The Id-protein family in developmental and cancer-associated pathways
- PMID: 28122577
- PMCID: PMC5267474
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-016-0161-y
The Id-protein family in developmental and cancer-associated pathways
Abstract
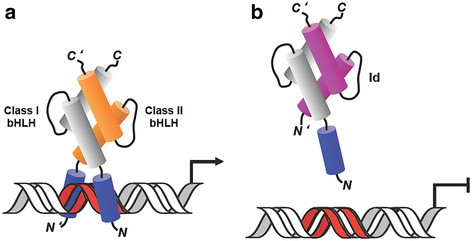
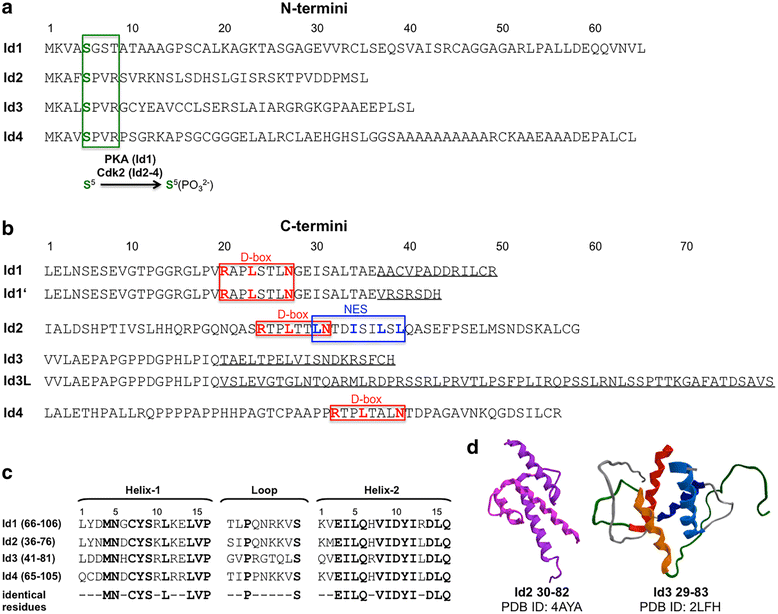
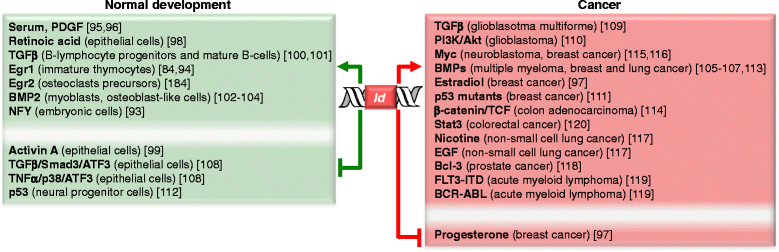
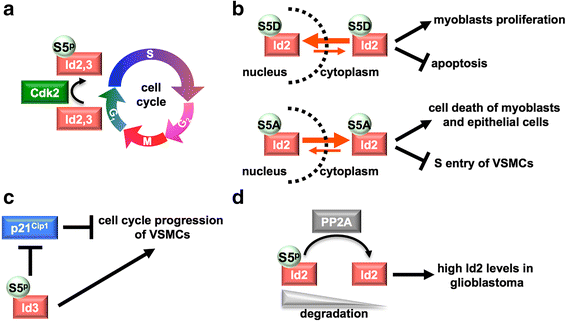
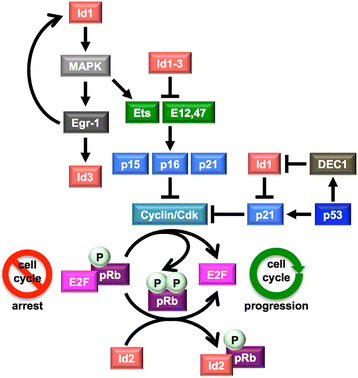
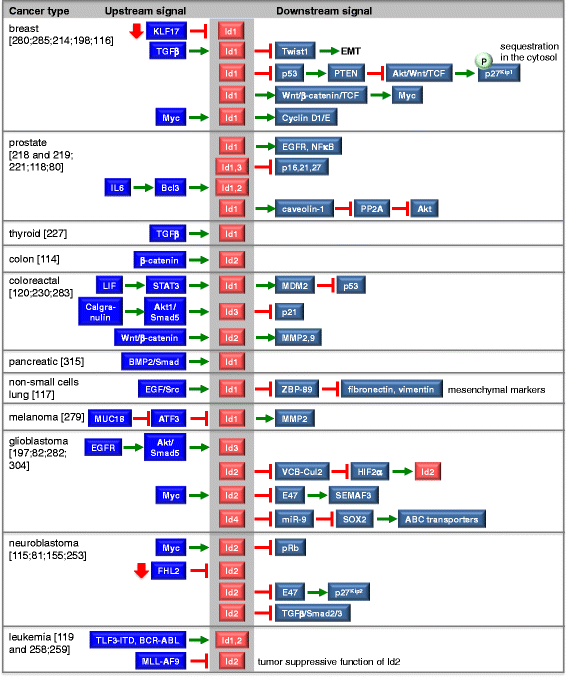
Inhibitors of DNA binding and cell differentiation (Id) proteins are members of the large family of the helix-loop-helix (HLH) transcription factors, but they lack any DNA-binding motif. During development, the Id proteins play a key role in the regulation of cell-cycle progression and cell differentiation by modulating different cell-cycle regulators both by direct and indirect mechanisms. Several Id-protein interacting partners have been identified thus far, which belong to structurally and functionally unrelated families, including, among others, the class I and II bHLH transcription factors, the retinoblastoma protein and related pocket proteins, the paired-box transcription factors, and the S5a subunit of the 26 S proteasome. Although the HLH domain of the Id proteins is involved in most of their protein-protein interaction events, additional motifs located in their N-terminal and C-terminal regions are required for the recognition of diverse protein partners. The ability of the Id proteins to interact with structurally different proteins is likely to arise from their conformational flexibility: indeed, these proteins contain intrinsically disordered regions that, in the case of the HLH region, undergo folding upon self- or heteroassociation. Besides their crucial role for cell-fate determination and cell-cycle progression during development, other important cellular events have been related to the Id-protein expression in a number of pathologies. Dysregulated Id-protein expression has been associated with tumor growth, vascularization, invasiveness, metastasis, chemoresistance and stemness, as well as with various developmental defects and diseases. Herein we provide an overview on the structural properties, mode of action, biological function and therapeutic potential of these regulatory proteins.
Keywords: Cancer stemness; Cell differentiation; Cell-cycle regulation; Chemoresistance; Development; Helix-loop-helix protein; Id protein; Intrinsically disordered protein.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibitor of differentiation 4 (ID4) acts as an inhibitor of ID-1, -2 and -3 and promotes basic helix loop helix (bHLH) E47 DNA binding and transcriptional activity.Biochimie. 2015 May;112:139-50. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2015.03.006. Epub 2015 Mar 13. Biochimie. 2015. PMID: 25778840 Free PMC article.
