Long-Term Outcomes of Imatinib Treatment for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
- PMID: 28273028
- PMCID: PMC5901965
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1609324
Long-Term Outcomes of Imatinib Treatment for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
Background: Imatinib, a selective BCR-ABL1 kinase inhibitor, improved the prognosis for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). We conducted efficacy and safety analyses on the basis of more than 10 years of follow-up in patients with CML who were treated with imatinib as initial therapy.
Methods: In this open-label, multicenter trial with crossover design, we randomly assigned patients with newly diagnosed CML in the chronic phase to receive either imatinib or interferon alfa plus cytarabine. Long-term analyses included overall survival, response to treatment, and serious adverse events.
Results: The median follow-up was 10.9 years. Given the high rate of crossover among patients who had been randomly assigned to receive interferon alfa plus cytarabine (65.6%) and the short duration of therapy before crossover in these patients (median, 0.8 years), the current analyses focused on patients who had been randomly assigned to receive imatinib. Among the patients in the imatinib group, the estimated overall survival rate at 10 years was 83.3%. Approximately half the patients (48.3%) who had been randomly assigned to imatinib completed study treatment with imatinib, and 82.8% had a complete cytogenetic response. Serious adverse events that were considered by the investigators to be related to imatinib were uncommon and most frequently occurred during the first year of treatment.
Conclusions: Almost 11 years of follow-up showed that the efficacy of imatinib persisted over time and that long-term administration of imatinib was not associated with unacceptable cumulative or late toxic effects. (Funded by Novartis Pharmaceuticals; IRIS ClinicalTrials.gov numbers, NCT00006343 and NCT00333840 .).
Conflict of interest statement
No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
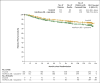
Comment in
-
Imatinib Changed Everything.N Engl J Med. 2017 Mar 9;376(10):982-983. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1700833. N Engl J Med. 2017. PMID: 28273011 No abstract available.
-
[Treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia with imatinib : IRIS study].Internist (Berl). 2017 Nov;58(11):1220-1221. doi: 10.1007/s00108-017-0322-0. Internist (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28929180 German. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia.N Engl J Med. 2006 Dec 7;355(23):2408-17. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa062867. N Engl J Med. 2006. PMID: 17151364 Clinical Trial.
-
Frequency of major molecular responses to imatinib or interferon alfa plus cytarabine in newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia.N Engl J Med. 2003 Oct 9;349(15):1423-32. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa030513. N Engl J Med. 2003. PMID: 14534335 Clinical Trial.
-
Imatinib compared with interferon and low-dose cytarabine for newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia.N Engl J Med. 2003 Mar 13;348(11):994-1004. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa022457. N Engl J Med. 2003. PMID: 12637609 Clinical Trial.
-
[Tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of CML].Ther Umsch. 2006 Apr;63(4):249-54. doi: 10.1024/0040-5930.63.4.249. Ther Umsch. 2006. PMID: 16689455 Review. German.
-
Targeted chronic myeloid leukemia therapy: Seeking a cure.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2007 Dec 15;64(24 Suppl 15):S9-15. doi: 10.2146/ajhp070482. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2007. PMID: 18056932 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the PTP1B-Bcr-Abl1 interaction for the degradation of T315I mutant Bcr-Abl1 in chronic myeloid leukemia.Cancer Sci. 2023 Jan;114(1):247-258. doi: 10.1111/cas.15580. Epub 2022 Sep 26. Cancer Sci. 2023. PMID: 36086954 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating Single-Cell Transcriptome and Network Analysis to Characterize the Therapeutic Response of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 18;23(22):14335. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214335. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430822 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple-low-dose therapy: effective killing of high-grade serous ovarian cancer cells with ATR and CHK1 inhibitors.NAR Cancer. 2022 Nov 12;4(4):zcac036. doi: 10.1093/narcan/zcac036. eCollection 2022 Dec. NAR Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36381271 Free PMC article.
-
Successful kidney transplantation in a patient with pre-existing chronic myeloid leukemia treated with imatinib.Am J Transplant. 2021 Jan;21(1):405-409. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16194. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Am J Transplant. 2021. PMID: 32654389 Free PMC article.
-
Early Management of CML.Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2019 Dec;14(6):480-491. doi: 10.1007/s11899-019-00550-8. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2019. PMID: 31701368 Review.
References
-
- Rumpold H, Webersinke G. Molecular pathogenesis of Philadelphia-positive chronic myeloid leukemia — is it all BCR-ABL? Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2011;11:3–19. - PubMed
-
- Cohen MH, Williams G, Johnson JR, et al. Approval summary for imatinib mesylate capsules in the treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:935–42. - PubMed
-
- O’Brien SG, Guilhot F, Larson RA, et al. Imatinib compared with interferon and low-dose cytarabine for newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:994–1004. - PubMed
-
- Druker BJ, Guilhot F, O’Brien SG, et al. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2408–17. - PubMed
-
- Hochhaus A, O’Brien SG, Guilhot F, et al. Six-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for the first-line treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2009;23:1054–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
