The Complex Roles of Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin in Adipocytes and Beyond
- PMID: 28237819
- PMCID: PMC5682923
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2017.01.004
The Complex Roles of Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin in Adipocytes and Beyond
Abstract
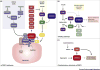
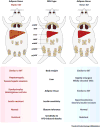
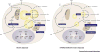
Having healthy adipose tissue is essential for metabolic fitness. This is clear from the obesity epidemic, which is unveiling a myriad of comorbidities associated with excess adipose tissue including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer. Lipodystrophy also causes insulin resistance, emphasizing the importance of having a balanced amount of fat. In cells, the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) complexes 1 and 2 (mTORC1 and mTORC2, respectively) link nutrient and hormonal signaling with metabolism, and recent studies are shedding new light on their in vivo roles in adipocytes. In this review, we discuss how recent advances in adipose tissue and mTOR biology are converging to reveal new mechanisms that maintain healthy adipose tissue, and discuss ongoing mysteries of mTOR signaling, particularly for the less understood complex mTORC2.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Elucidating the role of Lkb1 and mTOR in adipose tissue.Adipocyte. 2019 Dec;8(1):26-30. doi: 10.1080/21623945.2018.1535743. Epub 2018 Oct 20. Adipocyte. 2019. PMID: 30318987 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Adipocyte and Macrophage Functions by mTORC1 and 2 in Metabolic Diseases.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2021 Jan;65(1):e1900768. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201900768. Epub 2020 Mar 8. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2021. PMID: 32103588 Review.
-
The Role of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) in Insulin Signaling.Nutrients. 2017 Oct 27;9(11):1176. doi: 10.3390/nu9111176. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 29077002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation and metabolic functions of mTORC1 and mTORC2.Physiol Rev. 2021 Jul 1;101(3):1371-1426. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00026.2020. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Physiol Rev. 2021. PMID: 33599151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mTORC2 Signaling: A Path for Pancreatic β Cell's Growth and Function.J Mol Biol. 2018 Mar 30;430(7):904-918. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2018.02.013. Epub 2018 Feb 23. J Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29481838 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteome and Phosphoproteome Analysis of Brown Adipocytes Reveals That RICTOR Loss Dampens Global Insulin/AKT Signaling.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020 Jul;19(7):1104-1119. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA120.001946. Epub 2020 Mar 31. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 32234964 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-enriched RagB isoforms regulate the dynamics of mTORC1 activity through GATOR1 inhibition.Nat Cell Biol. 2022 Sep;24(9):1407-1421. doi: 10.1038/s41556-022-00977-x. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Nat Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 36097071 Free PMC article.
-
RNA based individualized drug selection in breast cancer patients without patient-matched normal tissue.Oncotarget. 2018 Aug 17;9(64):32362-32372. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25981. eCollection 2018 Aug 17. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30190792 Free PMC article.
-
Non-canonical mTORC2 Signaling Regulates Brown Adipocyte Lipid Catabolism through SIRT6-FoxO1.Mol Cell. 2019 Aug 22;75(4):807-822.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.07.023. Mol Cell. 2019. PMID: 31442424 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Its Impact on Adipogenesis: Molecular Mechanisms Implicated.Nutrients. 2023 Dec 12;15(24):5082. doi: 10.3390/nu15245082. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 38140341 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wullschleger S, Loewith R, Hall MN. TOR Signaling in Growth and Metabolism. Cell. 2006;124(3):471–484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

