A novel recombinant antibody specific to full-length stromal derived factor-1 for potential application in biomarker studies
- PMID: 28379992
- PMCID: PMC5381782
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174447
A novel recombinant antibody specific to full-length stromal derived factor-1 for potential application in biomarker studies
Abstract
Background: Stromal derived factor-1α (SDF-1α/CXCL12) is a chemokine that is up-regulated in diseases characterised by tissue hypoxia, including myocardial infarction, ischaemic cardiomyopathy and remote ischaemic conditioning (RIC), a technique of cyclical, non-injurious ischaemia applied remote from the heart that protects the heat from lethal ischaemia-reperfusion injury. Accordingly, there is considerable interest in SDF-1α as a potential biomarker of such conditions. However, SDF-1α is rapidly degraded and inactivated by dipeptidyl peptidase 4 and other peptidases, and the kinetics of intact SDF-1α remain unknown.
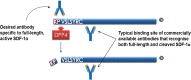
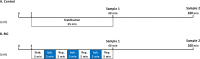
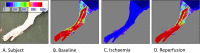
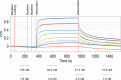
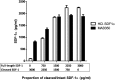
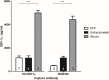
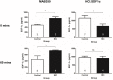
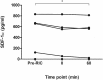
Methods & results: To facilitate investigation of full-length SDF-1α we established an ELISA using a novel recombinant human antibody we developed called HCI.SDF1. HCI.SDF1 is specific to the N-terminal sequence of all isoforms of SDF-1 and has a comparable KD to commercially available antibodies. Together with a detection antibody specific to the α-isoform, HCI.SDF1 was used to specifically quantify full-length SDF-1α in blood for the first time. Using RIC applied to the hind limb of Sprague-Dawley rats or the arms of healthy human volunteers, we demonstrate an increase in SDF-1α using a commercially available antibody, as previously reported, but an unexpected decrease in full-length SDF-1α after RIC in both species.
Conclusions: We report for the first time the development of a novel recombinant antibody specific to full-length SDF-1. Applied to RIC, we demonstrate a significant decrease in SDF-1α that is at odds with the literature and suggests a need to investigate the kinetics of full-length SDF-1α in conditions characterised by tissue hypoxia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Therapeutic strategies utilizing SDF-1α in ischaemic cardiomyopathy.Cardiovasc Res. 2018 Mar 1;114(3):358-367. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvx203. Cardiovasc Res. 2018. PMID: 29040423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Remote ischaemic preconditioning involves signalling through the SDF-1α/CXCR4 signalling axis.Basic Res Cardiol. 2013 Sep;108(5):377. doi: 10.1007/s00395-013-0377-6. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Basic Res Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23917520
-
Stromal derived factor 1α: a chemokine that delivers a two-pronged defence of the myocardium.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Sep;143(3):305-15. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.03.009. Epub 2014 Apr 1. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24704323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stromal cell derived factor-1 alpha confers protection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury: role of the cardiac stromal cell derived factor-1 alpha CXCR4 axis.Circulation. 2007 Aug 7;116(6):654-63. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.672451. Epub 2007 Jul 23. Circulation. 2007. PMID: 17646584 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of intact and truncated stromal cell-derived factor-1α in circulation by immunoaffinity enrichment and tandem mass spectrometry.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2014 Apr;25(4):614-25. doi: 10.1007/s13361-013-0822-7. Epub 2014 Feb 6. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2014. PMID: 24500701
Cited by
-
Stromal cell-derived factor-1α signals via the endothelium to protect the heart against ischaemia-reperfusion injury.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019 Mar;128:187-197. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2019.02.002. Epub 2019 Feb 7. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30738798 Free PMC article.
-
What doesn't kill you makes you stranger: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (CD26) proteolysis differentially modulates the activity of many peptide hormones and cytokines generating novel cryptic bioactive ligands.Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Jun;198:90-108. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.02.005. Epub 2019 Feb 10. Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30759373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevated levels of plasma inactive stromal cell derived factor-1α predict poor long-term outcomes in diabetic patients following percutaneous coronary intervention.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Mar 30;23(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02197-z. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 38555431 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic strategies utilizing SDF-1α in ischaemic cardiomyopathy.Cardiovasc Res. 2018 Mar 1;114(3):358-367. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvx203. Cardiovasc Res. 2018. PMID: 29040423 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kucia M, Reca R, Miekus K, Wanzeck J, Wojakowski W, Janowska-Wieczorek A, et al. Trafficking of normal stem cells and metastasis of cancer stem cells involve similar mechanisms: pivotal role of the SDF-1-CXCR4 axis. Stem Cells. 2005;23(7):879–94. Epub 2005/05/13. 10.1634/stemcells.2004-0342 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nagasawa T, Nakajima T, Tachibana K, Iizasa H, Bleul CC, Yoshie O, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of a murine pre-B-cell growth-stimulating factor/stromal cell-derived factor 1 receptor, a murine homolog of the human immunodeficiency virus 1 entry coreceptor fusin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93(25):14726–9. Epub 1996/12/10. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chatterjee M, Gawaz M. Platelet-Derived CXCL12 (SDF-1alpha): Basic Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Journal of thrombosis and haemostasis: JTH. 2013. Epub 2013/09/13. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

