Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): an open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial
- PMID: 28434648
- PMCID: PMC7539326
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31046-2
Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): an open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial
Abstract
Background: For patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma, sorafenib is the only approved drug worldwide, and outcomes remain poor. We aimed to assess the safety and efficacy of nivolumab, a programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) immune checkpoint inhibitor, in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with or without chronic viral hepatitis.
Methods: We did a phase 1/2, open-label, non-comparative, dose escalation and expansion trial (CheckMate 040) of nivolumab in adults (≥18 years) with histologically confirmed advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with or without hepatitis C or B (HCV or HBV) infection. Previous sorafenib treatment was allowed. A dose-escalation phase was conducted at seven hospitals or academic centres in four countries or territories (USA, Spain, Hong Kong, and Singapore) and a dose-expansion phase was conducted at an additional 39 sites in 11 countries (Canada, UK, Germany, Italy, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan). At screening, eligible patients had Child-Pugh scores of 7 or less (Child-Pugh A or B7) for the dose-escalation phase and 6 or less (Child-Pugh A) for the dose-expansion phase, and an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 1 or less. Patients with HBV infection had to be receiving effective antiviral therapy (viral load <100 IU/mL); antiviral therapy was not required for patients with HCV infection. We excluded patients previously treated with an agent targeting T-cell costimulation or checkpoint pathways. Patients received intravenous nivolumab 0·1-10 mg/kg every 2 weeks in the dose-escalation phase (3+3 design). Nivolumab 3 mg/kg was given every 2 weeks in the dose-expansion phase to patients in four cohorts: sorafenib untreated or intolerant without viral hepatitis, sorafenib progressor without viral hepatitis, HCV infected, and HBV infected. Primary endpoints were safety and tolerability for the escalation phase and objective response rate (Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors version 1.1) for the expansion phase. This study is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT01658878.
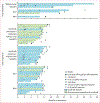
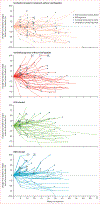
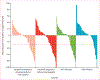
Findings: Between Nov 26, 2012, and Aug 8, 2016, 262 eligible patients were treated (48 patients in the dose-escalation phase and 214 in the dose-expansion phase). 202 (77%) of 262 patients have completed treatment and follow-up is ongoing. During dose escalation, nivolumab showed a manageable safety profile, including acceptable tolerability. In this phase, 46 (96%) of 48 patients discontinued treatment, 42 (88%) due to disease progression. Incidence of treatment-related adverse events did not seem to be associated with dose and no maximum tolerated dose was reached. 12 (25%) of 48 patients had grade 3/4 treatment-related adverse events. Three (6%) patients had treatment-related serious adverse events (pemphigoid, adrenal insufficiency, liver disorder). 30 (63%) of 48 patients in the dose-escalation phase died (not determined to be related to nivolumab therapy). Nivolumab 3 mg/kg was chosen for dose expansion. The objective response rate was 20% (95% CI 15-26) in patients treated with nivolumab 3 mg/kg in the dose-expansion phase and 15% (95% CI 6-28) in the dose-escalation phase.
Interpretation: Nivolumab had a manageable safety profile and no new signals were observed in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Durable objective responses show the potential of nivolumab for treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.
Funding: Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Immunotherapy: Nivolumab keeps HCC in check and opens avenues for checkmate.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2017 Jul;14(7):392. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.70. Epub 2017 May 9. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28485409 No abstract available.
-
Liver cancer: Nivolumab: checkmate for hepatocellular carcinoma?Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Jun;14(6):326. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.62. Epub 2017 May 10. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 28487550 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Nivolumab versus sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 459): a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2022 Jan;23(1):77-90. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00604-5. Epub 2021 Dec 13. Lancet Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34914889 Clinical Trial.
-
Sintilimab plus a bevacizumab biosimilar (IBI305) versus sorafenib in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (ORIENT-32): a randomised, open-label, phase 2-3 study.Lancet Oncol. 2021 Jul;22(7):977-990. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00252-7. Epub 2021 Jun 15. Lancet Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34143971 Clinical Trial.
-
Pembrolizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma previously treated with sorafenib (KEYNOTE-224): a non-randomised, open-label phase 2 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2018 Jul;19(7):940-952. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30351-6. Epub 2018 Jun 3. Lancet Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29875066 Clinical Trial.
-
Immune Checkpoint Inhibition in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Basics and Ongoing Clinical Trials.Oncology. 2017;92 Suppl 1:50-62. doi: 10.1159/000451016. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Oncology. 2017. PMID: 28147363 Review.
-
Nivolumab + Ipilimumab for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma previously treated with Sorafenib.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Jun;15(6):589-598. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2021.1899808. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33666530 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in immunotherapy for hepatitis B virus associated hepatocellular carcinoma patients.World J Hepatol. 2024 Oct 27;16(10):1158-1168. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i10.1158. World J Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 39474576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conversion therapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Advances and challenges.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Oct 15;16(10):4289-4297. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i10.4289. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39473953 Free PMC article.
-
Unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Transarterial chemoembolization combined with lenvatinib in combination with programmed death-1 inhibition is a possible approach.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Oct 15;16(10):4042-4044. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i10.4042. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39473949 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Immunotherapy: Predictors of Response, Issues, and Challenges.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 15;25(20):11091. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011091. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparing Lenvatinib/Pembrolizumab with Atezolizumab/Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Real-World Experience with Propensity Score Matching Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Oct 12;16(20):3458. doi: 10.3390/cancers16203458. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456553 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2015; 65: 87–108. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Zucman-Rossi J, Pikarsky E, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2016; 2: 16018. - PubMed
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver, European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 2012; 56: 908–43. - PubMed
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Hepatobiliary Cancers. Version 1.2017. 2017. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/f_guidelines.asp (accessed April 3, 2017).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

