The Importance of Dendritic Cells in Maintaining Immune Tolerance
- PMID: 28264998
- PMCID: PMC5343761
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601629
The Importance of Dendritic Cells in Maintaining Immune Tolerance
Abstract
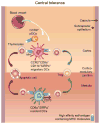
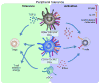
Immune tolerance is necessary to prevent the immune system from reacting against self, and thus to avoid the development of autoimmune diseases. In this review, we discuss key findings that position dendritic cells (DCs) as critical modulators of both thymic and peripheral immune tolerance. Although DCs are important for inducing both immunity and tolerance, increased autoimmunity associated with decreased DCs suggests their nonredundant role in tolerance induction. DC-mediated T cell immune tolerance is an active process that is influenced by genetic variants, environmental signals, as well as the nature of the specific DC subset presenting Ag to T cells. Answering the many open questions with regard to the role of DCs in immune tolerance could lead to the development of novel therapies for the prevention of autoimmune diseases.
Copyright © 2017 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulatory dendritic cells in autoimmunity: A comprehensive review.J Autoimmun. 2015 Sep;63:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2015.07.011. Epub 2015 Aug 5. J Autoimmun. 2015. PMID: 26255250 Review.
-
Dendritic cells, T cells and their interaction in rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2019 Apr;196(1):12-27. doi: 10.1111/cei.13256. Epub 2019 Jan 21. Clin Exp Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30589082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune checkpoints and the regulation of tolerogenicity in dendritic cells: Implications for autoimmunity and immunotherapy.Autoimmun Rev. 2019 Apr;18(4):359-368. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2019.02.006. Epub 2019 Feb 8. Autoimmun Rev. 2019. PMID: 30738957 Review.
-
Immunotherapy with costimulatory dendritic cells to control autoimmune inflammation.J Immunol. 2011 Oct 15;187(8):4018-30. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1101727. Epub 2011 Sep 7. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21900177
-
Dendritic Cells As Inducers of Peripheral Tolerance.Trends Immunol. 2017 Nov;38(11):793-804. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2017.07.007. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Trends Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28826942 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Adjusting to self in the thymus: CD4 versus CD8 lineage commitment and regulatory T cell development.J Exp Med. 2024 Oct 7;221(10):e20230896. doi: 10.1084/jem.20230896. Epub 2024 Jul 9. J Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 38980291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The PDE4 Inhibitor Tanimilast Blunts Proinflammatory Dendritic Cell Activation by SARS-CoV-2 ssRNAs.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 24;12:797390. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.797390. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35140709 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of antigen-specific immune tolerance using biodegradable nanoparticles containing antigen and dexamethasone.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Jul 12;14:5229-5242. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S210546. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31371958 Free PMC article.
-
Volatile organic compounds: A proinflammatory activator in autoimmune diseases.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 29;13:928379. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.928379. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35967306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Basic and Clinical Aspects of Rheumatoid Arthritis-associated Interstitial Lung Diseases.J Rheum Dis. 2022 Apr 1;29(2):61-70. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2022.29.2.61. J Rheum Dis. 2022. PMID: 37475899 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Steinman RM. The dendritic cell system and its role in immunogenicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:271–296. - PubMed
-
- Birnberg T, Bar-On L, Sapoznikov A, Caton ML, Cervantes-Barragan L, Makia D, Krauthgamer R, Brenner O, Ludewig B, Brockschnieder D, Riethmacher D, Reizis B, Jung S. Lack of conventional dendritic cells is compatible with normal development and T cell homeostasis, but causes myeloid proliferative syndrome. Immunity. 2008;29:986–997. - PubMed
-
- Singh RP, Hasan S, Sharma S, Nagra S, Yamaguchi DT, Wong DT, Hahn BH, Hossain A. Th17 cells in inflammation and autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13:1174–1181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