-
Id proteins: small molecules, mighty regulators.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2014;110:189-216. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-405943-6.00005-1. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 25248477 Review.
-
Id helix-loop-helix proteins antagonize pax transcription factor activity by inhibiting DNA binding.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Jan;21(2):524-33. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.2.524-533.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11134340 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and conformational properties of protein fragments based on the Id family of DNA-binding and cell-differentiation inhibitors.Biopolymers. 2005;80(6):762-74. doi: 10.1002/bip.20287. Biopolymers. 2005. PMID: 15880794
-
Id proteins in cell cycle control and cellular senescence.Oncogene. 2001 Dec 20;20(58):8317-25. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205092. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11840324 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive analysis of ID genes reveals the clinical and prognostic value of ID3 expression in acute myeloid leukemia using bioinformatics identification and experimental validation.BMC Cancer. 2022 Nov 29;22(1):1229. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10352-6. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36443709 Free PMC article.
-
Neurogenesis From Neural Crest Cells: Molecular Mechanisms in the Formation of Cranial Nerves and Ganglia.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Aug 7;8:635. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00635. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32850790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of BMP7 in cervical cancer and inhibition of epithelial‑mesenchymal transition by BMP7 knockdown in HeLa cells.Int J Mol Med. 2020 May;45(5):1417-1424. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4519. Epub 2020 Feb 27. Int J Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32323730 Free PMC article.
-
The sound of tumor cell-microenvironment communication - composed by the Cancer Cluster Salzburg research network.Cell Commun Signal. 2017 Jun 2;15(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s12964-017-0176-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2017. PMID: 28577565 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Micellar Casein and Whey Powder Hold a TGF-β Activity and Regulate ID Genes In Vitro.Molecules. 2021 Jan 19;26(2):507. doi: 10.3390/molecules26020507. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33477984 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

