Selection of Prebiotic Molecules in Amphiphilic Environments
- PMID: 28067845
- PMCID: PMC5370403
- DOI: 10.3390/life7010003
Selection of Prebiotic Molecules in Amphiphilic Environments
Abstract
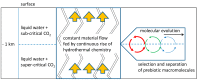
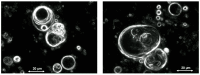
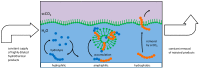
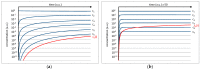
A basic problem in all postulated pathways of prebiotic chemistry is the low concentration which generally is expected for interesting reactants in fluid environments. Even though compounds, like nucleobases, sugars or peptides, principally may form spontaneously under environmental conditions, they will always be rapidly diluted in an aqueous environment. In addition, any such reaction leads to side products which often exceed the desired compound and generally hamper the first steps of a subsequent molecular evolution. Therefore, a mechanism of selection and accumulation of relevant prebiotic compounds seems to be crucial for molecular evolution. A very efficient environment for selection and accumulation can be found in the fluid continuum circulating in tectonic fault zones. Vesicles which form spontaneously at a depth of approximately 1 km present a selective trap for amphiphilic molecules, especially for peptides composed of hydrophilic and hydrophobic amino acids in a suitable sequence. The accumulation effect is shown in a numeric simulation on a simplified model. Further, possible mechanisms of a molecular evolution in vesicle membranes are discussed. Altogether, the proposed scenario can be seen as an ideal environment for constant, undisturbed molecular evolution in and on cell-like compartments.
Keywords: accumulation; molecular evolution; origin of life; prebiotic chemistry; selection; vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Periodic Vesicle Formation in Tectonic Fault Zones--an Ideal Scenario for Molecular Evolution.Orig Life Evol Biosph. 2015 Jun;45(1-2):139-48. doi: 10.1007/s11084-015-9411-z. Epub 2015 Feb 27. Orig Life Evol Biosph. 2015. PMID: 25716918 Free PMC article.
-
Replication of Simulated Prebiotic Amphiphilic Vesicles in a Finite Environment Exhibits Complex Behavior That Includes High Progeny Variability and Competition.Astrobiology. 2018 Apr;18(4):419-430. doi: 10.1089/ast.2016.1615. Epub 2018 Mar 16. Astrobiology. 2018. PMID: 29634319 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Evolution in a Peptide-Vesicle System.Life (Basel). 2018 May 24;8(2):16. doi: 10.3390/life8020016. Life (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29795023 Free PMC article.
-
Prebiotic Lipidic Amphiphiles and Condensing Agents on the Early Earth.Life (Basel). 2016 Mar 28;6(2):17. doi: 10.3390/life6020017. Life (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27043635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemomimesis and Molecular Darwinism in Action: From Abiotic Generation of Nucleobases to Nucleosides and RNA.Life (Basel). 2018 Jun 20;8(2):24. doi: 10.3390/life8020024. Life (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29925796 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Origin of Species before Origin of Life: The Role of Speciation in Chemical Evolution.Life (Basel). 2021 Feb 17;11(2):154. doi: 10.3390/life11020154. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33671365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyesters as a Model System for Building Primitive Biologies from Non-Biological Prebiotic Chemistry.Life (Basel). 2020 Jan 19;10(1):6. doi: 10.3390/life10010006. Life (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31963928 Free PMC article.
-
Is pre-Darwinian evolution plausible?Biol Direct. 2018 Sep 21;13(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s13062-018-0216-7. Biol Direct. 2018. PMID: 30241560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Connecting primitive phase separation to biotechnology, synthetic biology, and engineering.J Biosci. 2021;46(3):79. doi: 10.1007/s12038-021-00204-z. J Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34373367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aliphatic Aldehydes in the Earth's Crust-Remains of Prebiotic Chemistry?Life (Basel). 2022 Jun 21;12(7):925. doi: 10.3390/life12070925. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35888015 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dyson F.J. Origins of Life. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: 1999.
-
- Airapetian V.S., Glocer A., Gronoff G., Hébrard E., Danchi W. Prebiotic chemistry and atmospheric warming of early Earth by an active young sun. Nat. Geosci. 2016;9:452–455. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2719. - DOI
-
- Simoneit B.R.T. Prebiotic organic synthesis under hydrothermal conditions: An overview. Adv. Space Res. 2004;33:88–94. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2003.05.006. - DOI
-
- Matsuno K. Encyclopedia of Astrobiology. Springer; Berlin, Germany: 2011. Hydrothermal reaction; pp. 788–790.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

