Bone Marrow Protein Oxidation in Response to Ionizing Radiation in C57BL/6J Mice
- PMID: 28250382
- PMCID: PMC5302751
- DOI: 10.3390/proteomes2030291
Bone Marrow Protein Oxidation in Response to Ionizing Radiation in C57BL/6J Mice
Abstract
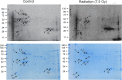
The bone marrow is one of the most radio-sensitive tissues. Accidental ionizing radiation exposure can damage mature blood cells and hematopoietic progenitor/stem cells, and mortality can result from hematopoietic insufficiency and infection. Ionizing radiation induces alterations in gene and protein expression in hematopoietic tissue. Here we investigated radiation effects on protein carbonylation, a primary marker for protein oxidative damage. C57BL/6 mice were either sham irradiated or exposed to 7.5 Gy 60Co (0.6 Gy/min) total body irradiation. Bone marrow was obtained 24 h post-irradiation. Two dimensional (2-D) gel electrophoresis and Oxyblot immunodetection were used to discover carbonylated proteins, and peptide mass fingerprinting was performed for identification. 2D gels allowed the detection of 13 carbonylated proteins in the bone marrow; seven of these were identified, with two pairs of the same protein. Baseline levels of carbonylation were found in 78 kDa glucose-related protein, heat shock protein cognate 71 KDa, actin, chitinase-like protein 3 (CHI3L1), and carbonic anhydrase 2 (CAII). Radiation increased carbonylation in four proteins, including CHI3L1 and CAII, and induced carbonylation of one additional protein (not identified). Our findings indicate that the profile of specific protein carbonylation in bone marrow is substantially altered by ionizing radiation. Accordingly, protein oxidation may be a mechanism for reduced cell viability.
Keywords: acute radiation syndrome; protein carbonylation; proteomic analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protracted Oxidative Alterations in the Mechanism of Hematopoietic Acute Radiation Syndrome.Antioxidants (Basel). 2015 Feb 27;4(1):134-52. doi: 10.3390/antiox4010134. Antioxidants (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26785342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Oxidation in the Lungs of C57BL/6J Mice Following X-Irradiation.Proteomes. 2015 Aug 19;3(3):249-265. doi: 10.3390/proteomes3030249. Proteomes. 2015. PMID: 28248270 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of ionizing radiation on liver protein oxidation and metabolic function in C57BL/6J mice.Int J Radiat Biol. 2014 Dec;90(12):1169-78. doi: 10.3109/09553002.2014.930536. Epub 2014 Aug 11. Int J Radiat Biol. 2014. PMID: 24899392
-
28Si total body irradiation injures bone marrow hematopoietic stem cells via induction of cellular apoptosis.Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2017 May;13:39-44. doi: 10.1016/j.lssr.2017.03.003. Epub 2017 Apr 5. Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2017. PMID: 28554508 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of bone marrow hemopoiesis: mechanisms of response to ionizing radiation exposure.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2002 Aug;17(4):405-26. doi: 10.1089/108497802760363204. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2002. PMID: 12396705 Review.
Cited by
-
Bone Marrow and Peripheral Blood Cells Toxicity of a Single 2.0 Gy Cobalt60 Ionizing Radiation: An Animal Model.Ethiop J Health Sci. 2019 Mar;29(2):195-202. doi: 10.4314/ejhs.v29i2.6. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2019. PMID: 31011267 Free PMC article.
-
Protracted Oxidative Alterations in the Mechanism of Hematopoietic Acute Radiation Syndrome.Antioxidants (Basel). 2015 Feb 27;4(1):134-52. doi: 10.3390/antiox4010134. Antioxidants (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26785342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological Effects of Scattered Versus Scanned Proton Beams on Normal Tissues in Total Body Irradiated Mice: Survival, Genotoxicity, Oxidative Stress and Inflammation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Nov 24;9(12):1170. doi: 10.3390/antiox9121170. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33255388 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the Medical Uses and Cellular Effects of High and Low Linear Energy Transfer Radiation.Toxics. 2022 Oct 21;10(10):628. doi: 10.3390/toxics10100628. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 36287908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Oxidation in the Lungs of C57BL/6J Mice Following X-Irradiation.Proteomes. 2015 Aug 19;3(3):249-265. doi: 10.3390/proteomes3030249. Proteomes. 2015. PMID: 28248270 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meder J., Michalowski A. Changes in cellularity and/or weight of mouse hemopoietic Tissues as a measure of acute radiation effects. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. (Warsz) 1980;28:9–18. - PubMed
-
- Davis T.A., Landauer M.R., Mog S.R., Barshishat-Kupper M., Zins S.R., Amare M.F., Day R.M. Timing of captopril administration determines radiation protection or radiation sensitization in a murine model of total body irradiation. Exp. Hematol. 2010;38:270–281. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2010.01.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cheng T., Rodrigues N., Shen H., Yang Y., Dombkowski D., Sykes M., Scadden D.T. Hematopoietic stem cell quiescence maintained by p21cip1/waf1. Science. 2000;287:1804–1808. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

