Disordered clusters of Bak dimers rupture mitochondria during apoptosis
- PMID: 28182867
- PMCID: PMC5302884
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.19944
Disordered clusters of Bak dimers rupture mitochondria during apoptosis
Abstract
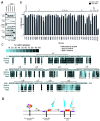
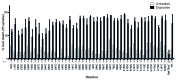
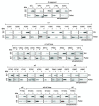
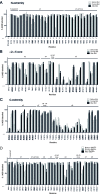
During apoptosis, Bak and Bax undergo major conformational change and form symmetric dimers that coalesce to perforate the mitochondrial outer membrane via an unknown mechanism. We have employed cysteine labelling and linkage analysis to the full length of Bak in mitochondria. This comprehensive survey showed that in each Bak dimer the N-termini are fully solvent-exposed and mobile, the core is highly structured, and the C-termini are flexible but restrained by their contact with the membrane. Dimer-dimer interactions were more labile than the BH3:groove interaction within dimers, suggesting there is no extensive protein interface between dimers. In addition, linkage in the mobile Bak N-terminus (V61C) specifically quantified association between dimers, allowing mathematical simulations of dimer arrangement. Together, our data show that Bak dimers form disordered clusters to generate lipidic pores. These findings provide a molecular explanation for the observed structural heterogeneity of the apoptotic pore.
Keywords: Bak; Bcl-2 proteins; apoptotic pore; biophysics; cell biology; cell death; disordered cluster; human; oligomer; structural biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bak apoptotic pores involve a flexible C-terminal region and juxtaposition of the C-terminal transmembrane domains.Cell Death Differ. 2015 Oct;22(10):1665-75. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.15. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Cell Death Differ. 2015. PMID: 25744027 Free PMC article.
-
Pore formation by dimeric Bak and Bax: an unusual pore?Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017 Aug 5;372(1726):20160218. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2016.0218. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28630157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BAK α6 permits activation by BH3-only proteins and homooligomerization via the canonical hydrophobic groove.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jul 18;114(29):7629-7634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1702453114. Epub 2017 Jul 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28673969 Free PMC article.
-
Organization of the mitochondrial apoptotic BAK pore: oligomerization of the BAK homodimers.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jan 31;289(5):2537-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.526806. Epub 2013 Dec 11. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24337568 Free PMC article.
-
Bax, Bak and beyond - mitochondrial performance in apoptosis.FEBS J. 2018 Feb;285(3):416-431. doi: 10.1111/febs.14186. Epub 2017 Sep 4. FEBS J. 2018. PMID: 28755482 Review.
Cited by
-
A BAK subdomain that binds mitochondrial lipids selectively and releases cytochrome C.Cell Death Differ. 2023 Mar;30(3):794-808. doi: 10.1038/s41418-022-01083-z. Epub 2022 Nov 14. Cell Death Differ. 2023. PMID: 36376382 Free PMC article.
-
Pore-forming proteins as drivers of membrane permeabilization in cell death pathways.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023 May;24(5):312-333. doi: 10.1038/s41580-022-00564-w. Epub 2022 Dec 21. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36543934 Review.
-
[Physiological Function and Structural Basis of Bcl-2 Family Proteins].Zhongguo Xi Bao Sheng Wu Xue Xue Bao. 2019 Aug;41(8):1477-1489. Epub 2019 Sep 12. Zhongguo Xi Bao Sheng Wu Xue Xue Bao. 2019. PMID: 34249113 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
High-dose radiation-induced immunogenic cell death of bladder cancer cells leads to dendritic cell activation.PLoS One. 2024 Sep 4;19(9):e0307024. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307024. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39231199 Free PMC article.
-
Study of the Bcl-2 Interactome by BiFC Reveals Differences in the Activation Mechanism of Bax and Bak.Cells. 2023 Mar 3;12(5):800. doi: 10.3390/cells12050800. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36899936 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basañez G, Nechushtan A, Drozhinin O, Chanturiya A, Choe E, Tutt S, Wood KA, Hsu Y, Zimmerberg J, Youle RJ. Bax, but not Bcl-xL, decreases the lifetime of planar phospholipid bilayer membranes at subnanomolar concentrations. PNAS. 1999;96:5492–5497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.10.5492. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

