The ND10 Component Promyelocytic Leukemia Protein Acts as an E3 Ligase for SUMOylation of the Major Immediate Early Protein IE1 of Human Cytomegalovirus
- PMID: 28250117
- PMCID: PMC5411614
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02335-16
The ND10 Component Promyelocytic Leukemia Protein Acts as an E3 Ligase for SUMOylation of the Major Immediate Early Protein IE1 of Human Cytomegalovirus
Abstract
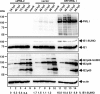
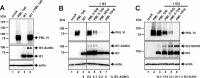
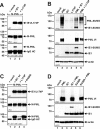
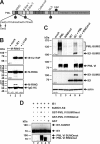
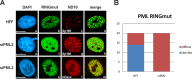
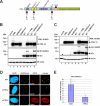
Previous studies identified the nuclear domain 10 (ND10) components promyelocytic leukemia protein (PML), hDaxx, and Sp100 as factors of an intrinsic immune response against human cytomegalovirus (HCMV). This antiviral function of ND10, however, is antagonized by viral effector proteins like IE1p72, which induces dispersal of ND10. Furthermore, we have shown that both major immediate early proteins of HCMV, IE1p72 and IE2p86, transiently colocalize with ND10 subnuclear structures and undergo modification by the covalent attachment of SUMO. Since recent reports indicate that PML acts as a SUMO E3 ligase, we asked whether the SUMOylation of IE1p72 and IE2p86 is regulated by PML. To address this, PML-depleted fibroblasts, as well as cells overexpressing individual PML isoforms, were infected with HCMV. Western blot experiments revealed a clear correlation between the degree of IE1p72 SUMO conjugation and the abundance of PML. On the other hand, the SUMOylation of IE2p86 was not affected by PML. By performing in vitro SUMOylation assays, we were able to provide direct evidence that IE1p72 is a substrate for PML-mediated SUMOylation. Interestingly, disruption of the RING finger domain of PML, which is proposed to confer SUMO E3 ligase activity, abolished PML-induced SUMOylation of IE1p72. In contrast, IE1p72 was still efficiently SUMO modified by a SUMOylation-defective PML mutant, indicating that intact ND10 bodies are not necessary for this effect. Thus, this is the first report that the E3 ligase PML is capable of stimulating the SUMOylation of a viral protein which is supposed to serve as a cellular mechanism to compromise specific functions of IE1p72.IMPORTANCE The major immediate early proteins of human cytomegalovirus, termed IE1p72 and IE2p86, have previously been shown to undergo posttranslational modification by covalent coupling to SUMO moieties at specific lysine residues. However, the enzymatic activities that are responsible for this modification have not been identified. Here, we demonstrate that the PML protein, which mediates an intrinsic immune response against HCMV, specifically serves as an E3 ligase for SUMO modification of IE1p72. Since SUMO modification of IE1p72 has previously been shown to interfere with STAT factor binding, thus compromising the interferon-antagonistic function of this viral effector protein, our finding highlights an additional mechanism through which PML is able to restrict viral infections.
Keywords: human cytomegalovirus; immediate early protein IE1; nuclear domain 10; promyelocytic leukemia protein PML; sumoylation.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Human Cytomegalovirus IE1 Protein Antagonizes PML Nuclear Body-Mediated Intrinsic Immunity via the Inhibition of PML De Novo SUMOylation.J Virol. 2017 Jan 31;91(4):e02049-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02049-16. Print 2017 Feb 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 27903803 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Human Cytomegalovirus IE1 Leads to Accumulation of Mono-SUMOylated PML That Is Protected from Degradation by Herpes Simplex Virus 1 ICP0.J Virol. 2018 Nov 12;92(23):e01452-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01452-18. Print 2018 Dec 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 30258013 Free PMC article.
-
Proteasome-independent disruption of PML oncogenic domains (PODs), but not covalent modification by SUMO-1, is required for human cytomegalovirus immediate-early protein IE1 to inhibit PML-mediated transcriptional repression.J Virol. 2001 Nov;75(22):10683-95. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.22.10683-10695.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11602710 Free PMC article.
-
The Human CMV IE1 Protein: An Offender of PML Nuclear Bodies.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2017;223:77-94. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-53168-7_4. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28528440 Review.
-
Intrinsic cellular defense mechanisms targeting human cytomegalovirus.Virus Res. 2011 May;157(2):128-33. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.10.002. Epub 2010 Oct 8. Virus Res. 2011. PMID: 20934469 Review.
Cited by
-
Modification of Nuclear Compartments and the 3D Genome in the Course of a Viral Infection.Acta Naturae. 2020 Oct-Dec;12(4):34-46. doi: 10.32607/actanaturae.11041. Acta Naturae. 2020. PMID: 33456976 Free PMC article.
-
Killer cell proteases can target viral immediate-early proteins to control human cytomegalovirus infection in a noncytotoxic manner.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Apr 13;16(4):e1008426. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008426. eCollection 2020 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32282833 Free PMC article.
-
Site-specific SUMOylation of viral polymerase processivity factor: a way of localizingtoND10 subnuclear domains for restricted and self-controlled reproduction of herpesvirus.Virulence. 2021 Dec;12(1):2883-2901. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.2000689. Virulence. 2021. PMID: 34747321 Free PMC article.
-
RING tetramerization is required for nuclear body biogenesis and PML sumoylation.Nat Commun. 2018 Mar 29;9(1):1277. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03498-0. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29599493 Free PMC article.
-
The Fate of Speckled Protein 100 (Sp100) During Herpesviruses Infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Feb 1;10:607526. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.607526. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33598438 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

