Applications of Immunogenomics to Cancer
- PMID: 28187283
- PMCID: PMC5972371
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.01.014
Applications of Immunogenomics to Cancer
Abstract
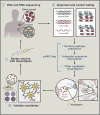
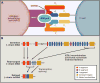
Cancer immunogenomics originally was framed by research supporting the hypothesis that cancer mutations generated novel peptides seen as "non-self" by the immune system. The search for these "neoantigens" has been facilitated by the combination of new sequencing technologies, specialized computational analyses, and HLA binding predictions that evaluate somatic alterations in a cancer genome and interpret their ability to produce an immune-stimulatory peptide. The resulting information can characterize a tumor's neoantigen load, its cadre of infiltrating immune cell types, the T or B cell receptor repertoire, and direct the design of a personalized therapeutic.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Best practices for bioinformatic characterization of neoantigens for clinical utility.Genome Med. 2019 Aug 28;11(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s13073-019-0666-2. Genome Med. 2019. PMID: 31462330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Personalized neoantigen vaccines: A new approach to cancer immunotherapy.Bioorg Med Chem. 2018 Jun 1;26(10):2842-2849. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2017.10.021. Epub 2017 Oct 19. Bioorg Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29111369 Review.
-
TSNAdb: A Database for Tumor-specific Neoantigens from Immunogenomics Data Analysis.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2018 Aug;16(4):276-282. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2018.06.003. Epub 2018 Sep 15. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 30223042 Free PMC article.
-
Landscape of tumor-infiltrating T cell repertoire of human cancers.Nat Genet. 2016 Jul;48(7):725-32. doi: 10.1038/ng.3581. Epub 2016 May 30. Nat Genet. 2016. PMID: 27240091 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic analysis of 63,220 tumors reveals insights into tumor uniqueness and targeted cancer immunotherapy strategies.Genome Med. 2017 Feb 24;9(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13073-017-0408-2. Genome Med. 2017. PMID: 28231819 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Investigating the correlation between DNA methylation and immune‑associated genes of lung adenocarcinoma based on a competing endogenous RNA network.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Oct;22(4):3173-3182. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11445. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32945447 Free PMC article.
-
Residue substitution enhances the immunogenicity of neoepitopes from gastric cancers.Cancer Biol Med. 2021 Nov 24;18(4):1053-65. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2021.0022. Cancer Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 35959968 Free PMC article.
-
CD8 T cell function and cross-reactivity explored by stepwise increased peptide-HLA versus TCR affinity.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 10;13:973986. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.973986. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36032094 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the potential of the TCR repertoire as a tumor biomarker (Review).Oncol Lett. 2024 Jun 28;28(3):413. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14546. eCollection 2024 Sep. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38988449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Immunogenicity and Anti-tumor Efficacy of a Rationally Designed Neoantigen Vaccine for B16F10 Mouse Melanoma.Front Immunol. 2019 Nov 5;10:2472. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02472. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31749795 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alamyar E, Duroux P, Lefranc M-P, Giudicelli V. IMGT(®) tools for the nucleotide analysis of immunoglobulin (IG) and T cell receptor (TR) V-(D)-J repertoires, polymorphisms, and IG mutations: IMGT/V-QUEST and IMGT/HighV-QUEST for NGS. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012;882:569–604. - PubMed
-
- Angelova M, Charoentong P, Hackl H, Fischer ML, Snajder R, Krogsdam AM, Waldner MJ, Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Galon J, et al. Characterization of the immunophenotypes and antigenomes of colorectal cancers reveals distinct tumor escape mechanisms and novel targets for immunotherapy. Genome Biol. 2015;16:64. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aouinti S, Malouche D, Giudicelli V, Kossida S, Lefranc M-P. IMGT/HighV-QUEST Statistical Significance of IMGT Clonotype (AA) Diversity per Gene for Standardized Comparisons of Next Generation Sequencing Immunoprofiles of Immunoglobulins and T Cell Receptors. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0142353. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Babbitt BP, Allen PM, Matsueda G, Haber E, Unanue ER. Binding of immunogenic peptides to Ia histocompatibility molecules. Nature. 1985;317:359–361. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

