Alveolar nonselective channels are ASIC1a/α-ENaC channels and contribute to AFC
- PMID: 28283476
- PMCID: PMC5495939
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00379.2016
Alveolar nonselective channels are ASIC1a/α-ENaC channels and contribute to AFC
Abstract
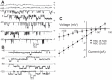
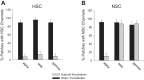
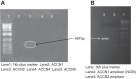
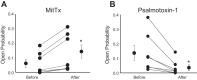
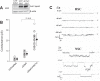
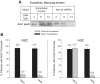
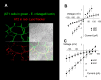
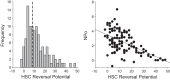
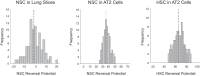
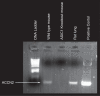
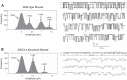
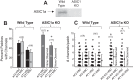
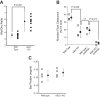
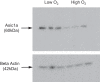
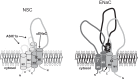
A thin fluid layer in alveoli is normal and results from a balance of fluid entry and fluid uptake by transepithelial salt and water reabsorption. Conventional wisdom suggests the reabsorption is via epithelial Na+ channels (ENaC), but if all Na+ reabsorption were via ENaC, then amiloride, an ENaC inhibitor, should block alveolar fluid clearance (AFC). However, amiloride blocks only half of AFC. The reason for failure to block is clear from single-channel measurements from alveolar epithelial cells: ENaC channels are observed, but another channel is present at the same frequency that is nonselective for Na+ over K+, has a larger conductance, and has shorter open and closed times. These two channel types are known as highly selective channels (HSC) and nonselective cation channels (NSC). HSC channels are made up of three ENaC subunits since knocking down any of the subunits reduces HSC number. NSC channels contain α-ENaC since knocking down α-ENaC reduces the number of NSC (knocking down β- or γ-ENaC has no effect on NSC, but the molecular composition of NSC channels remains unclear). We show that NSC channels consist of at least one α-ENaC and one or more acid-sensing ion channel 1a (ASIC1a) proteins. Knocking down either α-ENaC or ASIC1a reduces both NSC and HSC number, and no NSC channels are observable in single-channel patches on lung slices from ASIC1a knockout mice. AFC is reduced in knockout mice, and wet wt-to-dry wt ratio is increased, but the percentage increase in wet wt-to-dry wt ratio is larger than expected based on the reduction in AFC.
Keywords: acid-sensing ion channel 1a; alveolar fluid clearance; alveoli; lung fluid balance; nonselective cation channels; α-epithelial Na+ channels.
Copyright © 2017 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
beta-Liddle mutation of the epithelial sodium channel increases alveolar fluid clearance and reduces the severity of hydrostatic pulmonary oedema in mice.J Physiol. 2007 Jul 15;582(Pt 2):777-88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.131078. Epub 2007 Apr 12. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17430990 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine A2B receptor activation stimulates alveolar fluid clearance through alveolar epithelial sodium channel via cAMP pathway in endotoxin-induced lung injury.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020 Apr 1;318(4):L787-L800. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00195.2019. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32129084
-
Expression of highly selective sodium channels in alveolar type II cells is determined by culture conditions.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2001 Apr;280(4):L646-58. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.2001.280.4.L646. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11238004
-
ASIC and ENaC type sodium channels: conformational states and the structures of the ion selectivity filters.FEBS J. 2017 Feb;284(4):525-545. doi: 10.1111/febs.13840. Epub 2016 Sep 15. FEBS J. 2017. PMID: 27580245 Review.
-
Importance of ENaC-mediated sodium transport in alveolar fluid clearance using genetically-engineered mice.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2010;25(1):63-70. doi: 10.1159/000272051. Epub 2009 Dec 22. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20054145 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Basis for Mambalgin-2 Interaction with Heterotrimeric α-ENaC/ASIC1a/γ-ENaC Channels in Cancer Cells.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Oct 13;15(10):612. doi: 10.3390/toxins15100612. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37888643 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine-Ion Channel Interactions in Pulmonary Inflammation.Front Immunol. 2018 Jan 4;8:1644. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01644. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29354115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Epithelial Sodium Channel-An Underestimated Drug Target.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 24;24(9):7775. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097775. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deletion of the Gamma Subunit of ENaC in Endothelial Cells Does Not Protect against Renal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 9;22(20):10914. doi: 10.3390/ijms222010914. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681576 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of impaired alveolar fluid clearance.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2023 Jan 23:10.1002/ar.25166. doi: 10.1002/ar.25166. Online ahead of print. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2023. PMID: 36688689 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alli AA, Bao HF, Alli AA, Aldrugh Y, Zhou Y, Yu L, Eaton DC. Calmodulin and CaM kinase II govern MARCKS-mediated PIP2-dependent regulation of ENaC. FASEB J 26, Suppl: 867.815, 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

