Contrast-enhanced micro-CT imaging in murine carotid arteries: a new protocol for computing wall shear stress
- PMID: 28155699
- PMCID: PMC5259814
- DOI: 10.1186/s12938-016-0270-2
Contrast-enhanced micro-CT imaging in murine carotid arteries: a new protocol for computing wall shear stress
Abstract
Background: Wall shear stress (WSS) is involved in the pathophysiology of atherosclerosis. The correlation between WSS and atherosclerosis can be investigated over time using a WSS-manipulated atherosclerotic mouse model. To determine WSS in vivo, detailed 3D geometry of the vessel network is required. However, a protocol to reconstruct 3D murine vasculature using this animal model is lacking. In this project, we evaluated the adequacy of eXIA 160, a small animal contrast agent, for assessing murine vascular network on micro-CT. Also, a protocol was established for vessel geometry segmentation and WSS analysis.
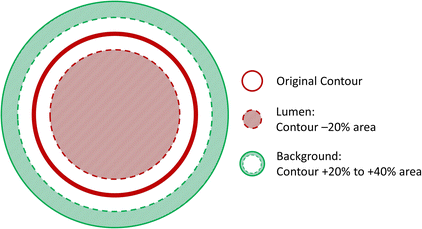
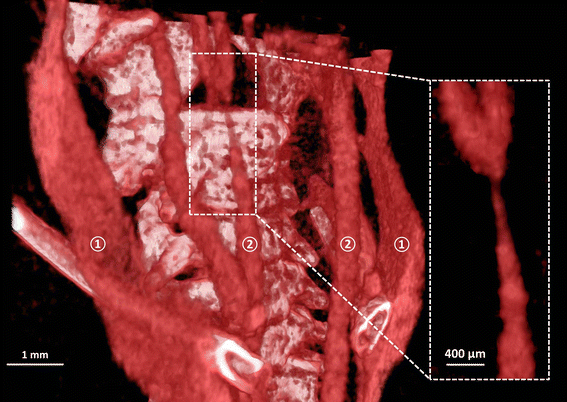
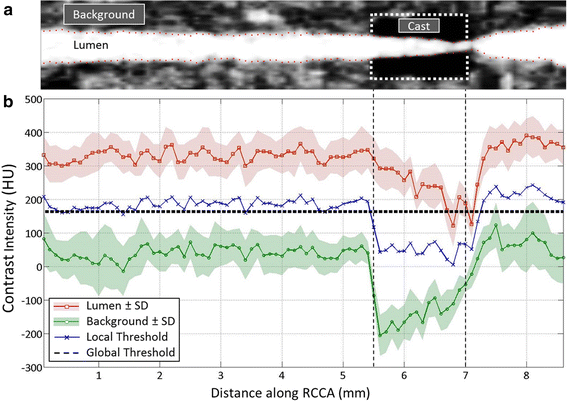
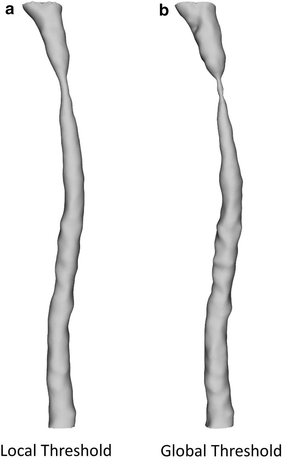
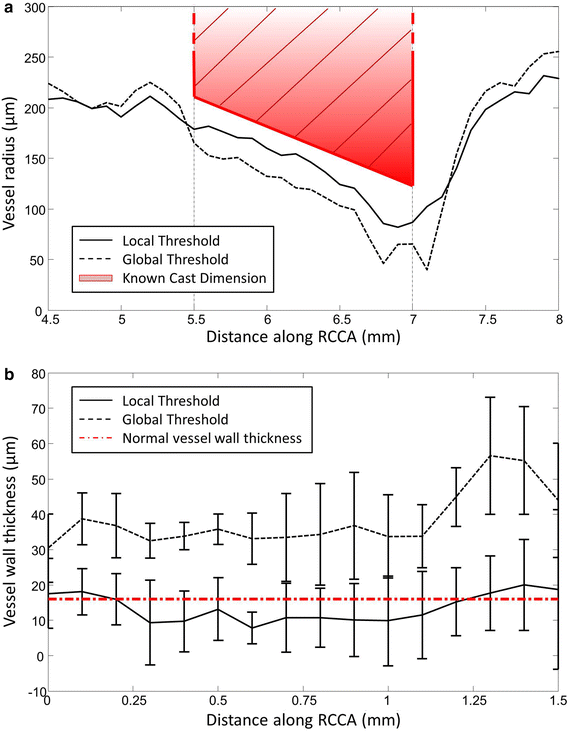
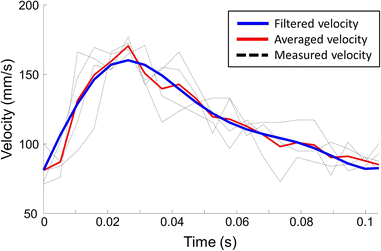
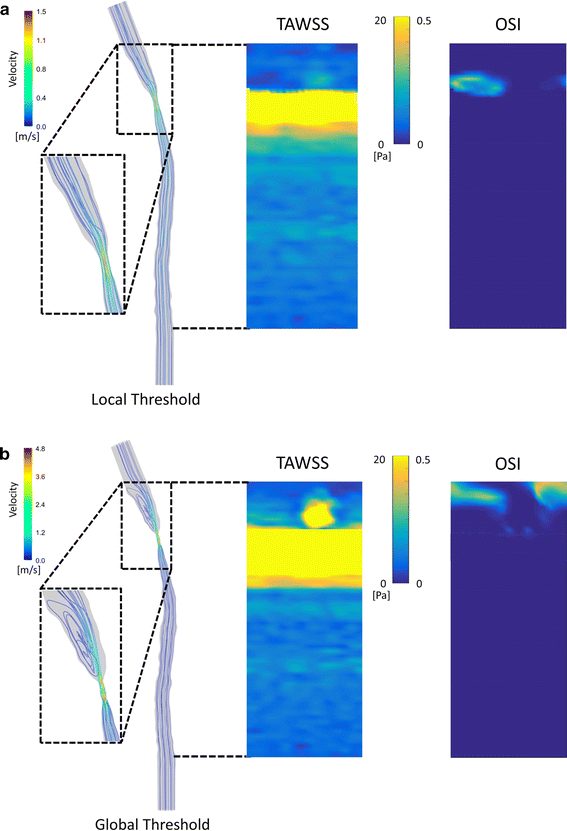
Methods: A tapering cast was placed around the right common carotid artery (RCCA) of ApoE-/- mice (n = 8). Contrast-enhanced micro-CT was performed using eXIA 160. An innovative local threshold-based segmentation procedure was implemented to reconstruct 3D geometry of the RCCA. The reconstructed RCCA was compared to the vessel geometry using a global threshold-based segmentation method. Computational fluid dynamics was applied to compute the velocity field and WSS distribution along the RCCA.
Results: eXIA 160-enhanced micro-CT allowed clear visualization and assessment of the RCCA in all eight animals. No adverse biological effects were observed from the use of eXIA 160. Segmentation using local threshold values generated more accurate RCCA geometry than the global threshold-based approach. Mouse-specific velocity data and the RCCA geometry generated 3D WSS maps with high resolution, enabling quantitative analysis of WSS. In all animals, we observed low WSS upstream of the cast. Downstream of the cast, asymmetric WSS patterns were revealed with variation in size and location between animals.
Conclusions: eXIA 160 provided good contrast to reconstruct 3D vessel geometry and determine WSS patterns in the RCCA of the atherosclerotic mouse model. We established a novel local threshold-based segmentation protocol for RCCA reconstruction and WSS computation. The observed differences between animals indicate the necessity to use mouse-specific data for WSS analysis. For our future work, our protocol makes it possible to study in vivo WSS longitudinally over a growing plaque.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Contrast media; Image segmentation; Micro-CT imaging; Wall shear stress.