The crystal structure of Trz1, the long form RNase Z from yeast
- PMID: 28379452
- PMCID: PMC5449637
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkx216
The crystal structure of Trz1, the long form RNase Z from yeast
Abstract
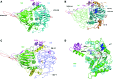
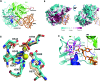
tRNAs are synthesized as precursor RNAs that have to undergo processing steps to become functional. Yeast Trz1 is a key endoribonuclease involved in the 3΄ maturation of tRNAs in all domains of life. It is a member of the β-lactamase family of RNases, characterized by an HxHxDH sequence motif involved in coordination of catalytic Zn-ions. The RNase Z family consists of two subfamilies: the short (250-400 residues) and the long forms (about double in size). Short form RNase Z enzymes act as homodimers: one subunit embraces tRNA with a protruding arm, while the other provides the catalytic site. The long form is thought to contain two fused β-lactamase domains within a single polypeptide. Only structures of short form RNase Z enzymes are known. Here we present the 3.1 Å crystal structure of the long-form Trz1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Trz1 is organized into two β-lactamase domains connected by a long linker. The N-terminal domain has lost its catalytic residues, but retains the long flexible arm that is important for tRNA binding, while it is the other way around in the C-terminal domain. Trz1 likely evolved from a duplication and fusion of the gene encoding the monomeric short form RNase Z.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Trz1, the long form RNase Z from yeast, forms a stable heterohexamer with endonuclease Nuc1 and mutarotase.Biochem J. 2017 Oct 18;474(21):3599-3613. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170435. Biochem J. 2017. PMID: 28899942
-
Substitutions in conserved regions preceding and within the linker affect activity and flexibility of tRNase ZL, the long form of tRNase Z.PLoS One. 2017 Oct 18;12(10):e0186277. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186277. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29045449 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of TRZ1, a yeast homolog of the human candidate prostate cancer susceptibility gene ELAC2 encoding tRNase Z.BMC Mol Biol. 2005 May 13;6:12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-6-12. BMC Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 15892892 Free PMC article.
-
The tRNase Z family of proteins: physiological functions, substrate specificity and structural properties.Biol Chem. 2005 Dec;386(12):1253-64. doi: 10.1515/BC.2005.142. Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16336119 Review.
-
When all's zed and done: the structure and function of RNase Z in prokaryotes.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007 Apr;5(4):278-86. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1622. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17363966 Review.
Cited by
-
Metallo-β-lactamases in the Age of Multidrug Resistance: From Structure and Mechanism to Evolution, Dissemination, and Inhibitor Design.Chem Rev. 2021 Jul 14;121(13):7957-8094. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00138. Epub 2021 Jun 15. Chem Rev. 2021. PMID: 34129337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The S. pombe mitochondrial transcriptome.RNA. 2018 Sep;24(9):1241-1254. doi: 10.1261/rna.064477.117. Epub 2018 Jun 28. RNA. 2018. PMID: 29954949 Free PMC article.
-
The making and breaking of tRNAs by ribonucleases.Trends Genet. 2024 Jun;40(6):511-525. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2024.03.007. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Trends Genet. 2024. PMID: 38641471 Review.
-
A protein of the metallo-hydrolase/oxidoreductase superfamily with both beta-lactamase and ribonuclease activity is linked with translation in giant viruses.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 10;10(1):21685. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78658-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33303919 Free PMC article.
-
ELAC2/RNaseZ-linked cardiac hypertrophy in Drosophila melanogaster.Dis Model Mech. 2021 Aug 1;14(8):dmm048931. doi: 10.1242/dmm.048931. Epub 2021 Aug 31. Dis Model Mech. 2021. PMID: 34338278 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hartmann R.K., Gossringer M., Spath B., Fischer S., Marchfelder A.. The making of tRNAs and more - RNase P and tRNase Z. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2009; 85:319–368. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

