Lychee Seed Saponins Improve Cognitive Function and Prevent Neuronal Injury via Inhibiting Neuronal Apoptosis in a Rat Model of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 28165366
- PMCID: PMC5331536
- DOI: 10.3390/nu9020105
Lychee Seed Saponins Improve Cognitive Function and Prevent Neuronal Injury via Inhibiting Neuronal Apoptosis in a Rat Model of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
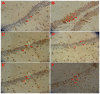
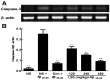
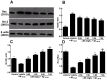
Lychee seed is a traditional Chinese medicine and possesses many activities, including hypoglycemia, liver protection, antioxidation, antivirus, and antitumor. However, its effect on neuroprotection is still unclear. The present study investigated the effects of lychee seed saponins (LSS) on neuroprotection and associated mechanisms. We established a rat model of Alzheimer's disease (AD) by injecting Aβ25-35 into the lateral ventricle of rats and evaluated the effect of LSS on spatial learning and memory ability via the Morris water maze. Neuronal apoptosis was analyzed by hematoxylin and eosin stain and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (Tdt)-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling analysis, and mRNA expression of caspase-3 and protein expressions of Bax and Bcl-2 by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and Western blotting, respectively. The results showed that LSS remarkably improved cognitive function and alleviated neuronal injury by inhibiting apoptosis in the hippocampus of AD rats. Furthermore, the mRNA expression of caspase-3 and the protein expression of Bax were downregulated, while the protein expression of Bcl-2 and the ratio of Bcl-2/Bax were increased by LSS. We demonstrate that LSS significantly improves cognitive function and prevent neuronal injury in the AD rats via regulation of the apoptosis pathway. Therefore, LSS may be developed as a nutritional supplement and sold as a drug for AD prevention and/or treatment.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; apoptosis; cognitive function; lychee seed saponins; neuronal injury; rat model of Alzheimer’s disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
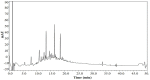
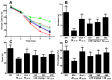
 LSS 480 mg/kg; (B) Number of times across the platform; (C) platform quadrant dwell time; and (D) percentage of the total distance run in the platform quadrant. There were 10 rats used for each experimental group and expressed as the mean ± SD. ** p < 0.01 vs. the AD rats treated with NS (control).
LSS 480 mg/kg; (B) Number of times across the platform; (C) platform quadrant dwell time; and (D) percentage of the total distance run in the platform quadrant. There were 10 rats used for each experimental group and expressed as the mean ± SD. ** p < 0.01 vs. the AD rats treated with NS (control).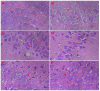
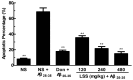
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic Candidates for Alzheimer's Disease: Saponins.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 22;24(13):10505. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310505. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitory Effect of Lychee Seed Saponins on Apoptosis Induced by Aβ25-35 through Regulation of the Apoptotic and NF-κB Pathways in PC12 Cells.Nutrients. 2017 Mar 29;9(4):337. doi: 10.3390/nu9040337. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28353652 Free PMC article.
-
The seed of Litchi chinensis fraction ameliorates hippocampal neuronal injury in an Aβ25-35-induced Alzheimer's disease rat model via the AKT/GSK-3β pathway.Pharm Biol. 2020 Dec;58(1):35-43. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2019.1697298. Pharm Biol. 2020. PMID: 31881157 Free PMC article.
-
Isorhynchophylline treatment improves the amyloid-β-induced cognitive impairment in rats via inhibition of neuronal apoptosis and tau protein hyperphosphorylation.J Alzheimers Dis. 2014;39(2):331-46. doi: 10.3233/JAD-131457. J Alzheimers Dis. 2014. PMID: 24164737
-
Neuroprotection by saponins.Phytother Res. 2015 Feb;29(2):187-200. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5246. Epub 2014 Nov 19. Phytother Res. 2015. PMID: 25408503 Review.
Cited by
-
Protective roles of isoastilbin against Alzheimer's disease via Nrf2‑mediated antioxidation and anti‑apoptosis.Int J Mol Med. 2019 Mar;43(3):1406-1416. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4058. Epub 2019 Jan 10. Int J Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30664148 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Changes in the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System and the Beneficial Effects of Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Inhibitors on Spatial Learning and Memory in a Rat Model of Chronic Cerebral Ischemia.Front Neurosci. 2017 Jun 23;11:359. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00359. eCollection 2017. Front Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28690496 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Candidates for Alzheimer's Disease: Saponins.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 22;24(13):10505. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310505. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cognitive effects of guarana supplementation with maximal intensity cycling.Br J Nutr. 2023 Jul 28;130(2):253-260. doi: 10.1017/S0007114522002859. Epub 2022 Sep 23. Br J Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36146946 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dietary Plant Polyphenols as the Potential Drugs in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Current Evidence, Advances, and Opportunities.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Feb 21;2022:5288698. doi: 10.1155/2022/5288698. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35237381 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cairns N.J. Alzheimer’s disease: Neurodegeneration. In: Squire L.R., editor. Encyclopedia of Neuroscience. Academic Press; Oxford, UK: 2009. pp. 275–281.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

