Cholinergic, Glutamatergic, and GABAergic Neurons of the Pedunculopontine Tegmental Nucleus Have Distinct Effects on Sleep/Wake Behavior in Mice
- PMID: 28039375
- PMCID: PMC5296799
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1405-16.2016
Cholinergic, Glutamatergic, and GABAergic Neurons of the Pedunculopontine Tegmental Nucleus Have Distinct Effects on Sleep/Wake Behavior in Mice
Abstract
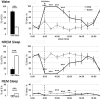
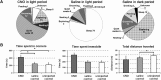
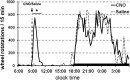
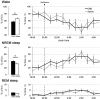
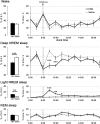
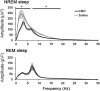
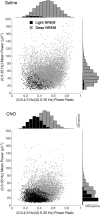
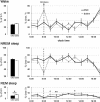
The pedunculopontine tegmental (PPT) nucleus has long been implicated in the regulation of cortical activity and behavioral states, including rapid eye-movement (REM) sleep. For example, electrical stimulation of the PPT region during sleep leads to rapid awakening, whereas lesions of the PPT in cats reduce REM sleep. Though these effects have been linked with the activity of cholinergic PPT neurons, the PPT also includes intermingled glutamatergic and GABAergic cell populations, and the precise roles of cholinergic, glutamatergic, and GABAergic PPT cell groups in regulating cortical activity and behavioral state remain unknown. Using a chemogenetic approach in three Cre-driver mouse lines, we found that selective activation of glutamatergic PPT neurons induced prolonged cortical activation and behavioral wakefulness, whereas inhibition reduced wakefulness and increased non-REM (NREM) sleep. Activation of cholinergic PPT neurons suppressed lower-frequency electroencephalogram rhythms during NREM sleep. Last, activation of GABAergic PPT neurons slightly reduced REM sleep. These findings reveal that glutamatergic, cholinergic, and GABAergic PPT neurons differentially influence cortical activity and sleep/wake states.
Significance statement: More than 40 million Americans suffer from chronic sleep disruption, and the development of effective treatments requires a more detailed understanding of the neuronal mechanisms controlling sleep and arousal. The pedunculopontine tegmental (PPT) nucleus has long been considered a key site for regulating wakefulness and REM sleep. This is mainly because of the cholinergic neurons contained in the PPT nucleus. However, the PPT nucleus also contains glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons that likely contribute to the regulation of cortical activity and sleep-wake states. The chemogenetic experiments in the present study reveal that cholinergic, glutamatergic, and GABAergic PPT neurons each have distinct effects on sleep/wake behavior, improving our understanding of how the PPT nucleus regulates cortical activity and behavioral states.
Keywords: PPT; chemogenetic; mouse; sleep.
Copyright © 2017 the authors 0270-6474/17/371352-15$15.00/0.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lesion of the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus in rat augments cortical activation and disturbs sleep/wake state transitions structure.Exp Neurol. 2013 Sep;247:562-71. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2013.02.007. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Exp Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23481548
-
Topography of the sleep/wake states related EEG microstructure and transitions structure differentiates the functionally distinct cholinergic innervation disorders in rat.Behav Brain Res. 2013 Nov 1;256:108-18. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.07.047. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Behav Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23933142
-
[Selective stimulations and lesions of the rat brain nuclei as the models for research of the human sleep pathology mechanisms].Glas Srp Akad Nauka Med. 2011;(51):85-97. Glas Srp Akad Nauka Med. 2011. PMID: 22165729 Review. Serbian.
-
Discharge profiles across the sleep-waking cycle of identified cholinergic, GABAergic, and glutamatergic neurons in the pontomesencephalic tegmentum of the rat.J Neurosci. 2014 Mar 26;34(13):4708-27. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2617-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24672016 Free PMC article.
-
[Neurochemical mechanisms of sleep regulation].Glas Srp Akad Nauka Med. 2009;(50):97-109. Glas Srp Akad Nauka Med. 2009. PMID: 20666118 Review. Serbian.
Cited by
-
Zona Incerta GABAergic Neurons Facilitate Emergence from Isoflurane Anesthesia in Mice.Neurochem Res. 2024 Dec;49(12):3297-3307. doi: 10.1007/s11064-024-04230-9. Epub 2024 Sep 23. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 39312079 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory basal ganglia nuclei differentially innervate pedunculopontine nucleus subpopulations and evoke opposite motor and valence behaviors.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 6:2024.08.05.606694. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.05.606694. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39149277 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Activation of Pedunculopontine Tegmental Nucleus Alleviates the Pain Induced by the Lesion of Midbrain Dopaminergic Neurons.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 22;25(11):5636. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115636. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38891832 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in neural mechanism of general anesthesia induced unconsciousness: insights from optogenetics and chemogenetics.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Apr 9;15:1360864. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1360864. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38655183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Screening effects of HCN channel blockers on sleep/wake behavior in zebrafish.Front Neurosci. 2024 Mar 19;18:1375484. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1375484. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38567282 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander GM, Rogan SC, Abbas AI, Armbruster BN, Pei Y, Allen JA, Nonneman RJ, Hartmann J, Moy SS, Nicolelis MA, McNamara JO, Roth BL (2009) Remote control of neuronal activity in transgenic mice expressing evolved G protein-coupled receptors. Neuron 63:27–39. 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.06.014 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
