Vertex models: from cell mechanics to tissue morphogenesis
- PMID: 28348254
- PMCID: PMC5379026
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2015.0520
Vertex models: from cell mechanics to tissue morphogenesis
Abstract
Tissue morphogenesis requires the collective, coordinated motion and deformation of a large number of cells. Vertex model simulations for tissue mechanics have been developed to bridge the scales between force generation at the cellular level and tissue deformation and flows. We review here various formulations of vertex models that have been proposed for describing tissues in two and three dimensions. We discuss a generic formulation using a virtual work differential, and we review applications of vertex models to biological morphogenetic processes. We also highlight recent efforts to obtain continuum theories of tissue mechanics, which are effective, coarse-grained descriptions of vertex models.This article is part of the themed issue 'Systems morphodynamics: understanding the development of tissue hardware'.
Keywords: epithelial mechanics; morphogenesis; simulations; tissue mechanics; vertex models.
© 2017 The Authors.
Figures
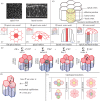
 can yield an additional contribution to the virtual work. (h) The force fv on a vertex v is obtained by taking the virtual work differential with respect to the vertex position xv. The tissue is in mechanical equilibrium when the force acting on all vertices is zero. (i) Topological transitions in epithelia are cell–cell intercalations (T1 transitions), cell extrusions (T2 transitions) and cell divisions.
can yield an additional contribution to the virtual work. (h) The force fv on a vertex v is obtained by taking the virtual work differential with respect to the vertex position xv. The tissue is in mechanical equilibrium when the force acting on all vertices is zero. (i) Topological transitions in epithelia are cell–cell intercalations (T1 transitions), cell extrusions (T2 transitions) and cell divisions.
Similar articles
-
Vertex models of epithelial morphogenesis.Biophys J. 2014 Jun 3;106(11):2291-304. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.11.4498. Biophys J. 2014. PMID: 24896108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex structures from patterned cell sheets.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017 May 19;372(1720):20150515. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2015.0515. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28348251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From cells to tissue: A continuum model of epithelial mechanics.Phys Rev E. 2017 Aug;96(2-1):022418. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.96.022418. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Phys Rev E. 2017. PMID: 28950595
-
Mechanocellular models of epithelial morphogenesis.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017 May 19;372(1720):20150519. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2015.0519. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28348253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Taking the strain: quantifying the contributions of all cell behaviours to changes in epithelial shape.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017 May 19;372(1720):20150513. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2015.0513. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28348250 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tailoring smart hydrogels through manipulation of heterogeneous subdomains.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 27;15(1):9268. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53552-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39465260 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical heterogeneity along single cell-cell junctions is driven by lateral clustering of cadherins during vertebrate axis elongation.Elife. 2021 May 25;10:e65390. doi: 10.7554/eLife.65390. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34032216 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between substrate rigidity and tissue fluidity regulates cell monolayer spreading.Soft Matter. 2022 Oct 19;18(40):7877-7886. doi: 10.1039/d2sm00757f. Soft Matter. 2022. PMID: 36205535 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle-dependent active stress drives epithelia remodeling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Mar 9;118(10):e1917853118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1917853118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33649197 Free PMC article.
-
How dynamic prestress governs the shape of living systems, from the subcellular to tissue scale.Interface Focus. 2022 Oct 14;12(6):20220038. doi: 10.1098/rsfs.2022.0038. eCollection 2022 Dec 6. Interface Focus. 2022. PMID: 36330322 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Howard J. 2001. Mechanics of motor proteins and the cytoskeleton. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

