c-MYC-Making Liver Sick: Role of c-MYC in Hepatic Cell Function, Homeostasis and Disease
- PMID: 28422055
- PMCID: PMC5406870
- DOI: 10.3390/genes8040123
c-MYC-Making Liver Sick: Role of c-MYC in Hepatic Cell Function, Homeostasis and Disease
Abstract
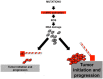
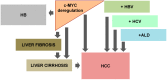
Over 35 years ago, c-MYC, a highly pleiotropic transcription factor that regulates hepatic cell function, was identified. In recent years, a considerable increment in the number of publications has significantly shifted the way that the c-MYC function is perceived. Overexpression of c-MYC alters a wide range of roles including cell proliferation, growth, metabolism, DNA replication, cell cycle progression, cell adhesion and differentiation. The purpose of this review is to broaden the understanding of the general functions of c-MYC, to focus on c-MYC-driven pathogenesis in the liver, explain its mode of action under basal conditions and during disease, and discuss efforts to target c-MYC as a plausible therapy for liver disease.
Keywords: Liver; alcoholic liver disease; c-Myc Avian Myelocytomatosis Viral Oncogene Homolog; hepatitis B virus; hepatitis C virus; hepatoblastoma; hepatocellular carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibitor of differentiation 1 transcription factor promotes metabolic reprogramming in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.FASEB J. 2016 Jan;30(1):262-75. doi: 10.1096/fj.15-277749. Epub 2015 Sep 1. FASEB J. 2016. PMID: 26330493 Free PMC article.
-
Pleiotropic effects of methionine adenosyltransferases deregulation as determinants of liver cancer progression and prognosis.J Hepatol. 2013 Oct;59(4):830-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.04.031. Epub 2013 May 7. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23665184 Review.
-
Immunohistochemical expression of CD95 (Fas), c-myc and epidermal growth factor receptor in hepatitis C virus infection, cirrhotic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma.APMIS. 2006 Jun;114(6):420-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0463.2006.apm_323.x. APMIS. 2006. PMID: 16856963
-
Expression of ras and c-myc oncoproteins and hepatitis B surface antigen in human liver disease.Hepatogastroenterology. 1993 Feb;40(1):37-40. Hepatogastroenterology. 1993. PMID: 8462926
-
MYC-associated and double-hit lymphomas: a review of pathobiology, prognosis, and therapeutic approaches.Cancer. 2014 Dec 15;120(24):3884-95. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28899. Epub 2014 Jul 24. Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25060588 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancing CRISPR/Cas gene editing through modulating cellular mechanical properties for cancer therapy.Nat Nanotechnol. 2022 Jul;17(7):777-787. doi: 10.1038/s41565-022-01122-3. Epub 2022 May 12. Nat Nanotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35551240 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant MFN2 transcription facilitates homocysteine-induced VSMCs proliferation via the increased binding of c-Myc to DNMT1 in atherosclerosis.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Jul;23(7):4611-4626. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14341. Epub 2019 May 18. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31104361 Free PMC article.
-
MF-094 nanodelivery inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting USP30.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022 Dec 6;27(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s11658-022-00407-8. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022. PMID: 36474192 Free PMC article.
-
The CpG Island-Binding Protein SAMD1 Contributes to an Unfavorable Gene Signature in HepG2 Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells.Biology (Basel). 2022 Apr 6;11(4):557. doi: 10.3390/biology11040557. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35453756 Free PMC article.
-
PTTG1 is involved in TNF-α-related hepatocellular carcinoma via the induction of c-myc.Cancer Med. 2019 Sep;8(12):5702-5715. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2473. Epub 2019 Aug 6. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 31385458 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

