CXCL12-induced macropinocytosis modulates two distinct pathways to activate mTORC1 in macrophages
- PMID: 28250113
- PMCID: PMC5295849
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.2A0316-141RR
CXCL12-induced macropinocytosis modulates two distinct pathways to activate mTORC1 in macrophages
Abstract
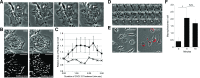
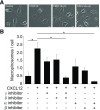
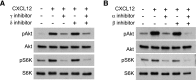
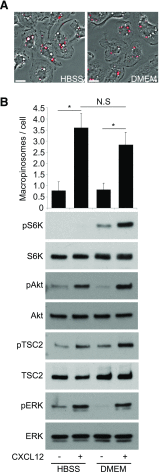
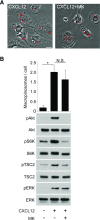
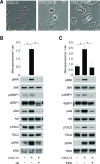
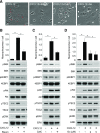
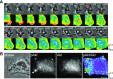
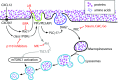
Although growth factors and chemokines elicit different overall effects on cells-growth and chemotaxis, respectively-and activate distinct classes of cell-surface receptors, nonetheless, they trigger similar cellular activities and signaling pathways. The growth factor M-CSF and the chemokine CXCL12 both stimulate the endocytic process of macropinocytosis, and both activate the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1), a protein complex that regulates cell metabolism. Recent studies of signaling by M-CSF in macrophages identified a role for macropinocytosis in the activation of mTORC1, in which delivery of extracellular amino acids into lysosomes via macropinocytosis was required for activation of mTORC1. Here, we analyzed the regulation of macropinosome (MP) formation in response to CXCL12 and identified 2 roles for macropinocytosis in the activation of mTORC1. Within 5 min of adding CXCL12, murine macrophages increased ruffling, macropinocytosis and amino acid-dependent activation of mTORC1. Inhibitors of macropinocytosis blocked activation of mTORC1, and various isoform-specific inhibitors of type 1 PI3K and protein kinase C (PKC) showed similar patterns of inhibition of macropinocytosis and mTORC1 activity. However, unlike the response to M-CSF, Akt phosphorylation (pAkt) in response to CXCL12 required the actin cytoskeleton and the formation of macropinocytic cups. Quantitative fluorescence microscopy showed that phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate (PIP3), a product of PI3K and an upstream activator of Akt, localized to macropinocytic cups and that pAkt occurred primarily in cups. These results indicate that CXCL12 activates mTORC1 via 2 mechanisms: 1) that the macropinocytic cup localizes Akt signaling and 2) that MPs convey extracellular nutrients to lysosomes.
Keywords: Akt; PI3K; live-cell imaging.
© Society for Leukocyte Biology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Macropinosomes as units of signal transduction.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2019 Feb 4;374(1765):20180157. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2018.0157. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30967006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macropinocytic cups function as signal platforms for the mTORC2-AKT pathway to modulate LPS-induced cytokine expression in macrophages.J Leukoc Biol. 2024 Oct 1;116(4):738-752. doi: 10.1093/jleuko/qiae074. J Leukoc Biol. 2024. PMID: 38513294
-
Growth factor signaling to mTORC1 by amino acid-laden macropinosomes.J Cell Biol. 2015 Oct 12;211(1):159-72. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201504097. Epub 2015 Oct 5. J Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26438830 Free PMC article.
-
Serine 302 Phosphorylation of Mouse Insulin Receptor Substrate 1 (IRS1) Is Dispensable for Normal Insulin Signaling and Feedback Regulation by Hepatic S6 Kinase.J Biol Chem. 2016 Apr 15;291(16):8602-17. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.714915. Epub 2016 Feb 4. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26846849 Free PMC article.
-
Growing knowledge of the mTOR signaling network.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014 Dec;36:79-90. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.09.011. Epub 2014 Sep 19. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 25242279 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SP-R210 isoforms of Myosin18A modulate endosomal sorting and recognition of influenza A virus infection in macrophages.Microbes Infect. 2024 Mar-Apr;26(3):105280. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2023.105280. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Microbes Infect. 2024. PMID: 38135024
-
Akt and SGK protein kinases are required for efficient feeding by macropinocytosis.J Cell Sci. 2019 Jan 24;132(2):jcs224998. doi: 10.1242/jcs.224998. J Cell Sci. 2019. PMID: 30617109 Free PMC article.
-
Macropinosomes as units of signal transduction.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2019 Feb 4;374(1765):20180157. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2018.0157. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30967006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chaperone-assisted selective autophagy targets filovirus VP40 as a client and restricts egress of virus particles.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Jan 10;120(2):e2210690120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2210690120. Epub 2023 Jan 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 36598950 Free PMC article.
-
Dark-Side of Exosomes.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1275:101-131. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-49844-3_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33539013
References
-
- Lewis W. H. (1931) Pinocytosis. Bull. Johns Hopkins Hosp. Bull. 49, 17–27.
-
- Mercer J., Greber U. F. (2013) Virus interactions with endocytic pathways in macrophages and dendritic cells. Trends Microbiol. 21, 380–388. - PubMed
-
- Kerr M. C., Teasdale R. D. (2009) Defining macropinocytosis. Traffic 10, 364–371. - PubMed
-
- Commisso C., Davidson S. M., Soydaner-Azeloglu R. G., Parker S. J., Kamphorst J. J., Hackett S., Grabocka E., Nofal M., Drebin J. A., Thompson C. B., Rabinowitz J. D., Metallo C. M., Vander Heiden M. G., Bar-Sagi D. (2013) Macropinocytosis of protein is an amino acid supply route in Ras-transformed cells. Nature 497, 633–637. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

