Toll-like receptor 4 as a predictor of clinical outcomes of estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer in Saudi women
- PMID: 28280355
- PMCID: PMC5338938
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S112165
Toll-like receptor 4 as a predictor of clinical outcomes of estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer in Saudi women
Abstract
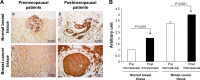
The aim of this study was to investigate the association of the common polymorphisms of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR-4) with breast cancer development in the Saudi Arabian population. Four TLR-4 polymorphisms (rs2770150, rs10759931, rs10759932, and rs4986790) were studied using 127 breast cancer patients and 117 controls. Relative expression of TLR-4 protein in the breast tumor and the matched normal breast tissues was determined in a large cohort of 70 clinical breast samples in a tissue micro-array format by immunohistochemistry using a specific anti-TLR-4 antibody. Our results demonstrated an increase in TLR-4 expression in estrogen receptor (ER)-, postmenopausal breast cancer patients compared to normal. We also demonstrated that the G allele of single-nucleotide polymorphism rs10759931 was found to be significantly higher in frequency among patients (36.3%) compared to the control group (26.7%), suggesting that this polymorphism is strongly associated with the development of breast cancer in this ethnic population. In addition, the TLR-4 polymorphism rs2770150 was shown to be highly correlated with breast cancer in patients over 48 years of age. The TLR-4 polymorphism rs4986790 was also found to be associated with this malignancy in the ER- patient groups. Our results suggested firstly that the variation in TLR-4 gene expression may influence breast cancer development and secondly a closely linked association between TLR-4 gene polymorphism and ER status. Our study provides support for a better understanding of the implication of TLR-4 polymorphism in breast tumorigenesis and for its eventual use as a cancer biomarker.
Keywords: Saudi population; Toll-like receptor 4; breast cancer; estrogen receptor; innate immunity; single-nucleotide polymorphisms.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Toll-like receptor 4 polymorphisms in Saudi population with cardiovascular diseases.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019 Sep;7(9):e852. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.852. Epub 2019 Jul 21. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019. PMID: 31328431 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Nod-like receptor protein-1 (rs2670660) and Toll-like receptor-4 (rs4986790) with non-segmental vitiligo: A case-control study in South Indian population.Int J Immunogenet. 2019 Oct;46(5):321-330. doi: 10.1111/iji.12429. Epub 2019 Jul 10. Int J Immunogenet. 2019. PMID: 31293094
-
Expression and Polymorphism of Toll-Like Receptor 4 and Effect on NF-κB Mediated Inflammation in Colon Cancer Patients.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 15;11(1):e0146333. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146333. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26771524 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of toll-like receptor signaling pathways to breast tumorigenesis and treatment.Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2013 Jun 28;5:43-51. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S29172. eCollection 2013. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2013. PMID: 24648757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Should a Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR-4) agonist or antagonist be designed to treat cancer? TLR-4: its expression and effects in the ten most common cancers.Onco Targets Ther. 2013 Nov 5;6:1573-87. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S50838. Onco Targets Ther. 2013. PMID: 24235843 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TSLP and TSLP receptors variants are associated with smoking.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019 Aug;7(8):e842. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.842. Epub 2019 Jul 9. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019. PMID: 31290290 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Effect of Variants in Toll-like Receptor 4 Gene in Saudi Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Cells. 2023 Sep 23;12(19):2340. doi: 10.3390/cells12192340. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37830554 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and allele frequencies of Thymic stromal lymphopoietin are a key factor of breast cancer risk.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019 Aug;7(8):e813. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.813. Epub 2019 Jun 17. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019. PMID: 31210014 Free PMC article.
-
Pathomorphological Manifestations and the Course of the Cervical Cancer Disease Determined by Variations in the TLR4 Gene.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jun 7;13(12):1999. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13121999. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370894 Free PMC article.
-
Novel sequence variants in the TLR6 gene associated with advanced breast cancer risk in the Saudi Arabian population.PLoS One. 2018 Nov 2;13(11):e0203376. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203376. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30388713 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Cancer Society Cancer Facts & Figures 2013. [Accessed February 8, 2017]. Available from: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts....
-
- Yu H, Kortylewski M, Pardoll D. Crosstalk between cancer and immune cells: role of STAT3 in the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7(1):41–51. - PubMed
-
- Yu JC, Ding SL, Chang CH, et al. Genetic susceptibility to the development and progression of breast cancer associated with polymorphism of cell cycle and ubiquitin ligase genes. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30(9):1562–1570. - PubMed
-
- de Visser KE, Eichten A, Coussens LM. Paradoxical roles of the immune system during cancer development. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6(1):24–37. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

