Heterologous desensitization of cardiac β-adrenergic signal via hormone-induced βAR/arrestin/PDE4 complexes
- PMID: 28339772
- PMCID: PMC5852637
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvx036
Heterologous desensitization of cardiac β-adrenergic signal via hormone-induced βAR/arrestin/PDE4 complexes
Abstract
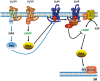
Aims: Cardiac β-adrenergic receptor (βAR) signalling is susceptible to heterologous desensitization by different neurohormonal stimuli in clinical conditions associated with heart failure. We aim to examine the underlying mechanism of cross talk between βARs and a set of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) activated by hormones/agonists.
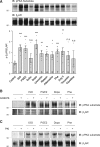
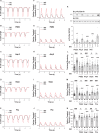
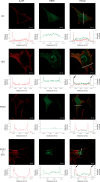
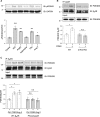
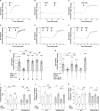
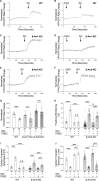
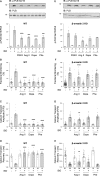
Methods and results: Rat ventricular cardiomyocytes were used to determine heterologous phosphorylation of βARs under a series of GPCR agonists. Activation of Gs-coupled dopamine receptor, adenosine receptor, relaxin receptor and prostaglandin E2 receptor, and Gq-coupled α1 adrenergic receptor and angiotensin II type 1 receptor promotes phosphorylation of β1AR and β2AR at putative protein kinase A (PKA) phosphorylation sites; but activation of Gi-coupled α2 adrenergic receptor and activation of protease-activated receptor does not. The GPCR agonists that promote β2AR phosphorylation effectively inhibit βAR agonist isoproterenol-induced PKA phosphorylation of phospholamban and contractile function in ventricular cardiomyocytes. Heterologous GPCR stimuli have minimal to small effect on isoproterenol-induced β2AR activation and G-protein coupling for cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) production. However, these GPCR stimuli significantly promote phosphorylation of phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D), and recruit PDE4D to the phosphorylated β2AR in a β-arrestin 2 dependent manner without promoting β2AR endocytosis. The increased binding between β2AR and PDE4D effectively hydrolyzes cAMP signal generated by subsequent stimulation with isoproterenol. Mutation of PKA phosphorylation sites in β2AR, inhibition of PDE4, or genetic ablation of PDE4D or β-arrestin 2 abolishes this heterologous inhibitory effect. Ablation of β-arrestin 2 or PDE4D gene also rescues β-adrenergic stimuli-induced myocyte contractile function.
Conclusions: These data reveal essential roles of β-arrestin 2 and PDE4D in a common mechanism for heterologous desensitization of cardiac βARs under hormonal stimulation, which is associated with impaired cardiac function during the development of pathophysiological conditions.
Keywords: Heterologous desensitization; PKA; PKC; Phosphodiesterase 4; β-Arrestin 2.
Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. © The Author 2017. For permissions please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dynamic protein kinase a activities induced by beta-adrenoceptors dictate signaling propagation for substrate phosphorylation and myocyte contraction.Circ Res. 2009 Mar 27;104(6):770-9. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.187880. Epub 2009 Feb 12. Circ Res. 2009. PMID: 19213958 Free PMC article.
-
A long lasting β1 adrenergic receptor stimulation of cAMP/protein kinase A (PKA) signal in cardiac myocytes.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 23;289(21):14771-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.542589. Epub 2014 Apr 8. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24713698 Free PMC article.
-
Palmitoylation regulates intracellular trafficking of β2 adrenergic receptor/arrestin/phosphodiesterase 4D complexes in cardiomyocytes.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e42658. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042658. Epub 2012 Aug 9. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22912718 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-adrenergic signaling in the heart: dual coupling of the beta2-adrenergic receptor to G(s) and G(i) proteins.Sci STKE. 2001 Oct 16;2001(104):re15. doi: 10.1126/stke.2001.104.re15. Sci STKE. 2001. PMID: 11604549 Review.
-
Insulin and β Adrenergic Receptor Signaling: Crosstalk in Heart.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Jun;28(6):416-427. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2017.02.002. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28256297 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Opposing functions of β-arrestin 1 and 2 in Parkinson's disease via microglia inflammation and Nprl3.Cell Death Differ. 2021 Jun;28(6):1822-1836. doi: 10.1038/s41418-020-00704-9. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Cell Death Differ. 2021. PMID: 33686256 Free PMC article.
-
Pathological cardiac hypertrophy: the synergy of adenylyl cyclases inhibition in cardiac and immune cells during chronic catecholamine stress.J Mol Med (Berl). 2019 Jul;97(7):897-907. doi: 10.1007/s00109-019-01790-0. Epub 2019 May 6. J Mol Med (Berl). 2019. PMID: 31062036 Review.
-
Arrestin-dependent nuclear export of phosphodiesterase 4D promotes GPCR-induced nuclear cAMP signaling required for learning and memory.Sci Signal. 2023 Mar 28;16(778):eade3380. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.ade3380. Epub 2023 Mar 28. Sci Signal. 2023. PMID: 36976866 Free PMC article.
-
G-Protein-Coupled Receptors in Heart Disease.Circ Res. 2018 Aug 31;123(6):716-735. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.311403. Circ Res. 2018. PMID: 30355236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Continuous exposure of isoprenaline inhibits myoblast differentiation and fusion through PKA/ERK1/2-FOXO1 signaling pathway.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Feb 28;10(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1160-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 30819239 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gainetdinov RR, Premont RT, Bohn LM, Lefkowitz RJ, Caron MG.. Desensitization of G protein-coupled receptors and neuronal functions. Annu Rev Neurosci 2004;27:107–144. - PubMed
-
- Chuang TT, Iacovelli L, Sallese M, De Blasi A. . G protein-coupled receptors: heterologous regulation of homologous desensitization and its implications. Trends Pharmacol Sci 1996;17:416–421. - PubMed
-
- Rockman HA, Koch WJ, Lefkowitz RJ.. Seven-transmembrane-spanning receptors and heart function. Nature 2002;415:206–212. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

