Biased G Protein-Coupled Receptor Signaling: New Player in Modulating Physiology and Pathology
- PMID: 28035079
- PMCID: PMC5207460
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2016.165
Biased G Protein-Coupled Receptor Signaling: New Player in Modulating Physiology and Pathology
Abstract
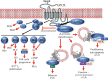
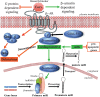
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are a family of cell-surface proteins that play critical roles in regulating a variety of pathophysiological processes and thus are targeted by almost a third of currently available therapeutics. It was originally thought that GPCRs convert extracellular stimuli into intracellular signals through activating G proteins, whereas β-arrestins have important roles in internalization and desensitization of the receptor. Over the past decade, several novel functional aspects of β-arrestins in regulating GPCR signaling have been discovered. These previously unanticipated roles of β-arrestins to act as signal transducers and mediators of G protein-independent signaling have led to the concept of biased agonism. Biased GPCR ligands are able to engage with their target receptors in a manner that preferentially activates only G protein- or β-arrestin-mediated downstream signaling. This offers the potential for next generation drugs with high selectivity to therapeutically relevant GPCR signaling pathways. In this review, we provide a summary of the recent studies highlighting G protein- or β-arrestin-biased GPCR signaling and the effects of biased ligands on disease pathogenesis and regulation.
Keywords: G protein; G protein-coupled receptor; biased signaling; β-arrestin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biased signaling of G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs): Molecular determinants of GPCR/transducer selectivity and therapeutic potential.Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Aug;200:148-178. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.05.006. Epub 2019 May 8. Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31075355 Review.
-
Beta-arrestin biased agonism/antagonism at cardiovascular seven transmembrane-spanning receptors.Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(2):192-8. doi: 10.2174/138161212799040475. Curr Pharm Des. 2012. PMID: 22229558 Review.
-
Multiple functions of G protein-coupled receptor kinases.J Mol Signal. 2014 Mar 6;9(1):1. doi: 10.1186/1750-2187-9-1. J Mol Signal. 2014. PMID: 24597858 Free PMC article.
-
Structural mechanism of GPCR-arrestin interaction: recent breakthroughs.Arch Pharm Res. 2016 Mar;39(3):293-301. doi: 10.1007/s12272-016-0712-1. Epub 2016 Jan 29. Arch Pharm Res. 2016. PMID: 26825061 Review.
-
GPCR systems pharmacology: a different perspective on the development of biased therapeutics.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022 May 1;322(5):C887-C895. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00449.2021. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35196164 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ste2 receptor-mediated chemotropism of Fusarium graminearum contributes to its pathogenicity against wheat.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 1;10(1):10770. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67597-z. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32612109 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous Derivatives of Linoleic Acid and their Stable Analogs Are Potential Pain Mediators.JID Innov. 2022 Dec 26;3(2):100177. doi: 10.1016/j.xjidi.2022.100177. eCollection 2023 Mar. JID Innov. 2022. PMID: 36876220 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Novel pERK1/2- or β-Arrestin-Preferring 5-HT1A Receptor-Biased Agonists: Diversified Therapeutic-like versus Side Effect Profile.J Med Chem. 2020 Oct 8;63(19):10946-10971. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c00814. Epub 2020 Sep 23. J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32883072 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacognosy and Effects of Cannabinoids in the Vascular System.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2022 Oct 28;5(11):1034-1049. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.2c00141. eCollection 2022 Nov 11. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2022. PMID: 36407955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of G Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs) and Calcium Signaling in Schizophrenia. Focus on GPCRs Activated by Neurotransmitters and Chemokines.Cells. 2021 May 17;10(5):1228. doi: 10.3390/cells10051228. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34067760 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aplin M, Christensen GL, Schneider M, Heydorn A, Gammeltoft S, Kjolbye AL, Sheikh SP, Hansen JL. The angiotensin type 1 receptor activates extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 by G protein-dependent and -independent pathways in cardiac myocytes and Langendorff-perfused hearts. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2007;100:289–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2007.00063.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aurora AB, Mahmoud AI, Luo X, Johnson BA, van Rooij E, Matsuzaki S, Humphries KM, Hill JA, Bassel-Duby R, Sadek HA, Olson EN. MicroRNA-214 protects the mouse heart from ischemic injury by controlling Ca2+ overload and cell death. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:1222–1232. doi: 10.1172/JCI59327. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

