Cyclic AMP-Elevating Capacity of Adenylate Cyclase Toxin-Hemolysin Is Sufficient for Lung Infection but Not for Full Virulence of Bordetella pertussis
- PMID: 28396322
- PMCID: PMC5442630
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00937-16
Cyclic AMP-Elevating Capacity of Adenylate Cyclase Toxin-Hemolysin Is Sufficient for Lung Infection but Not for Full Virulence of Bordetella pertussis
Abstract
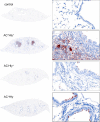
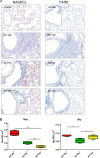
The adenylate cyclase toxin-hemolysin (CyaA, ACT, or AC-Hly) of Bordetella pertussis targets phagocytic cells expressing the complement receptor 3 (CR3, Mac-1, αMβ2 integrin, or CD11b/CD18). CyaA delivers into cells an N-terminal adenylyl cyclase (AC) enzyme domain that is activated by cytosolic calmodulin and catalyzes unregulated conversion of cellular ATP into cyclic AMP (cAMP), a key second messenger subverting bactericidal activities of phagocytes. In parallel, the hemolysin (Hly) moiety of CyaA forms cation-selective hemolytic pores that permeabilize target cell membranes. We constructed the first B. pertussis mutant secreting a CyaA toxin having an intact capacity to deliver the AC enzyme into CD11b-expressing (CD11b+) host phagocytes but impaired in formation of cell-permeabilizing pores and defective in cAMP elevation in CD11b- cells. The nonhemolytic AC+ Hly- bacteria inhibited the antigen-presenting capacities of coincubated mouse dendritic cells in vitro and skewed their Toll-like receptor (TLR)-triggered maturation toward a tolerogenic phenotype. The AC+ Hly- mutant also infected mouse lungs as efficiently as the parental AC+ Hly+ strain. Hence, elevation of cAMP in CD11b- cells and/or the pore-forming capacity of CyaA were not required for infection of mouse airways. The latter activities were, however, involved in bacterial penetration across the epithelial layer, enhanced neutrophil influx into lung parenchyma during sublethal infections, and the exacerbated lung pathology and lethality of B. pertussis infections at higher inoculation doses (>107 CFU/mouse). The pore-forming activity of CyaA further synergized with the cAMP-elevating activity in downregulation of major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II) molecules on infiltrating myeloid cells, likely contributing to immune subversion of host defenses by the whooping cough agent.
Keywords: Bordetella pertussis; adenylate cyclase toxin-hemolysin; cAMP intoxication; lung colonization; pore-forming activity; virulence.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Selective Enhancement of the Cell-Permeabilizing Activity of Adenylate Cyclase Toxin Does Not Increase Virulence of Bordetella pertussis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 28;22(21):11655. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111655. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769101 Free PMC article.
-
Transmembrane segments of complement receptor 3 do not participate in cytotoxic activities but determine receptor structure required for action of Bordetella adenylate cyclase toxin.Pathog Dis. 2016 Apr;74(3):ftw008. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftw008. Epub 2016 Jan 21. Pathog Dis. 2016. PMID: 26802078
-
Bordetella adenylate cyclase toxin: a unique combination of a pore-forming moiety with a cell-invading adenylate cyclase enzyme.Pathog Dis. 2015 Nov;73(8):ftv075. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftv075. Epub 2015 Sep 20. Pathog Dis. 2015. PMID: 26391732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retargeting from the CR3 to the LFA-1 receptor uncovers the adenylyl cyclase enzyme-translocating segment of Bordetella adenylate cyclase toxin.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jul 10;295(28):9349-9365. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013630. Epub 2020 May 11. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32393579 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-Function Relationships Underlying the Capacity of Bordetella Adenylate Cyclase Toxin to Disarm Host Phagocytes.Toxins (Basel). 2017 Sep 24;9(10):300. doi: 10.3390/toxins9100300. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28946636 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of Bacterial Extracellular Membrane Nanovesicles in Infectious Diseases and Their Application in Medicine.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Nov 25;14(12):2597. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122597. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36559091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pertussis toxin suppresses dendritic cell-mediated delivery of B. pertussis into lung-draining lymph nodes.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Jun 6;18(6):e1010577. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010577. eCollection 2022 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35666769 Free PMC article.
-
CyaA translocation across eukaryotic cell membranes.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Mar 22;11:1359408. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1359408. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38584704 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Eukaryotic Host Factor 14-3-3 Inactivates Adenylate Cyclase Toxins of Bordetella bronchiseptica and B. parapertussis, but Not B. pertussis.mBio. 2018 Aug 28;9(4):e00628-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00628-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 30154257 Free PMC article.
-
Invasion of Dendritic Cells, Macrophages and Neutrophils by the Bordetella Adenylate Cyclase Toxin: A Subversive Move to Fool Host Immunity.Toxins (Basel). 2017 Sep 21;9(10):293. doi: 10.3390/toxins9100293. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28934122 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

