LIM kinases: cofilin and beyond
- PMID: 28445157
- PMCID: PMC5522193
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16978
LIM kinases: cofilin and beyond
Abstract
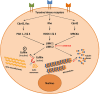
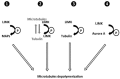
LIM kinases are common downstream effectors of several signalization pathways and function as a signaling node that controls cytoskeleton dynamics through the phosphorylation of the cofilin family proteins. These last 10 years, several reports indicate that the functions of LIM kinases are more extended than initially described and, specifically, that LIM kinases also control microtubule dynamics, independently of their regulation of actin microfilament. In this review we analyze the data supporting these conclusions and the possible mechanisms that could be involved in the control of microtubules by LIM kinases. The demonstration that LIM kinases also control microtubule dynamics has pointed to new therapeutic opportunities. Consistently, several new LIM kinase inhibitors have been recently developed. We provide a comprehensive comparison of these inhibitors, of their chemical structure, their specificity, their cellular effects as well as their effects in animal models of various diseases including cancer.
Keywords: LIM kinases; cytoskeleton; inhibitors; microtubules.
Conflict of interest statement
I would like to mention that, as shareholders of Cellipse S.A.S., L.Lafanechère and R. Prudent disclose a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LIM Kinases, Promising but Reluctant Therapeutic Targets: Chemistry and Preclinical Validation In Vivo.Cells. 2022 Jun 30;11(13):2090. doi: 10.3390/cells11132090. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35805176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A quantitative proteomic analysis of cofilin phosphorylation in myeloid cells and its modulation using the LIM kinase inhibitor Pyr1.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 14;13(12):e0208979. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208979. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30550596 Free PMC article.
-
LIMK2-1, a new isoform of human LIMK2, regulates actin cytoskeleton remodeling via a different signaling pathway than that of its two homologs, LIMK2a and LIMK2b.Biochem J. 2018 Dec 6;475(23):3745-3761. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170961. Biochem J. 2018. PMID: 30373762
-
Regulation of actin dynamics through phosphorylation of cofilin by LIM-kinase.Nature. 1998 Jun 25;393(6687):805-9. doi: 10.1038/31729. Nature. 1998. PMID: 9655397
-
LIM Kinases, LIMK1 and LIMK2, Are Crucial Node Actors of the Cell Fate: Molecular to Pathological Features.Cells. 2023 Mar 4;12(5):805. doi: 10.3390/cells12050805. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36899941 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Nature of Diamino Linker and Halogen Bonding Define Selectivity of Pyrrolopyrimidine-Based LIMK1 Inhibitors.Front Chem. 2021 Dec 13;9:781213. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.781213. eCollection 2021. Front Chem. 2021. PMID: 34966720 Free PMC article.
-
A spatial model of YAP/TAZ signaling reveals how stiffness, dimensionality, and shape contribute to emergent outcomes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 May 18;118(20):e2021571118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2021571118. Epub 2021 May 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33990464 Free PMC article.
-
LIM Kinases, Promising but Reluctant Therapeutic Targets: Chemistry and Preclinical Validation In Vivo.Cells. 2022 Jun 30;11(13):2090. doi: 10.3390/cells11132090. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35805176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MMP9 Differentially Regulates Proteins Involved in Actin Polymerization and Cell Migration during TGF-β-Induced EMT in the Lens.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 5;22(21):11988. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111988. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769418 Free PMC article.
-
Autoregulation of the LIM kinases by their PDZ domain.Nat Commun. 2023 Dec 19;14(1):8441. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44148-4. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 38114480 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Manetti F. LIM kinases are attractive targets with many macromolecular partners and only a few small molecule regulators. Med Res Rev. 2012;32:968–98. - PubMed
-
- Scott RW, Olson MF. LIM kinases: function, regulation and association with human disease. J Mol Med (Berl) 2007;85:555–68. - PubMed
-
- Okano I, Hiraoka J, Otera H, Nunoue K, Ohashi K, Iwashita S, Hirai M, Mizuno K. Identification and characterization of a novel family of serine/threonine kinases containing two N-terminal LIM motifs. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:31321–30. - PubMed
-
- Manning G, Whyte DB, Martinez R, Hunter T, Sudarsanam S. The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science. 2002;298:1912–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources