IL-21 promotes myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury through the modulation of neutrophil infiltration
- PMID: 28294304
- PMCID: PMC5866974
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.13781
IL-21 promotes myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury through the modulation of neutrophil infiltration
Abstract
Background and purpose: The immune system plays an important role in driving the acute inflammatory response following myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury (MIRI). IL-21 is a pleiotropic cytokine with multiple immunomodulatory effects, but its role in MIRI is not known.
Experimental approach: Myocardial injury, neutrophil infiltration and the expression of neutrophil chemokines KC (CXCL1) and MIP-2 (CXCL2) were studied in a mouse model of MIRI. Effects of IL-21 on the expression of KC and MIP-2 in neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes (CMs) and cardiac fibroblasts (CFs) were determined by real-time PCR and ELISA. The signalling mechanisms underlying these effects were explored by western blot analysis.
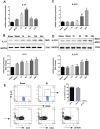
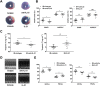
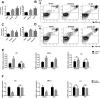
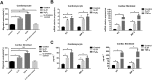
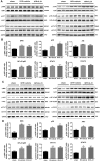
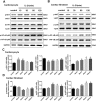
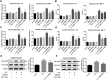
Key results: IL-21 was elevated within the acute phase of murine MIRI. Neutralization of IL-21 attenuated myocardial injury, as illustrated by reduced infarct size, decreased cardiac troponin T levels and improved cardiac function, whereas exogenous IL-21 administration exerted opposite effects. IL-21 increased the infiltration of neutrophils and increased the expression of KC and MIP-2 in myocardial tissue following MIRI. Moreover, neutrophil depletion attenuated the IL-21-induced myocardial injury. Mechanistically, IL-21 increased the production of KC and MIP-2 in neonatal CMs and CFs, and enhanced neutrophil migration, as revealed by the migration assay. Furthermore, we demonstrated that this IL-21-mediated increase in chemokine expression involved the activation of Akt/NF-κB signalling in CMs and p38 MAPK/NF-κB signalling in CFs.
Conclusions and implications: Our data provide novel evidence that IL-21 plays a pathogenic role in MIRI, most likely by promoting cardiac neutrophil infiltration. Therefore, targeting IL-21 may have therapeutic potential as a treatment for MIRI.
Linked articles: This article is part of a themed section on Spotlight on Small Molecules in Cardiovascular Diseases. To view the other articles in this section visit http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bph.v175.8/issuetoc.
© 2017 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interleukin-17A contributes to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating cardiomyocyte apoptosis and neutrophil infiltration.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012 Jan 24;59(4):420-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.10.863. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22261166 Free PMC article.
-
The IL-2/Anti-IL-2 Complex Attenuates Cardiac Ischaemia-Reperfusion Injury Through Expansion of Regulatory T Cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(5):1810-1827. doi: 10.1159/000485818. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 29224017
-
Ischemia-reperfusion of rat myocardium activates nuclear factor-KappaB and induces neutrophil infiltration via lipopolysaccharide-induced CXC chemokine.Circulation. 2001 May 8;103(18):2296-302. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.103.18.2296. Circulation. 2001. PMID: 11342480
-
Ageing, sex, and cardioprotection.Br J Pharmacol. 2020 Dec;177(23):5270-5286. doi: 10.1111/bph.14951. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Br J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31863453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting phosphodiesterase 5 as a therapeutic option against myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury and for treating heart failure.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Jan;175(2):223-231. doi: 10.1111/bph.13749. Epub 2017 Mar 23. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28213937 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Molecular Targets Participating in Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury and Cardioprotection.Cardiol Res Pract. 2019 May 28;2019:6935147. doi: 10.1155/2019/6935147. eCollection 2019. Cardiol Res Pract. 2019. PMID: 31275641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spotlight on small molecules in cardiovascular diseases.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Apr;175(8):1111-1113. doi: 10.1111/bph.14154. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29574891 Free PMC article.
-
PPARβ/δ Is Required for Mesenchymal Stem Cell Cardioprotective Effects Independently of Their Anti-inflammatory Properties in Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Sep 20;8:681002. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.681002. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34616778 Free PMC article.
-
High plasma levels of pro-inflammatory factors interleukin-17 and interleukin-23 are associated with poor outcome of cardiac-arrest patients: a single center experience.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020 Apr 15;20(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12872-020-01451-y. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020. PMID: 32293300 Free PMC article.
-
T-cell regulation of fibroblasts and cardiac fibrosis.Matrix Biol. 2020 Sep;91-92:167-175. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2020.04.001. Epub 2020 May 11. Matrix Biol. 2020. PMID: 32438054 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brenne AT, Ro TB, Waage A, Sundan A, Borset M, Hjorth‐Hansen H (2002). Interleukin‐21 is a growth and survival factor for human myeloma cells. Blood 99: 3756–3762. - PubMed
-
- Caruso R, Botti E, Sarra M, Esposito M, Stolfi C, Diluvio L et al. (2009). Involvement of interleukin‐21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis. Nat Med 15: 1013–1015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

