KSHV-encoded viral interferon regulatory factor 4 (vIRF4) interacts with IRF7 and inhibits interferon alpha production
- PMID: 28342865
- PMCID: PMC5490377
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.03.101
KSHV-encoded viral interferon regulatory factor 4 (vIRF4) interacts with IRF7 and inhibits interferon alpha production
Abstract
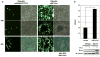
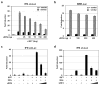
Before an infection can be completely established, the host immediately turns on the innate immune system through activating the interferon (IFN)-mediated antiviral pathway. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) utilizes a unique antagonistic mechanism of type I IFN-mediated host antiviral immunity by incorporating four viral interferon regulatory factors (vIRF1-4). Herein, we characterized novel immune evasion strategies of vIRF4 to inhibit the IRF7-mediated IFN-α production. KSHV vIRF4 specifically interacts with IRF7, resulting in inhibition of IRF7 dimerization and ultimately suppresses IRF7-mediated activation of type I IFN. These results suggest that each of the KSHV vIRFs, including vIRF4, subvert IFN-mediated anti-viral response via different mechanisms. Therefore, it is indicated that KSHV vIRFs are indeed a crucial immunomodulatory component of their life cycles.
Keywords: IFN-alpha; IRF7; Innate immunity; KSHV; vIRF4.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Beyond Viral Interferon Regulatory Factors: Immune Evasion Strategies.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Dec 28;29(12):1873-1881. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1910.10004. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31650769 Review.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus viral interferon regulatory factor 4 targets MDM2 to deregulate the p53 tumor suppressor pathway.J Virol. 2009 Jul;83(13):6739-47. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02353-08. Epub 2009 Apr 15. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19369353 Free PMC article.
-
A Rhesus Rhadinovirus Viral Interferon (IFN) Regulatory Factor Is Virion Associated and Inhibits the Early IFN Antiviral Response.J Virol. 2015 Aug;89(15):7707-21. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01175-15. Epub 2015 May 13. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25972548 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperation between viral interferon regulatory factor 4 and RTA to activate a subset of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus lytic promoters.J Virol. 2012 Jan;86(2):1021-33. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00694-11. Epub 2011 Nov 16. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22090118 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct roles of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded viral interferon regulatory factors in inflammatory response and cancer.J Virol. 2013 Sep;87(17):9398-410. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03315-12. Epub 2013 Jun 19. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23785197 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Transcriptional Roles of KSHV Viral Interferon Regulatory Factors in Oral Epithelial Cells.Viruses. 2024 May 25;16(6):846. doi: 10.3390/v16060846. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38932139 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Kaposi's sarcoma associated herpesvirus encoded protease (ORF17) by a lysophosphatidic acid molecule for treating KSHV associated diseases.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jan 17;11:1060156. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1060156. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36733461 Free PMC article.
-
Activation and counteraction of antiviral innate immunity by KSHV: an Update.Sci Bull (Beijing). 2018 Sep 30;63(18):1223-1234. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2018.07.009. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Sci Bull (Beijing). 2018. PMID: 30906617 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Degradation by Gammaherpesvirus RTAs: More Than Just Viral Transactivators.Viruses. 2023 Mar 11;15(3):730. doi: 10.3390/v15030730. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36992439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biologically significant interaction of human herpesvirus 8 viral interferon regulatory factor 4 with ubiquitin-specific protease 7.J Virol. 2024 Jun 13;98(6):e0025524. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00255-24. Epub 2024 May 16. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38752725 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Honda K, Taniguchi T. IRFs: master regulators of signalling by Toll-like receptors and cytosolic pattern-recognition receptors. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:644–658. - PubMed
-
- Cesarman E, Chang Y, Moore PS, Said JW, Knowles DM. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-related body-cavity-based lymphomas. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:1186–1191. - PubMed
-
- Dupin N, Diss TL, Kellam P, Tulliez M, Du MQ, Sicard D, Weiss RA, Isaacson PG, Boshoff C. HHV-8 is associated with a plasmablastic variant of Castleman disease that is linked to HHV-8-positive plasmablastic lymphoma. Blood. 2000;95:1406–1412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

