Histological and Metabolic State of Dams Suckling Small Litter or MSG-Treated Pups
- PMID: 28004032
- PMCID: PMC5149680
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/1678541
Histological and Metabolic State of Dams Suckling Small Litter or MSG-Treated Pups
Abstract
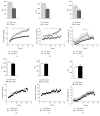
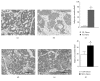
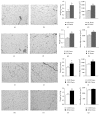
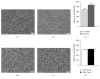
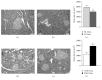
Lactation is an important function that is dependent on changes in the maternal homeostasis and sustained by histological maternal adjustments. We evaluated how offspring manipulations during the lactational phase can modulate maternal morphologic aspects in the mammary gland, adipose tissue, and pancreatic islets of lactating dams. Two different models of litter-manipulation-during-lactation were used: litter sizes, small litters (SL) or normal litters (NL) and subcutaneous injections in the puppies of monosodium glutamate (MSG), or saline (CON). SL Dams and MSG Dams presented an increase in WAT content and higher plasma levels of glucose, triglycerides, and insulin, in relation to NL Dams and CON Dams, respectively. The MG of SL Dams and MSG Dams presented a high adipocyte content and reduced alveoli development and the milk of the SL Dams presented a higher calorie and triglyceride content, compared to that of the NL Dams. SL Dams presented a reduction in islet size and greater lipid droplet accumulation in BAT, in relation to NL Dams. SL Dams and MSG Dams present similar responses to offspring manipulation during lactation, resulting in changes in metabolic parameters. These alterations were associated with higher fat accumulation in BAT and changes in milk composition only in SL Dams.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors declared a conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Litter Size Reduction Induces Metabolic and Histological Adjustments in Dams throughout Lactation with Early Effects on Offspring.An Acad Bras Cienc. 2019 Mar 21;91(1):e20170971. doi: 10.1590/0001-3765201920170971. An Acad Bras Cienc. 2019. PMID: 30916150
-
Cross-fostering reduces obesity induced by early exposure to monosodium glutamate in male rats.Endocrine. 2017 Jan;55(1):101-112. doi: 10.1007/s12020-016-0965-y. Epub 2016 Apr 26. Endocrine. 2017. PMID: 27116693
-
Reduction of litter size during lactation in rats greatly influences fatty acid profiles in dams.J Physiol Biochem. 2021 Nov;77(4):531-538. doi: 10.1007/s13105-021-00809-w. Epub 2021 Apr 28. J Physiol Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33909240
-
Obesity and changes of alkaline phosphatase activity in the small intestine of 40- and 80-day-old rats subjected to early postnatal overfeeding or monosodium glutamate.Physiol Res. 2004;53(2):177-86. Physiol Res. 2004. PMID: 15046554
-
Glucose-restricted diets alter milk composition and mammary gland development in lactating rat dams.J Nutr. 1994 Jan;124(1):94-102. doi: 10.1093/jn/124.1.94. J Nutr. 1994. PMID: 8283299
Cited by
-
Swimming training prevents obesity installation and normalizes hypothalamic expressions of GLP1 and leptin receptors in adult offspring born in small litters.Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2024 Sep 9;22:eAO0619. doi: 10.31744/einstein_journal/2024AO0619. eCollection 2024. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2024. PMID: 39258689 Free PMC article.
-
Fish oil supplementation in obese rats ameliorates metabolic syndrome response.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2024 May 20;57:e13172. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2024e13172. eCollection 2024. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2024. PMID: 38808884 Free PMC article.
-
Factors contributing to the swimmer puppy syndrome found in Labrador retrievers.BMC Vet Res. 2022 Mar 29;18(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s12917-022-03226-3. BMC Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 35351139 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Del Prado M., Delgado G., Villalpando S. Maternal lipid intake during pregnancy and lactation alters milk composition and production and litter growth in rats. The Journal of Nutrition. 1997;127(3):458–462. - PubMed
-
- King R. H., Toner M. S., Dove H., Atwood C. S., Brown W. G. The response of first-litter sows to dietary protein level during lactation. Journal of Animal Science. 1993;71(9):2457–2463. - PubMed
-
- Aoki N., Yamaguchi Y., Ohira S., Matsuda T. High fat feeding of lactating mice causing a drastic reduction in fat and energy content in milk without affecting the apparent growth of their pups and the production of major milk fat globule membrane components MFG-E8 and butyrophilin. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry. 1999;63(10):1749–1755. doi: 10.1271/bbb.63.1749. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

