Canonical and Cross-reactive Binding of NK Cell Inhibitory Receptors to HLA-C Allotypes Is Dictated by Peptides Bound to HLA-C
- PMID: 28352266
- PMCID: PMC5348643
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00193
Canonical and Cross-reactive Binding of NK Cell Inhibitory Receptors to HLA-C Allotypes Is Dictated by Peptides Bound to HLA-C
Abstract
Background: Human natural killer (NK) cell activity is regulated by a family of killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) that bind human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class I. Combinations of KIR and HLA genotypes are associated with disease, including susceptibility to viral infection and disorders of pregnancy. KIR2DL1 binds HLA-C alleles of group C2 (Lys80). KIR2DL2 and KIR2DL3 bind HLA-C alleles of group C1 (Asn80). However, this model cannot explain HLA-C allelic effects in disease or the impact of HLA-bound peptides. The goal of this study was to determine the extent to which the endogenous HLA-C peptide repertoire can influence the specific binding of inhibitory KIR to HLA-C allotypes.
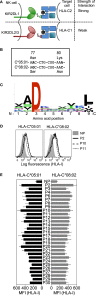
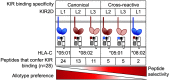
Results: The impact of HLA-C bound peptide on inhibitory KIR binding was investigated taking advantage of the fact that HLA-C*05:01 (HLA-C group 2, C2) and HLA-C*08:02 (HLA-C group 1, C1) have identical sequences apart from the key KIR specificity determining epitope at residues 77 and 80. Endogenous peptides were eluted from HLA-C*05:01 and used to test the peptide dependence of KIR2DL1 and KIR2DL2/3 binding to HLA-C*05:01 and HLA-C*08:02 and subsequent impact on NK cell function. Specific binding of KIR2DL1 to the C2 allotype occurred with the majority of peptides tested. In contrast, KIR2DL2/3 binding to the C1 allotype occurred with only a subset of peptides. Cross-reactive binding of KIR2DL2/3 with the C2 allotype was restricted to even fewer peptides. Unexpectedly, two peptides promoted binding of the C2 allotype-specific KIR2DL1 to the C1 allotype. We showed that presentation of endogenous peptides or HIV Gag peptides by HLA-C can promote KIR cross-reactive binding.
Conclusion: KIR2DL2/3 binding to C1 is more peptide selective than that of KIR2DL1 binding to C2, providing an explanation for KIR2DL3-C1 interactions appearing weaker than KIR2DL1-C2. In addition, cross-reactive binding of KIR is characterized by even higher peptide selectivity. We demonstrate a hierarchy of functional peptide selectivity of KIR-HLA-C interactions with relevance to NK cell biology and human disease associations. This selective peptide sequence-driven binding of KIR provides a potential mechanism for pathogen as well as self-peptide to modulate NK cell activation through altering levels of inhibition.
Keywords: human leukocyte antigen; immunogenetics; innate immunity; killer cell Ig-like receptors; natural killer cell.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Large spectrum of HLA-C recognition by killer Ig-like receptor (KIR)2DL2 and KIR2DL3 and restricted C1 SPECIFICITY of KIR2DS2: dominant impact of KIR2DL2/KIR2DS2 on KIR2D NK cell repertoire formation.J Immunol. 2013 Nov 1;191(9):4778-88. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301580. Epub 2013 Sep 27. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24078689
-
Polymorphic HLA-C Receptors Balance the Functional Characteristics of KIR Haplotypes.J Immunol. 2015 Oct 1;195(7):3160-70. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501358. Epub 2015 Aug 26. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26311903 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation at positively selected positions in the binding site for HLA-C shows that KIR2DL1 is a more refined but less adaptable NK cell receptor than KIR2DL3.J Immunol. 2012 Aug 1;189(3):1418-30. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100431. Epub 2012 Jul 6. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22772445 Free PMC article.
-
Missing or altered self: human NK cell receptors that recognize HLA-C.Immunogenetics. 2017 Aug;69(8-9):567-579. doi: 10.1007/s00251-017-1001-y. Epub 2017 Jul 10. Immunogenetics. 2017. PMID: 28695291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural killer cell recognition of HLA class I molecules.Rev Immunogenet. 2000;2(3):433-48. Rev Immunogenet. 2000. PMID: 11256749 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic differences between smokers and never-smokers with lung cancer.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 2;14:1063716. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1063716. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36817482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ERAP, KIR, and HLA-C Profile in Recurrent Implantation Failure.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 22;12:755624. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.755624. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34745129 Free PMC article.
-
Killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptors on the cusp of modern immunogenetics.Immunology. 2017 Dec;152(4):556-561. doi: 10.1111/imm.12802. Epub 2017 Sep 12. Immunology. 2017. PMID: 28755388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural killer cell transcriptional control, subsets, receptors and effector function.Immunology. 2019 Feb;156(2):109-110. doi: 10.1111/imm.13041. Immunology. 2019. PMID: 30632618 Free PMC article.
-
The Intergenic Recombinant HLA-B∗46:01 Has a Distinctive Peptidome that Includes KIR2DL3 Ligands.Cell Rep. 2017 May 16;19(7):1394-1405. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.04.059. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28514659 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Biassoni R, Falco M, Cambiaggi A, Costa P, Verdiani S, Pende D, et al. Amino acid substitutions can influence the natural killer (NK)-mediated recognition of HLA-C molecules. Role of serine-77 and lysine-80 in the target cell protection from lysis mediated by “group 2” or “group 1” NK clones. J Exp Med (1995) 182:605–9.10.1084/jem.182.2.605 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Winter CC, Long EO. A single amino acid in the p58 killer cell inhibitory receptor controls the ability of natural killer cells to discriminate between the two groups of HLA-C allotypes. J Immunol (1997) 158:4026–8. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

