miRNAs cooperate in apoptosis regulation during C. elegans development
- PMID: 28167500
- PMCID: PMC5322734
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.288555.116
miRNAs cooperate in apoptosis regulation during C. elegans development
Abstract
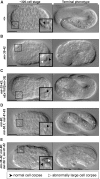
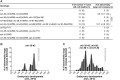
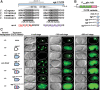
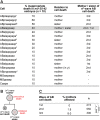
Programmed cell death occurs in a highly reproducible manner during Caenorhabditis elegans development. We demonstrate that, during embryogenesis, miR-35 and miR-58 bantam family microRNAs (miRNAs) cooperate to prevent the precocious death of mothers of cells programmed to die by repressing the gene egl-1, which encodes a proapoptotic BH3-only protein. In addition, we present evidence that repression of egl-1 is dependent on binding sites for miR-35 and miR-58 family miRNAs within the egl-1 3' untranslated region (UTR), which affect both mRNA copy number and translation. Furthermore, using single-molecule RNA fluorescent in situ hybridization (smRNA FISH), we show that egl-1 is transcribed in the mother of a cell programmed to die and that miR-35 and miR-58 family miRNAs prevent this mother from dying by keeping the copy number of egl-1 mRNA below a critical threshold. Finally, miR-35 and miR-58 family miRNAs can also dampen the transcriptional boost of egl-1 that occurs specifically in a daughter cell that is programmed to die. We propose that miRNAs compensate for lineage-specific differences in egl-1 transcriptional activation, thus ensuring that EGL-1 activity reaches the threshold necessary to trigger death only in daughter cells that are programmed to die.
Keywords: BH3-only; C. elegans; development; embryo; miRNA; programmed cell death.
© 2017 Sherrard et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MiR-35 buffers apoptosis thresholds in the C. elegans germline by antagonizing both MAPK and core apoptosis pathways.Cell Death Differ. 2019 Dec;26(12):2637-2651. doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0325-6. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Cell Death Differ. 2019. PMID: 30952991 Free PMC article.
-
Six and Eya promote apoptosis through direct transcriptional activation of the proapoptotic BH3-only gene egl-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Aug 31;107(35):15479-84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1010023107. Epub 2010 Aug 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20713707 Free PMC article.
-
HRPK-1, a conserved KH-domain protein, modulates microRNA activity during Caenorhabditis elegans development.PLoS Genet. 2019 Oct 4;15(10):e1008067. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008067. eCollection 2019 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31584932 Free PMC article.
-
Size Matters: How C. elegans Asymmetric Divisions Regulate Apoptosis.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2017;61:141-163. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-53150-2_6. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2017. PMID: 28409303 Review.
-
Roles of microRNAs in the Caenorhabditis elegans nervous system.J Genet Genomics. 2013 Sep 20;40(9):445-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Aug 7. J Genet Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24053946 Review.
Cited by
-
A genetic screen identifies C. elegans eif-3.H and hrpr-1 as pro-apoptotic genes and potential activators of egl-1 expression.MicroPubl Biol. 2024 Feb 16;2024:10.17912/micropub.biology.001126. doi: 10.17912/micropub.biology.001126. eCollection 2024. MicroPubl Biol. 2024. PMID: 38434221 Free PMC article.
-
A Compilation of the Diverse miRNA Functions in Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 9;24(8):6963. doi: 10.3390/ijms24086963. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell death in animal development.Development. 2020 Jul 24;147(14):dev191882. doi: 10.1242/dev.191882. Development. 2020. PMID: 32709690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo CRISPR screening for phenotypic targets of the mir-35-42 family in C. elegans.Genes Dev. 2020 Sep 1;34(17-18):1227-1238. doi: 10.1101/gad.339333.120. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Genes Dev. 2020. PMID: 32820039 Free PMC article.
-
PUF-8, a C. elegans ortholog of the RNA-binding proteins PUM1 and PUM2, is required for robustness of the cell death fate.Development. 2023 Oct 1;150(19):dev201167. doi: 10.1242/dev.201167. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Development. 2023. PMID: 37747106 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brennecke J, Hipfner DR, Stark A, Russell RB, Cohen SM. 2003. bantam encodes a developmentally regulated microRNA that controls cell proliferation and regulates the proapoptotic gene hid in Drosophila. Cell 113: 25–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
