MicroRNA-143-3p, up-regulated in H. pylori-positive gastric cancer, suppresses tumor growth, migration and invasion by directly targeting AKT2
- PMID: 28404925
- PMCID: PMC5438685
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15646
MicroRNA-143-3p, up-regulated in H. pylori-positive gastric cancer, suppresses tumor growth, migration and invasion by directly targeting AKT2
Abstract
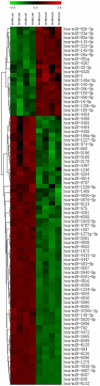
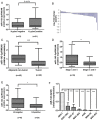
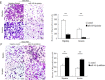
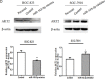
Our previous studies have suggested a protective role for H. pylori infection in the prognosis of gastric cancer. Based on those findings, we hypothesized that H. pylori-positive and -negative gastric cancers may exhibit different growth patterns and pathobiological behaviors, indicating different mechanisms of cancer progression. By microarray analysis, we studied miRNAs expression profiles in 42 gastric cancer patients, comparing 21 H. pylori-positive and 21 H. pylori-negative groups. Luciferase reporter assay and western blot were used to examine the potential target genes of the interested miRNA. In the present study, 53 miRNAs were significantly differentially expressed in H. pylori-positive and -negative gastric cancer tissues. We investigated the expression and function of one candidate, miR-143-3p, which was the most significantly increased miRNA in H. pylori-positive gastric cancer tissues. We observed that miR-143-3p expression was significantly decreased in gastric cancer tissues and cells, which correlated with late stage and lymph node metastasis. Using gain- and loss-of-function experiments in vitro, we demonstrate that miR-143-3p negatively regulated cell growth, apoptosis, migration and invasion. We further characterized AKT2 as a novel direct target of miR-143-3p. Knockdown of AKT2 expression mimicked the effects of miR-143-3p restoration. In conclusion, our data suggest that miR-143-3p acts as a novel tumor suppressive miRNA by regulating tumor growth, migration and invasion through directly targeting AKT2 gene. Further investigation is warranted to characterize the mechanisms underlying gastric cancer progression and may eventually contribute to its therapy.
Keywords: AKT2; Helicobacter pylori; gastric cancer; microRNA-143-3p; progression.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR-24-3p Regulates Progression of Gastric Mucosal Lesions and Suppresses Proliferation and Invasiveness of N87 Via Peroxiredoxin 6.Dig Dis Sci. 2016 Dec;61(12):3486-3497. doi: 10.1007/s10620-016-4309-9. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Dig Dis Sci. 2016. PMID: 27743162 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-29a-3p, Up-Regulated in Human Gastric Cells and Tissues with H.Pylori Infection, Promotes the Migration of GES-1 Cells via A20-Mediated EMT Pathway.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(3):1250-1263. doi: 10.1159/000495502. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30485838
-
MicroRNA-222-3p associated with Helicobacter pylori targets HIPK2 to promote cell proliferation, invasion, and inhibits apoptosis in gastric cancer.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Jul;119(7):5153-5162. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26542. Epub 2018 Mar 25. J Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29227536
-
The role of microRNAs in Helicobacter pylori pathogenesis and gastric carcinogenesis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012 Jan 3;1:21. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2011.00021. eCollection 2011. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22919587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric cancer: Function and clinical application.Pharmacol Res. 2024 Jul;205:107216. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107216. Epub 2024 May 16. Pharmacol Res. 2024. PMID: 38761883 Review.
Cited by
-
Function of Non-coding RNA in Helicobacter pylori-Infected Gastric Cancer.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 11;8:649105. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.649105. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34046430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SIRT1-targeted miR-543 autophagy inhibition and epithelial-mesenchymal transition promotion in Helicobacter pylori CagA-associated gastric cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Aug 19;10(9):625. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1859-8. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31423013 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs are involved in the development and progression of gastric cancer.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021 Jul;42(7):1018-1026. doi: 10.1038/s41401-020-00540-0. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021. PMID: 33037405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of miRNAs in placental extracellular vesicles in ovarian and endometrial cancer.Hum Cell. 2024 Jan;37(1):285-296. doi: 10.1007/s13577-023-00986-4. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Hum Cell. 2024. PMID: 37801261
-
MicroRNA-143-3p inhibits colorectal cancer metastases by targeting ITGA6 and ASAP3.Cancer Sci. 2019 Feb;110(2):805-816. doi: 10.1111/cas.13910. Epub 2019 Jan 4. Cancer Sci. 2019. PMID: 30536996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Forman D. The etiology of gastric cancer. IARC Sci Publ. 1991. pp. 22–32. - PubMed
-
- Meimarakis G, Winter H, Assmann I, Kopp R, Lehn N, Kist M, Stolte M, Jauch KW, Hatz RA. Helicobacter pylori as a prognostic indicator after curative resection of gastric carcinoma: a prospective study. Lancet Oncol. 2006;7:211–22. - PubMed
-
- He L, Hannon GJ. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:522–31. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

