Aortic dissection is associated with reduced polycystin-1 expression, an abnormality that leads to increased ERK phosphorylation in vascular smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 28076932
- PMCID: PMC5381529
- DOI: 10.4081/ejh.2016.2711
Aortic dissection is associated with reduced polycystin-1 expression, an abnormality that leads to increased ERK phosphorylation in vascular smooth muscle cells
Abstract
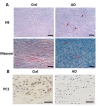
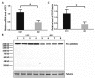
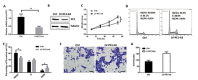
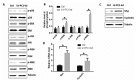
The vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) phenotypic switch is a key pathophysiological change in various cardiovascular diseases, such as aortic dissection (AD), with a high morbidity. Polycystin-1 (PC1) is significantly downregulated in the VSMCs of AD patients. PC1 is an integral membrane glycoprotein and kinase that regulates different biological processes, including cell proliferation, apoptosis, and cell polarity. However, the role of PC1 in intracellular signaling pathways remains poorly understood. In this study, PC1 downregulation in VSMCs promoted the expression of SM22α, ACTA2 and calponin 1 (CNN1) proteins. Furthermore, PC1 downregulation in VSMCs upregulated phospho-MEK, phospho-ERK and myc, but did not change phospho-JNK and phospho-p38. These findings suggest that the MEK/ERK/myc signaling pathway is involved in PC1-mediated human VSMC phenotypic switch. Opposite results were observed when an ERK inhibitor was used in VSMCs downregulated by PC1. When the C-terminal domain of PC1 (PC1 C-tail) was overexpressed in VSMCs, the expression levels of phosphor-ERK, myc, SM22α, ACTA2 and CNN1 proteins were downregulated. The group with the overexpressed mutant protein (S4166A) in the PC1 C-tail showed similar results to the group with the downregulated PC1 in VSMCs. These results suggest that the Ser at the 4166 site in PC1 is crucial in the PC1 mediated MEK/ERK/myc signaling pathway, which might be the key pathophysiological cause of AD.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MiR-4787-5p Regulates Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Apoptosis by Targeting PKD1 and Inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/FKHR Pathway.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 1;78(2):288-296. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000001051. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33958547
-
Positive regulation of the Egr-1/osteopontin positive feedback loop in rat vascular smooth muscle cells by TGF-beta, ERK, JNK, and p38 MAPK signaling.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 May 28;396(2):451-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.04.115. Epub 2010 Apr 22. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. PMID: 20417179
-
Src tyrosine kinase mediates endothelin-1-induced early growth response protein-1 expression via MAP kinase-dependent pathways in vascular smooth muscle cells.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Dec;38(6):1879-1886. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2767. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27748819
-
Calpain-mediated proteolysis of polycystin-1 C-terminus induces JAK2 and ERK signal alterations.Exp Cell Res. 2014 Jan 1;320(1):62-8. Exp Cell Res. 2014. PMID: 24416790
-
The Cytoskeletal Network Regulates Expression of the Profibrotic Genes PAI-1 and CTGF in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells.Adv Pharmacol. 2018;81:79-94. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2017.08.006. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Adv Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29310804 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Molecular Regulatory Features and Markers for Acute Type A Aortic Dissection.Comput Math Methods Med. 2021 Apr 12;2021:6697848. doi: 10.1155/2021/6697848. eCollection 2021. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021. PMID: 33953793 Free PMC article.
-
Novel non-cystic features of polycystic kidney disease: having new eyes or seeking new landscapes.Clin Kidney J. 2020 Sep 7;14(3):746-755. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfaa138. eCollection 2021 Mar. Clin Kidney J. 2020. PMID: 33777359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EZH2 inhibits autophagic cell death of aortic vascular smooth muscle cells to affect aortic dissection.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Feb 7;9(2):180. doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0213-2. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29416002 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Retrospective Study on the Mechanisms of Cyclic Mechanical Stretch-Induced Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Death Underlying Aortic Dissection and Potential Therapeutics for Preventing Acute Aortic Aneurysm and Associated Ruptures.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 22;25(5):2544. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052544. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38473793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crocin prevents platelet‑derived growth factor BB‑induced vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation and phenotypic switch.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Jun;17(6):7595-7602. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8854. Epub 2018 Apr 5. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29620234 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nienaber CA, Clough RE. Management of acute aortic dissection. Lancet, 2015;385:800-811 - PubMed
-
- Alexander MR, Owens GK. Epigenetic control of smooth muscle cell differentiation and phenotypic switching in vascular development and disease. Annu Rev Physiol, 2012; 74:13-40 - PubMed
-
- Chistiakov DA, Orekhov AN, Bobryshev YV. Vascular smooth muscle cell in atherosclerosis. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2015;214:33-50. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

