Metallothionein, Copper and Alpha-Synuclein in Alpha-Synucleinopathies
- PMID: 28420950
- PMCID: PMC5380005
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00114
Metallothionein, Copper and Alpha-Synuclein in Alpha-Synucleinopathies
Abstract
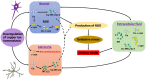
Metallothioneins (MTs) are proteins that function by metal exchange to regulate the bioavailability of metals, such as zinc and copper. Copper functions in the brain to regulate mitochondria, neurotransmitter production, and cell signaling. Inappropriate copper binding can result in loss of protein function and Cu(I)/(II) redox cycling can generate reactive oxygen species. Copper accumulates in the brain with aging and has been shown to bind alpha-synuclein and initiate its aggregation, the primary aetiological factor in Parkinson's disease (PD), and other alpha-synucleinopathies. In PD, total tissue copper is decreased, including neuromelanin-bound copper and there is a reduction in copper transporter CTR-1. Conversely cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) copper is increased. MT-1/2 expression is increased in activated astrocytes in alpha-synucleinopathies, yet expression of the neuronal MT-3 isoform may be reduced. MTs have been implicated in inflammatory states to perform one-way exchange of copper, releasing free zinc and recent studies have found copper bound to alpha-synuclein is transferred to the MT-3 isoform in vitro and MT-3 is found bound to pathological alpha-synuclein aggregates in the alpha-synucleinopathy, multiple systems atrophy. Moreover, both MT and alpha-synuclein can be released and taken up by neural cells via specific receptors and so may interact both intra- and extra-cellularly. Here, we critically review the role of MTs in copper dyshomeostasis and alpha-synuclein aggregation, and their potential as biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
Keywords: Parkinson's disease; copper; dementia with lewy bodies; metallothionein; multiple system atrophy; α-synuclein.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dexamethasone Inhibits Copper-Induced Alpha-Synuclein Aggregation by a Metallothionein-Dependent Mechanism.Neurotox Res. 2018 Feb;33(2):229-238. doi: 10.1007/s12640-017-9825-7. Epub 2017 Oct 24. Neurotox Res. 2018. PMID: 29064068
-
α-Synuclein and tau concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid of patients presenting with parkinsonism: a cohort study.Lancet Neurol. 2011 Mar;10(3):230-40. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70014-X. Lancet Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21317042
-
Membrane insertion exacerbates the α-Synuclein-Cu(II) dopamine oxidase activity: Metallothionein-3 targets and silences all α-synuclein-Cu(II) complexes.Free Radic Biol Med. 2020 Oct;158:149-161. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.07.006. Epub 2020 Jul 23. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 32712192 Free PMC article.
-
[Therapeutic strategy for Parkinson's disease: targeting zinc-binding protein in astrocytes].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2021;156(2):76-80. doi: 10.1254/fpj.20082. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2021. PMID: 33642534 Review. Japanese.
-
Distinct α-Synuclein strains and implications for heterogeneity among α-Synucleinopathies.Neurobiol Dis. 2018 Jan;109(Pt B):209-218. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2017.07.018. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Neurobiol Dis. 2018. PMID: 28751258 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ferritinophagy and α-Synuclein: Pharmacological Targeting of Autophagy to Restore Iron Regulation in Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 21;23(4):2378. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042378. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple System Atrophy: An Oligodendroglioneural Synucleinopathy1.J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;62(3):1141-1179. doi: 10.3233/JAD-170397. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018. PMID: 28984582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amyloids: Regulators of Metal Homeostasis in the Synapse.Molecules. 2020 Mar 23;25(6):1441. doi: 10.3390/molecules25061441. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32210005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in metabolic hormones and trace elements in CSF in active smokers indicate oxidative damage to brain cells.Endocr Connect. 2024 May 27;13(6):e240016. doi: 10.1530/EC-24-0016. Print 2024 Jun 1. Endocr Connect. 2024. PMID: 38688314 Free PMC article.
-
Zeolite and Neurodegenerative Diseases.Molecules. 2024 Jun 2;29(11):2614. doi: 10.3390/molecules29112614. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38893490 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anandhan A., Rodriguez-Rocha H., Bohovych I., Griggs A. M., Zavala-Flores L., Reyes-Reyes E. M., et al. . (2015). Overexpression of alpha-synuclein at non-toxic levels increases dopaminergic cell death induced by copper exposure via modulation of protein degradation pathways. Neurobiol. Dis. 81, 76–93. 10.1016/j.nbd.2014.11.018 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