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Temporal and spatial changes in wall shear stress during atherosclerotic plaque progression in mice.R Soc Open Sci. 2018 Mar 14;5(3):171447. doi: 10.1098/rsos.171447. eCollection 2018 Mar. R Soc Open Sci. 2018. PMID: 29657758 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of the heart rate lowering drug Ivabradine on hemodynamics in atherosclerotic mice.Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 18;8(1):14014. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32458-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30228313 Free PMC article.
-
Wall Shear Stress (WSS) Analysis in Atherosclerosis in Partial Ligated Apolipoprotein E Knockout Mouse Model through Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD).Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 12;25(18):9877. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189877. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337364 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo wall shear stress measurements using phase-contrast MRI.Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2007 Sep;5(5):927-38. doi: 10.1586/14779072.5.5.927. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2007. PMID: 17867922 Review.
-
A comparison of 4D flow MRI-derived wall shear stress with computational fluid dynamics methods for intracranial aneurysms and carotid bifurcations - A review.Magn Reson Imaging. 2018 May;48:62-69. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2017.12.005. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Magn Reson Imaging. 2018. PMID: 29223732 Review.
Cited by
-
Micro-CT - a digital 3D microstructural voyage into scaffolds: a systematic review of the reported methods and results.Biomater Res. 2018 Sep 26;22:26. doi: 10.1186/s40824-018-0136-8. eCollection 2018. Biomater Res. 2018. PMID: 30275969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Temporal and spatial changes in wall shear stress during atherosclerotic plaque progression in mice.R Soc Open Sci. 2018 Mar 14;5(3):171447. doi: 10.1098/rsos.171447. eCollection 2018 Mar. R Soc Open Sci. 2018. PMID: 29657758 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Plaque Characteristics and Inflammation Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging.Biomedicines. 2021 Feb 12;9(2):185. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9020185. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33673124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of the heart rate lowering drug Ivabradine on hemodynamics in atherosclerotic mice.Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 18;8(1):14014. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32458-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30228313 Free PMC article.
-
Current and Emerging Preclinical Approaches for Imaging-Based Characterization of Atherosclerosis.Mol Imaging Biol. 2018 Dec;20(6):869-887. doi: 10.1007/s11307-018-1264-1. Mol Imaging Biol. 2018. PMID: 30250990 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

