Alleviation of Ultraviolet B-Induced Photodamage by Coffea arabica Extract in Human Skin Fibroblasts and Hairless Mouse Skin
- PMID: 28387707
- PMCID: PMC5412366
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18040782
Alleviation of Ultraviolet B-Induced Photodamage by Coffea arabica Extract in Human Skin Fibroblasts and Hairless Mouse Skin
Abstract
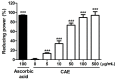
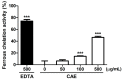
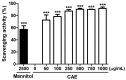
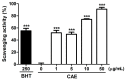
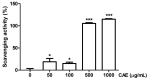
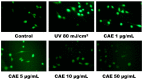
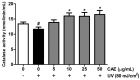
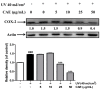
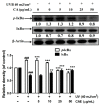
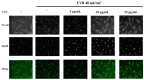
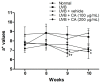
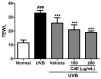
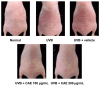
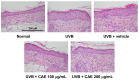
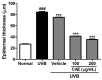
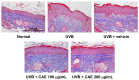
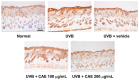
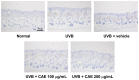
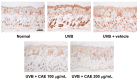
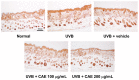
Coffea arabica extract (CAE) containing 48.3 ± 0.4 mg/g of chlorogenic acid and a trace amount of caffeic acid was found to alleviate photoaging activity in human skin fibroblasts. In this study, polyphenol-rich CAE was investigated for its antioxidant and antiinflammatory properties, as well as for its capability to alleviate ultraviolet B (UVB)-induced photodamage in BALB/c hairless mice. The results indicated that 500 μg/mL of CAE exhibited a reducing power of 94.7%, ferrous ion chelating activity of 46.4%, and hydroxyl radical scavenging activity of 20.3%. The CAE dose dependently reduced UVB-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation in fibroblasts. Furthermore, CAE inhibited the UVB-induced expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and p-inhibitor κB, and the translocation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) to the nucleus of fibroblasts. In addition, CAE alleviated UVB-induced photoaging and photodamage in BALB/c hairless mice by restoring the collagen content and reduced UVB-induced epidermal hyperplasia. CAE also inhibited UVB-induced NF-κB, interleukin-6, and matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression in the hairless mouse skin. The results indicated that CAE exhibits antiphotodamage activity by inhibiting UV-induced oxidative stress and inflammation. Therefore, CAE is a candidate for use in antioxidant, antiinflammatory, and antiphotodamage products.
Keywords: Coffea arabica; antioxidant; inflammatory; inhibitor κB (IκB); nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB); photodamage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protective Effects of Sesamin against UVB-Induced Skin Inflammation and Photodamage In Vitro and In Vivo.Biomolecules. 2019 Sep 12;9(9):479. doi: 10.3390/biom9090479. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31547364 Free PMC article.
-
N-(4-bromophenethyl) Caffeamide Protects Skin from UVB-Induced Inflammation Through MAPK/IL-6/NF-κB-Dependent Signaling in Human Skin Fibroblasts and Hairless Mouse Skin.Molecules. 2017 Sep 29;22(10):1639. doi: 10.3390/molecules22101639. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28961200 Free PMC article.
-
Hawthorn Polyphenol Extract Inhibits UVB-Induced Skin Photoaging by Regulating MMP Expression and Type I Procollagen Production in Mice.J Agric Food Chem. 2018 Aug 15;66(32):8537-8546. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b02785. Epub 2018 Jul 31. J Agric Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 30032605
-
Oxidative stress, nutritional antioxidants and beyond.Sci China Life Sci. 2020 Jun;63(6):866-874. doi: 10.1007/s11427-019-9591-5. Epub 2019 Nov 5. Sci China Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31705360 Review.
-
Polyphenols: well beyond the antioxidant capacity: polyphenol supplementation and exercise-induced oxidative stress and inflammation.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014;15(4):373-9. doi: 10.2174/1389201015666140813123843. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25312619 Review.
Cited by
-
Antioxidant Properties of Plant-Derived Phenolic Compounds and Their Effect on Skin Fibroblast Cells.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 May 5;10(5):726. doi: 10.3390/antiox10050726. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34063059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATRA protects skin fibroblasts against UV‑induced oxidative damage through inhibition of E3 ligase Hrd1.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Sep;20(3):2294-2302. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10450. Epub 2019 Jul 1. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31322186 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects and mechanisms of Terminalia catappa L. methenolic extract on hydrogen-peroxide-induced oxidative stress in human skin fibroblasts.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Oct 1;18(1):266. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2308-4. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 30285714 Free PMC article.
-
Coffea arabica Extract Attenuates Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin Lesions by Regulating NLRP3 Inflammasome Expression and Skin Barrier Functions.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 2;24(15):12367. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512367. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569742 Free PMC article.
-
1,2-Bis[(3-Methoxyphenyl)Methyl]Ethane-1,2-Dicarboxylic Acid Reduces UVB-Induced Photodamage In Vitro and In Vivo.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Oct 5;8(10):452. doi: 10.3390/antiox8100452. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31590372 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

