Consensus M2e peptide conjugated to gold nanoparticles confers protection against H1N1, H3N2 and H5N1 influenza A viruses
- PMID: 28161578
- PMCID: PMC5572660
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2017.01.021
Consensus M2e peptide conjugated to gold nanoparticles confers protection against H1N1, H3N2 and H5N1 influenza A viruses
Abstract
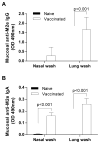
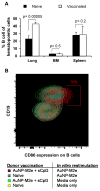
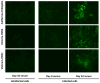
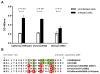
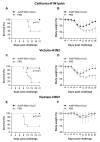
The extracellular domain of influenza A ion channel membrane matrix protein 2 (M2e) is considered to be a potential candidate to develop a universal influenza A vaccine. However poor immunogenicity of M2e presents a significant roadblock. We have developed a vaccine formulation comprising of the consensus M2e peptide conjugated to gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) with CpG as a soluble adjuvant (AuNP-M2e + sCpG). We demonstrate that intranasal delivery of AuNP-M2e + sCpG in mice induces lung B cell activation and robust serum anti-M2e immunoglobulin G (IgG) response, with stimulation of both IgG1 and IgG2a subtypes. Using Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells infected with A/California/04/2009 (H1N1pdm) pandemic strain, or A/Victoria/3/75 (H3N2), or the highly pathogenic avian influenza virus A/Vietnam/1203/2004 (H5N1) as immunosorbants we further show that the antibodies generated are also capable of binding to the homotetrameric form of M2 expressed on infected cells. Lethal challenge of vaccinated mice with A/California/04/2009 (H1N1pdm) pandemic strain, A/Victoria/3/75 (H3N2), and the highly pathogenic avian influenza virus A/Vietnam/1203/2004 (H5N1) led to 100%, 92%, and 100% protection, respectively. Overall, this study helps to lay the foundation of a potential universal influenza A vaccine.
Keywords: Adjuvants; CpG; Gold nanoparticles; Influenza vaccine; Intranasal vaccination; M2e; Universal influenza vaccine.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
An H5N1 M2e-based multiple antigenic peptide vaccine confers heterosubtypic protection from lethal infection with pandemic 2009 H1N1 virus.Virol J. 2010 Jul 12;7:151. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-151. Virol J. 2010. PMID: 20624292 Free PMC article.
-
Protection against influenza A virus by vaccination with a recombinant fusion protein linking influenza M2e to human serum albumin (HSA).J Virol Methods. 2016 Feb;228:84-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2015.11.014. Epub 2015 Nov 23. J Virol Methods. 2016. PMID: 26615805
-
Protection against multiple influenza A virus strains induced by candidate recombinant vaccine based on heterologous M2e peptides linked to flagellin.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 23;10(3):e0119520. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119520. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25799221 Free PMC article.
-
M2e-immobilized gold nanoparticles as influenza A vaccine: Role of soluble M2e and longevity of protection.Vaccine. 2015 May 11;33(20):2307-15. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.03.063. Epub 2015 Apr 2. Vaccine. 2015. PMID: 25842219 Free PMC article.
-
Influenza A viruses: why focusing on M2e-based universal vaccines.Virus Genes. 2011 Feb;42(1):1-8. doi: 10.1007/s11262-010-0547-7. Epub 2010 Nov 17. Virus Genes. 2011. PMID: 21082230 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging Advances of Nanotechnology in Drug and Vaccine Delivery against Viral Associated Respiratory Infectious Diseases (VARID).Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 28;22(13):6937. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136937. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34203268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Inhibition of H1N1 Influenza Virus-Induced Apoptosis by Surface Decoration of Selenium Nanoparticles with β-Thujaplicin through Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated AKT and p53 Signaling Pathways.ACS Omega. 2020 Nov 16;5(47):30633-30642. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c04624. eCollection 2020 Dec 1. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 33283112 Free PMC article.
-
The Next Generation of Influenza Vaccines: Towards a Universal Solution.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Jan 7;9(1):26. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9010026. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33430278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of tunable acetalated dextran microparticle platform to optimize M2e-based influenza vaccine efficacy.J Control Release. 2018 Nov 10;289:114-124. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.09.020. Epub 2018 Sep 24. J Control Release. 2018. PMID: 30261204 Free PMC article.
-
AuNP-M2e + sCpG vaccination of juvenile mice generates lifelong protective immunity to influenza A virus infection.Immun Ageing. 2019 Sep 2;16:23. doi: 10.1186/s12979-019-0162-y. eCollection 2019. Immun Ageing. 2019. PMID: 31507643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen PJ. Avian influenza pandemic: not if, but when. Pediatr Nurs. 2006;32:76–81. - PubMed
-
- Chowdhury MY, Li R, Kim J-H, Park M-E, Kim T-H, Pathinayake P, Weeratunga P, Song MK, Son H-Y, Hong S-P. Mucosal Vaccination with Recombinant Lactobacillus casei-Displayed CTA1-Conjugated Consensus Matrix Protein-2 (sM2) Induces Broad Protection against Divergent Influenza Subtypes in BALB/c Mice. PLoS One. 2014:9. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dawood FS, Iuliano AD, Reed C, Meltzer MI, Shay DK, Cheng PY, Bandaranayake D, Breiman RF, Brooks WA, Buchy P, Feikin DR, Fowler KB, Gordon A, Hien NT, Horby P, Huang QS, Katz MA, Krishnan A, Lal R, Montgomery JM, Molbak K, Pebody R, Presanis AM, Razuri H, Steens A, Tinoco YO, Wallinga J, Yu H, Vong S, Bresee J, Widdowson MA. Estimated global mortality associated with the first 12 months of 2009 pandemic influenza A H1N1 virus circulation: a modelling study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2012;12:687–695. - PubMed
-
- De Filette M, Martens W, Smet A, Schotsaert M, Birkett A, Londoño-Arcila P, Fiers W, Saelens X. Universal influenza A M2e-HBc vaccine protects against disease even in the presence of pre-existing anti-HBc antibodies. Vaccine. 2008;26:6503–6507. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

