov;20(5):234. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12097. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32968456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor promoting role of anti-tumor macrophages in tumor microenvironment.Cell Immunol. 2017 Jun;316:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2017.04.005. Epub 2017 Apr 13. Cell Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28433198 Review.
Cited by
-
The Crosstalk Between Tumor-Associated Macrophages (TAMs) and Tumor Cells and the Corresponding Targeted Therapy.Front Oncol. 2020 Nov 3;10:590941. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.590941. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33224886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomedicine-based co-delivery of a calcium channel inhibitor and a small molecule targeting CD47 for lung cancer immunotherapy.Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 11;14(1):7306. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42972-2. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37951973 Free PMC article.
-
Bleomycin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in TPC-1 cells through reversing M2-macrophages polarization.Oncol Lett. 2018 Sep;16(3):3858-3866. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9103. Epub 2018 Jul 6. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30127999 Free PMC article.
-
Haimufang decoction, a Chinese medicine formula for lung cancer, arrests cell cycle, stimulates apoptosis in NCI-H1975 cells, and induces M1 polarization in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020 Aug 5;20(1):243. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-03031-1. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020. PMID: 32758223 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the IL-4/STAT6 Signaling Pathway Promotes Lung Cancer Progression by Increasing M2 Myeloid Cells.Front Immunol. 2019 Nov 13;10:2638. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02638. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31798581 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
