Asiaticoside ameliorates β-amyloid-induced learning and memory deficits in rats by inhibiting mitochondrial apoptosis and reducing inflammatory factors
- PMID: 28352309
- PMCID: PMC5348711
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2016.4004
Asiaticoside ameliorates β-amyloid-induced learning and memory deficits in rats by inhibiting mitochondrial apoptosis and reducing inflammatory factors
Abstract
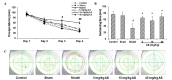
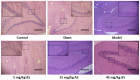
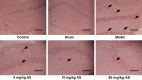
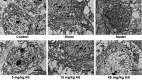
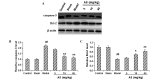
The present study aimed to investigate the effects of asiaticoside (AS) on the pathology and associated mechanisms of β-amyloid (Aβ)-induced Alzheimer's disease (AD) in rats. An AD rat model was established by lateral intracerebroventricular injection of Aβ 1-42 oligomers. Learning and memory function were evaluated by Morris water maze (MWM) test. In addition, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), immunohistochemistry, ELISA and western blot analysis were performed to evaluate the disease pathogenesis. The results indicated that AS exerted protective effects in rats treated with Aβ oligomers, in a dose-dependent manner, as evidenced by the improved learning and memory function in the MWM test. In addition, H&E staining of hippocampal tissue showed that the histological structure was damaged in the model group, which was restored by AS treatment. Aβ deposition was dramatically increased in the model group, and the pathological changes were reversed by AS treatment. TEM revealed that the subcellular structure was injured by Aβ oligomers, however, the structure was ameliorated by AS treatment. Furthermore, AS was found to reduce the elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α, in the brains of Aβ-treated rats. In addition, AS treatment resulted in a significant decrease in the expression of caspases-3, whereas the expression of B-cell lymphoma-2 was significantly increased, in these Aβ-treated rats. According to the findings of the observed study, AS has a marked protective effect on Aβ-induced AD pathology, and the underlying mechanism may be associated with the alleviation of the mitochondrial injuries, the anti-inflammatory activities, and the influence on the expression levels of apoptosis-associated proteins.
Keywords: B-cell lymphoma-2; anti-inflammatory; asiaticoside; caspase-3; β-amyloid.
Figures
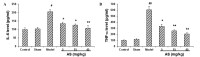
Similar articles
-
Huannao Yicong Decoction () extract reduces inflammation and cell apoptosis in Aβ1-42-induced Alzheimer's disease model of rats.Chin J Integr Med. 2017 Sep;23(9):672-680. doi: 10.1007/s11655-016-2255-1. Epub 2016 Mar 29. Chin J Integr Med. 2017. PMID: 27022730
-
Protective effect of Z-ligustilide against amyloid beta-induced neurotoxicity is associated with decreased pro-inflammatory markers in rat brains.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2009 Jun;92(4):635-41. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2009.03.007. Epub 2009 Mar 24. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2009. PMID: 19324070
-
Dexamethasone and Aβ₂₅-₃₅ accelerate learning and memory impairments due to elevate amyloid precursor protein expression and neuronal apoptosis in 12-month male rats.Behav Brain Res. 2012 Feb 1;227(1):142-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2011.10.038. Epub 2011 Oct 29. Behav Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22061800
-
Electroacupuncture improves memory and protects neurons by regulation of the autophagy pathway in a rat model of Alzheimer's disease.Acupunct Med. 2016 Dec;34(6):449-456. doi: 10.1136/acupmed-2015-010894. Epub 2016 Feb 19. Acupunct Med. 2016. PMID: 26895770
-
Cerebral inoculation of human A53T α-synuclein reduces spatial memory decline and amyloid-β aggregation in APP/PS1 transgenic mice of Alzheimer's disease.Brain Res Bull. 2018 Oct;143:116-122. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.10.003. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Brain Res Bull. 2018. PMID: 30366065
Cited by
-
Periodic Variation of AAK1 in an Aβ1-42-Induced Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.J Mol Neurosci. 2018 Jun;65(2):179-189. doi: 10.1007/s12031-018-1085-3. Epub 2018 May 17. J Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29774516
-
Asiaticoside attenuates neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage through inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB/STAT3 pathway.Ann Transl Med. 2020 May;8(10):641. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-3323. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32566578 Free PMC article.
-
Asiaticoside Alleviates Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via NOD2/Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK)/Nuclear Factor kappa B (NF-κB) Signaling Pathway.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Feb 1;26:e920325. doi: 10.12659/MSM.920325. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32006420 Free PMC article.
-
Asiaticoside Attenuates Cell Growth Inhibition and Apoptosis Induced by Aβ1-42 via Inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Jan 30;9:28. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00028. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29441018 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of mitochondrial dysfunction induced cell apoptosis is a potential therapeutic strategy for herbal medicine to treat neurodegenerative diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 22;13:937289. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.937289. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36210852 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang Zhuo, Liu Minghua, Zhang Hong, Wu Jianbo, Wan Jinyuan. Effects of Aisaticoside on Apoptosis of PC12 cells Induced by β-amylnid Peptide. Chinese Journal of New Drugs. 2012;21:206–210.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
