Angiotensin receptor blocker drugs and inhibition of adrenal beta-arrestin-1-dependent aldosterone production: Implications for heart failure therapy
- PMID: 28400916
- PMCID: PMC5368669
- DOI: 10.4330/wjc.v9.i3.200
Angiotensin receptor blocker drugs and inhibition of adrenal beta-arrestin-1-dependent aldosterone production: Implications for heart failure therapy
Abstract
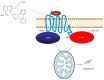
Aldosterone mediates many of the physiological and pathophysiological/cardio-toxic effects of angiotensin II (AngII). Its synthesis and secretion from the zona glomerulosa cells of the adrenal cortex, elevated in chronic heart failure (HF), is induced by AngII type 1 receptors (AT1Rs). The AT1R is a G protein-coupled receptor, mainly coupling to Gq/11 proteins. However, it can also signal through β-arrestin-1 (βarr1) or -2 (βarr2), both of which mediate G protein-independent signaling. Over the past decade, a second, Gq/11 protein-independent but βarr1-dependent signaling pathway emanating from the adrenocortical AT1R and leading to aldosterone production has become appreciated. Thus, it became apparent that AT1R antagonists that block both pathways equally well are warranted for fully effective aldosterone suppression in HF. This spurred the comparison of all of the currently marketed angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs, AT1R antagonists or sartans) at blocking activation of the two signaling modes (G protein-, and βarr1-dependent) at the AngII-activated AT1R and hence, at suppression of aldosterone in vitro and in vivo. Although all agents are very potent inhibitors of G protein activation at the AT1R, candesartan and valsartan were uncovered to be the most potent ARBs at blocking βarr activation by AngII and at suppressing aldosterone in vitro and in vivo in post-myocardial infarction HF animals. In contrast, irbesartan and losartan are virtually G protein-"biased" blockers at the human AT1R, with very low efficacy for βarr inhibition and aldosterone suppression. Therefore, candesartan and valsartan (and other, structurally similar compounds) may be the most preferred ARB agents for HF pharmacotherapy, as well as for treatment of other conditions characterized by elevated aldosterone.
Keywords: Adrenal cortex; Adrenocortical zona glomerulosa cell; Aldosterone; Angiotensin II type 1 receptor; Angiotensin receptor blocker; Heart failure; Suppression efficacy; β-arrestin-1.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Both authors declare no conflict of interest related to this publication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The place of ARBs in heart failure therapy: is aldosterone suppression the key?Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2019 Jan-Dec;13:1753944719868134. doi: 10.1177/1753944719868134. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2019. PMID: 31401939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adrenal angiotensin II type 1 receptor biased signaling: The case for "biased" inverse agonism for effective aldosterone suppression.Cell Signal. 2021 Jun;82:109967. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.109967. Epub 2021 Feb 25. Cell Signal. 2021. PMID: 33640432 Review.
-
Suppression of adrenal βarrestin1-dependent aldosterone production by ARBs: head-to-head comparison.Sci Rep. 2015 Jan 29;5:8116. doi: 10.1038/srep08116. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25631300 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II-dependent aldosterone production in the adrenal cortex.Vitam Horm. 2024;124:393-404. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2023.05.001. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Vitam Horm. 2024. PMID: 38408805
-
Structure-activity relationship study of angiotensin II analogs in terms of β-arrestin-dependent signaling to aldosterone production.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2016 Mar 8;4(2):e00226. doi: 10.1002/prp2.226. eCollection 2016 Apr. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2016. PMID: 27069636 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The place of ARBs in heart failure therapy: is aldosterone suppression the key?Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2019 Jan-Dec;13:1753944719868134. doi: 10.1177/1753944719868134. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2019. PMID: 31401939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Insights into the Crosstalk between Mineralocorticoid Receptor and G Protein-Coupled Receptors in Heart Adverse Remodeling and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 27;19(12):3764. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123764. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30486399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GRK5 is an essential co-repressor of the cardiac mineralocorticoid receptor and is selectively induced by finerenone.World J Cardiol. 2022 Apr 26;14(4):220-230. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v14.i4.220. World J Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35582468 Free PMC article.
-
Not all arrestins are created equal: Therapeutic implications of the functional diversity of the β-arrestins in the heart.World J Cardiol. 2019 Feb 26;11(2):47-56. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v11.i2.47. World J Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30820275 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Targeting ß-Arrestin.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Mar 6;10:124. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00124. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30894814 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Weber KT. Aldosterone in congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:1689–1697. - PubMed
-
- Connell JM, Davies E. The new biology of aldosterone. J Endocrinol. 2005;186:1–20. - PubMed
-
- Marney AM, Brown NJ. Aldosterone and end-organ damage. Clin Sci (Lond) 2007;113:267–278. - PubMed
-
- Zhao W, Ahokas RA, Weber KT, Sun Y. ANG II-induced cardiac molecular and cellular events: role of aldosterone. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006;291:H336–H343. - PubMed
-
- Ganguly A, Davis JS. Role of calcium and other mediators in aldosterone secretion from the adrenal glomerulosa cells. Pharmacol Rev. 1994;46:417–447. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

