Kemp Eliminase Activity of Ketosteroid Isomerase
- PMID: 28045505
- PMCID: PMC5446047
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00762
Kemp Eliminase Activity of Ketosteroid Isomerase
Abstract
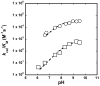
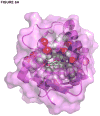
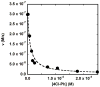
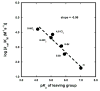
Kemp eliminases represent the most successful class of computationally designed enzymes, with rate accelerations of up to 109-fold relative to the rate of the same reaction in aqueous solution. Nevertheless, several other systems such as micelles, catalytic antibodies, and cavitands are known to accelerate the Kemp elimination by several orders of magnitude. We found that the naturally occurring enzyme ketosteroid isomerase (KSI) also catalyzes the Kemp elimination. Surprisingly, mutations of D38, the residue that acts as a general base for its natural substrate, produced variants that catalyze the Kemp elimination up to 7000-fold better than wild-type KSI does, and some of these variants accelerate the Kemp elimination more than the computationally designed Kemp eliminases. Analysis of the D38N general base KSI variant suggests that a different active site carboxylate residue, D99, performs the proton abstraction. Docking simulations and analysis of inhibition by active site binders suggest that the Kemp elimination takes place in the active site of KSI and that KSI uses the same catalytic strategies of the computationally designed enzymes. In agreement with prior observations, our results strengthen the conclusion that significant rate accelerations of the Kemp elimination can be achieved with very few, nonspecific interactions with the substrate if a suitable catalytic base is present in a hydrophobic environment. Computational design can fulfill these requirements, and the design of more complex and precise environments represents the next level of challenges for protein design.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Healthcare workers' informal uses of mobile phones and other mobile devices to support their work: a qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Aug 27;8(8):CD015705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015705.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39189465 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of abstinence-based and harm reduction-based interventions in reducing problematic substance use in adults who are experiencing homelessness in high income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2024 Apr 21;20(2):e1396. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1396. eCollection 2024 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38645303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medications for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a historical non-interventional cohort study with validation against RCT results.Health Technol Assess. 2021 Aug;25(51):1-70. doi: 10.3310/hta25510. Health Technol Assess. 2021. PMID: 34463610 Clinical Trial.
-
Far Posterior Approach for Rib Fracture Fixation: Surgical Technique and Tips.JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2024 Dec 6;14(4):e23.00094. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.ST.23.00094. eCollection 2024 Oct-Dec. JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2024. PMID: 39650795 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Kemp Eliminases of the AlleyCat Family Possess High Substrate Promiscuity.ChemCatChem. 2019 Mar 6;11(5):1425-1430. doi: 10.1002/cctc.201801994. Epub 2019 Jan 15. ChemCatChem. 2019. PMID: 31788134 Free PMC article.
-
NMR-guided directed evolution.Nature. 2022 Oct;610(7931):389-393. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05278-9. Epub 2022 Oct 5. Nature. 2022. PMID: 36198791 Free PMC article.
-
High throughput and quantitative enzymology in the genomic era.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2021 Dec;71:259-273. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2021.07.010. Epub 2021 Sep 27. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2021. PMID: 34592682 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Borsche W. Zur Kenntnis der Benzisoxazole. Liebigs Ann Chem. 1912;390:1–29.
-
- Casey ML, Kemp DS, Paul KG, Cox DD. Physical organic chemistry of benzisoxazoles. I. Mechanism of the base-catalyzed decomposition of benzisoxazoles. J Org Chem. 1973;38:2294–2301.
-
- Kemp DS, Casey ML. Physical organic chemistry of benzisoxazoles. II Linearity of the Broensted free energy relation for the base-catalyzed decomposition of benzisoxazoles. J Am Chem Soc. 1973;95:6670–6680.
-
- Rothlisberger D, Khersonsky O, Wollacott AM, Jiang L, DeChancie J, Betker J, Gallaher JL, Althoff EA, Zanghellini A, Dym O, Albeck S, Houk KN, Tawfik DS, Baker D. Kemp elimination catalysts by computational enzyme design. Nature. 2008;453:190–194. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

