Drude polarizable force field for aliphatic ketones and aldehydes, and their associated acyclic carbohydrates
- PMID: 28190218
- PMCID: PMC5392138
- DOI: 10.1007/s10822-017-0010-0
Drude polarizable force field for aliphatic ketones and aldehydes, and their associated acyclic carbohydrates
Abstract
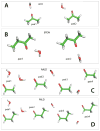
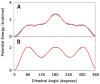
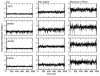
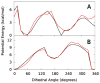
The majority of computer simulations exploring biomolecular function employ Class I additive force fields (FF), which do not treat polarization explicitly. Accordingly, much effort has been made into developing models that go beyond the additive approximation. Development and optimization of the Drude polarizable FF has yielded parameters for selected lipids, proteins, DNA and a limited number of carbohydrates. The work presented here details parametrization of aliphatic aldehydes and ketones (viz. acetaldehyde, propionaldehyde, butaryaldehyde, isobutaryaldehyde, acetone, and butanone) as well as their associated acyclic sugars (D-allose and D-psicose). LJ parameters are optimized targeting experimental heats of vaporization and molecular volumes, while the electrostatic parameters are optimized targeting QM water interactions, dipole moments, and molecular polarizabilities. Bonded parameters are targeted to both QM and crystal survey values, with the models for ketones and aldehydes shown to be in good agreement with QM and experimental target data. The reported heats of vaporization and molecular volumes represent a compromise between the studied model compounds. Simulations of the model compounds show an increase in the magnitude and the fluctuations of the dipole moments in moving from gas phase to condensed phases, which is a phenomenon that the additive FF is intrinsically unable to reproduce. The result is a polarizable model for aliphatic ketones and aldehydes including the acyclic sugars D-allose and D-psicose, thereby extending the available biomolecules in the Drude polarizable FF.
Keywords: CHARMM; Electronic polarization; Glycan; Molecular dynamics; Molecular mechanics; Potential energy function.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Further Optimization and Validation of the Classical Drude Polarizable Protein Force Field.J Chem Theory Comput. 2020 May 12;16(5):3221-3239. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.0c00057. Epub 2020 Apr 27. J Chem Theory Comput. 2020. PMID: 32282198 Free PMC article.
-
Improved Modeling of Halogenated Ligand-Protein Interactions Using the Drude Polarizable and CHARMM Additive Empirical Force Fields.J Chem Inf Model. 2019 Jan 28;59(1):215-228. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.8b00616. Epub 2018 Nov 27. J Chem Inf Model. 2019. PMID: 30418023 Free PMC article.
-
Drude Polarizable Force Field Parametrization of Carboxylate and N-Acetyl Amine Carbohydrate Derivatives.J Chem Theory Comput. 2019 Sep 10;15(9):4982-5000. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.9b00327. Epub 2019 Aug 29. J Chem Theory Comput. 2019. PMID: 31411469 Free PMC article.
-
CHARMM additive and polarizable force fields for biophysics and computer-aided drug design.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 May;1850(5):861-871. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.08.004. Epub 2014 Aug 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25149274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Empirical Polarizable Force Field Based on the Classical Drude Oscillator Model: Development History and Recent Applications.Chem Rev. 2016 May 11;116(9):4983-5013. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00505. Epub 2016 Jan 27. Chem Rev. 2016. PMID: 26815602 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Polarizable Empirical Force Field for Halogen-Containing Compounds Based on the Classical Drude Oscillator.J Chem Theory Comput. 2018 Feb 13;14(2):1083-1098. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.7b01086. Epub 2018 Jan 31. J Chem Theory Comput. 2018. PMID: 29357257 Free PMC article.
-
Extension of the CHARMM Classical Drude Polarizable Force Field to N- and O-Linked Glycopeptides and Glycoproteins.J Phys Chem B. 2022 Sep 8;126(35):6642-6653. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.2c04245. Epub 2022 Aug 25. J Phys Chem B. 2022. PMID: 36005290 Free PMC article.
-
CHARMM at 45: Enhancements in Accessibility, Functionality, and Speed.J Phys Chem B. 2024 Oct 17;128(41):9976-10042. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.4c04100. Epub 2024 Sep 20. J Phys Chem B. 2024. PMID: 39303207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improved Modeling of Cation-π and Anion-Ring Interactions Using the Drude Polarizable Empirical Force Field for Proteins.J Comput Chem. 2020 Feb 15;41(5):439-448. doi: 10.1002/jcc.26067. Epub 2019 Sep 13. J Comput Chem. 2020. PMID: 31518010 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Aspects of the O-glycosylation Linkage in Glycopeptides via MD Simulations and Comparison with NMR Experiments.Chemphyschem. 2019 Jun 4;20(11):1527-1537. doi: 10.1002/cphc.201900079. Epub 2019 May 6. Chemphyschem. 2019. PMID: 30920077 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

