Circulating miR-31 as an effective biomarker for detection and prognosis of human cancer: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 28404921
- PMCID: PMC5438681
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15638
Circulating miR-31 as an effective biomarker for detection and prognosis of human cancer: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Circulating miR-31 was found to be associated with cancers detection and prognosis. The present meta-analysis aimed to explore the effect of circulating miR-31 on cancer detection and prognosis.
Method: The studies were accessed using multiple databases. RevMan5.3, Meta-DiSc 1.4, and STATA14.0 were used to estimate the pooled effects, heterogeneity among studies, and publication bias.
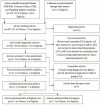
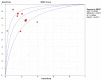
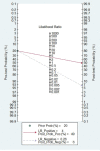
Results: A total of 14 studies with 1397 cancer patients and 1039 controls were included. For the 12 prognostic tests, the adjusted pooled-AUC was 0.79 (95% CI: 0.73-0.86) as the pooled sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio (PLR), negative likelihood ratio (NLR), diagnostic odd ratio (DOR) from 10 tests was 0.79 (95% CI: 0.76-0.82), 0.79 (95% CI: 0.76-0.82), 3.81 (95% CI: 2.90-5.01), 0.26 (95% CI: 0.20-0.35), and 16.81 (95% CI: 9.67-29.25), respectively. For the 5 prognosis analyses, the pooled HR (hazard ratio) of overall survival (OS) was 1.55 (95% CI 1.30-1.86) for high versus low circulating miR-31 expression. However, high expression of circulating miR-31 did not significantly increase the risk of poor differentiation (pooled OR=1.39, 95% CI: 0.56-3.47) and LNM (pooled OR=3.46, 95% CI: 0.96-12.42) in lung cancer.
Conclusion: Circulating miR-31 is an effective biomarker and could be used as a component of miRs signature for cancer detection and prognosis surveillance.
Keywords: carcinoma; detection; meta-analysis; miR-31; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Xiaoliang Chen, Yi Liu and Yong Cao have received research grants from Shenzhen Technology Research and Development Funds (JCYJ20150403095530583, 201604130086). Yunfang Chen has supported by Shenzhen Technology Research and Development Funds (JCYJ20140416094256880 and JCYJ20160428180919224). Jinbo Lin has supported by Shenzhen Technology Research and Development Funds (JCYJ20140411150916744) and the Science & Technology Project of Shenzhen Longgang District (201406063001026). Other authors declared no interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Diagnostic and prognostic value of circulating miR-21 for cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Gene. 2014 Jan 1;533(1):389-97. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.09.038. Epub 2013 Sep 26. Gene. 2014. PMID: 24076132 Review.
-
The value of miR-155 as a biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of lung cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2019 Nov 14;19(1):1103. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6297-6. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31727002 Free PMC article.
-
The diagnostic and prognostic values of microRNA-21 in patients with gastric cancer: a meta-analysis.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017 Jan;21(1):120-130. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28121346
-
Meta-analysis of diagnostic and prognostic value of miR-126 in non-small cell lung cancer.Biosci Rep. 2020 May 29;40(5):BSR20200349. doi: 10.1042/BSR20200349. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32329507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating microRNA-21 as a biomarker for the detection of various carcinomas: an updated meta-analysis based on 36 studies.Tumour Biol. 2015 Mar;36(3):1973-81. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2803-2. Epub 2014 Dec 20. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25527152
Cited by
-
Circulating MicroRNAs as Cancer Biomarkers in Liquid Biopsies.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1385:23-73. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-08356-3_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 36352210 Review.
-
Exploring the Potential of Non-Coding RNAs as Liquid Biopsy Biomarkers for Lung Cancer Screening: A Literature Review.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Sep 28;15(19):4774. doi: 10.3390/cancers15194774. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renal Oncocytoma: The Diagnostic Challenge to Unmask the Double of Renal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 26;23(5):2603. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052603. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-31-5p Is a Potential Circulating Biomarker and Therapeutic Target for Oral Cancer.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019 Jun 7;16:471-480. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.03.012. Epub 2019 Apr 11. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019. PMID: 31051332 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs as Urinary Biomarker for Oncocytoma.Dis Markers. 2018 Jul 16;2018:6979073. doi: 10.1155/2018/6979073. eCollection 2018. Dis Markers. 2018. PMID: 30116406 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim VN, Han J, Siomi MC. Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10:126–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

