DGK-α: A Checkpoint in Cancer-Mediated Immuno-Inhibition and Target for Immunotherapy
- PMID: 28316970
- PMCID: PMC5335622
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2017.00016
DGK-α: A Checkpoint in Cancer-Mediated Immuno-Inhibition and Target for Immunotherapy
Abstract
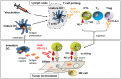
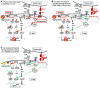
Immunotherapy is moving to the forefront of cancer treatments owing to impressive durable responses achieved with checkpoint blockade antibodies and adoptive T-cell therapy. Still, improvements are necessary since, overall, only a small percentage of patients benefit from current therapies. Here, I summarize evidence that DGK-α may represent an immunological checkpoint suppressing the activity of cytotoxic immunocytes in the tumor microenvironment. DGK-inhibitors can restore the antitumor function of tumor-suppressed adaptive and innate cytotoxic immunocytes. The activity of DGK-inhibitors lays downstream of current checkpoint blockade antibodies. Thus, synergistic effects are expected from combination strategies. Moreover, DGK-inhibitors may permit a double-strike attack on tumor cells as DGK-inhibition may not only re-instate immunological tumor attack but also may harm tumor cells directly by interfering with oncogenic survival pathways. Together, DGK-inhibitors have very promising characteristics and may be beneficially included into the armamentarium of cancer immunotherapeutics.
Keywords: anergy; diacylglycerol kinase; human tumor; immunotherapy; renal cell carcinoma; tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biological regulation of diacylglycerol kinases in normal and neoplastic tissues: New opportunities for cancer immunotherapy.Adv Biol Regul. 2020 Jan;75:100663. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2019.100663. Epub 2019 Oct 30. Adv Biol Regul. 2020. PMID: 31706704 Review.
-
Immune checkpoint blockade opens a new way to cancer immunotherapy.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jun;234(6):8541-8549. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27816. Epub 2018 Dec 3. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30511409 Review.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Knockout of DGK Improves Antitumor Activities of Human T Cells.Cancer Res. 2018 Aug 15;78(16):4692-4703. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-0030. Epub 2018 Jul 2. Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29967261
-
Disruption of diacylglycerol metabolism impairs the induction of T cell anergy.Nat Immunol. 2006 Nov;7(11):1174-81. doi: 10.1038/ni1400. Epub 2006 Oct 8. Nat Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17028587
-
NK-cell dysfunction in human renal carcinoma reveals diacylglycerol kinase as key regulator and target for therapeutic intervention.Int J Cancer. 2014 Oct 15;135(8):1832-41. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28837. Epub 2014 Mar 26. Int J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24615391
Cited by
-
New Era of Diacylglycerol Kinase, Phosphatidic Acid and Phosphatidic Acid-Binding Protein.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 16;21(18):6794. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186794. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32947951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR-based screens uncover determinants of immunotherapy response in multiple myeloma.Blood Adv. 2020 Jul 14;4(13):2899-2911. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019001346. Blood Adv. 2020. PMID: 32589729 Free PMC article.
-
Ca2+ -induced structural changes and intramolecular interactions in N-terminal region of diacylglycerol kinase alpha.Protein Sci. 2022 Jul;31(7):e4365. doi: 10.1002/pro.4365. Protein Sci. 2022. PMID: 35762720 Free PMC article.
-
DGKA Provides Platinum Resistance in Ovarian Cancer Through Activation of c-JUN-WEE1 Signaling.Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Jul 15;26(14):3843-3855. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-3790. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32341033 Free PMC article.
-
DGKα, Bridging Membrane Shape Changes with Specific Molecular Species of DAG/PA: Implications in Cancer and Immunosurveillance.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 26;14(21):5259. doi: 10.3390/cancers14215259. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358678 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dominguez C. L., Floyd D. H., Xiao A., Mullins G. R., Kefas B. A., Xin W., et al. . (2013). Diacylglycerol kinase α is a critical signaling node and novel therapeutic target in glioblastoma and other cancers. Cancer Discov. 3, 782–797. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0215 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

