Anticancer Effects of a New SIRT Inhibitor, MHY2256, against Human Breast Cancer MCF-7 Cells via Regulation of MDM2-p53 Binding
- PMID: 27994519
- PMCID: PMC5166496
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.13833
Anticancer Effects of a New SIRT Inhibitor, MHY2256, against Human Breast Cancer MCF-7 Cells via Regulation of MDM2-p53 Binding
Abstract
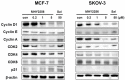
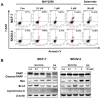
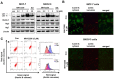
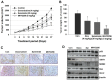
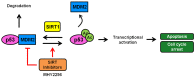
The sirtuins (SIRTs), a family of NAD+-dependent class III histone deacetylase, are involved in various biological processes including cell survival, division, senescence, and metabolism via activation of the stress-response pathway. Recently, inhibition of SIRTs has been considered a promising anticancer strategy, but their precise mechanisms of action are not well understood. In particular, the relevance of p53 to SIRT-induced effects has not been fully elucidated. We investigated the anticancer effects of a novel SIRT inhibitor, MHY2256, and its efficacy was compared to that of salermide in MCF-7 (wild-type p53) and SKOV-3 (null-type p53) cells. Cell viability, SIRT1 enzyme activity, cell cycle regulation, apoptosis, and autophagic cell death were measured. We compared sensitivity to cytotoxicity in MCF-7 and SKOV-3 cells. MHY2256 significantly decreased the viability of MCF-7 (IC50, 4.8 μM) and SKOV-3 (IC50, 5.6 μM) cells after a 48 h treatment period. MHY2256 showed potent inhibition (IC50, 0.27 mM) against SIRT1 enzyme activity compared with nicotinamide (IC50, >1 mM). Moreover, expression of SIRT (1, 2, or 3) protein levels was significantly reduced by MHY2256 treatment in both MCF-7 and SKOV-3 cells. Flow cytometry analysis revealed that MHY2256 significantly induced cell cycle arrest in the G1 phase, leading to an effective increase in apoptotic cell death in MCF-7 and SKOV-3 cells. A significant increase in acetylated p53, a target protein of SIRT, was observed in MCF-7 cells after MHY2256 treatment. MHY2256 up-regulated LC3-II and induced autophagic cell death in MCF-7 cells. Furthermore, MHY2256 markedly inhibited tumor growth in a tumor xenograft model of MCF-7 cells. These results suggest that a new SIRT inhibitor, MHY2256, has anticancer activity through p53 acetylation in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells.
Keywords: MDM2; MHY2256; SIRT inhibitor; apoptosis; autophagy.; p53.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
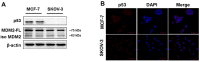
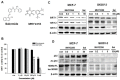
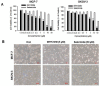
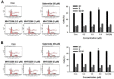
Similar articles
-
A New Synthetic Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, MHY2256, Induces Apoptosis and Autophagy Cell Death in Endometrial Cancer Cells via p53 Acetylation.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 13;19(9):2743. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092743. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30217020 Free PMC article.
-
Sirtinol, a class III HDAC inhibitor, induces apoptotic and autophagic cell death in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2012 Sep;41(3):1101-9. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1534. Epub 2012 Jun 26. Int J Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22751989
-
Psammaplin A induces Sirtuin 1-dependent autophagic cell death in doxorubicin-resistant MCF-7/adr human breast cancer cells and xenografts.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Feb;1850(2):401-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.11.007. Epub 2014 Nov 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25445714
-
Guardian of genome on the tract: Wild type p53-mdm2 complex inhibition in healing the breast cancer.Gene. 2021 Jun 20;786:145616. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2021.145616. Epub 2021 Apr 1. Gene. 2021. PMID: 33811963 Review.
-
Interplay between SIRT proteins and tumour suppressor transcription factors in chemotherapeutic resistance of cancer.Drug Resist Updat. 2011 Feb;14(1):35-44. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2010.12.001. Epub 2010 Dec 30. Drug Resist Updat. 2011. PMID: 21195657 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advancements in understanding the role of epigenetics in the auditory system.Gene. 2020 Nov 30;761:144996. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144996. Epub 2020 Jul 29. Gene. 2020. PMID: 32738421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Sirt-1 controls GVHD by inhibiting T-cell allo-response and promoting Treg stability in mice.Blood. 2019 Jan 17;133(3):266-279. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-07-863233. Epub 2018 Dec 4. Blood. 2019. PMID: 30514750 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol induces apoptosis by modulating the reciprocal crosstalk between p53 and Sirt-1 in the CRC tumor microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 27;14:1225530. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1225530. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37575245 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Targeting of Autophagy via HDAC Inhibition in Tumor Cells: Role of p53.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 8;19(12):3952. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123952. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30544838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual Hyaluronic Acid and Folic Acid Targeting pH-Sensitive Multifunctional 2DG@DCA@MgO-Nano-Core-Shell-Radiosensitizer for Breast Cancer Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 7;13(21):5571. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215571. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771733 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saunders LR, Verdin E. Sirtuins: critical regulators at the crossroads between cancer and aging. Oncogene. 2007;26(37):5489–504. - PubMed
-
- Cen Y. Sirtuins inhibitors: The approach to affinity and selectivity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2010;1804(8):1635–44. - PubMed
-
- Milner J. Cellular regulation of SIRT1. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009;15(1):39–44. - PubMed
-
- Vaziri H, Dessain SK, Ng Eaton E, Imai SI, Frye RA, Pandita TK, Guarente L, Weinberg RA. hSIR2(SIRT1) functions as an NAD-dependent p53 deacetylase. Cell. 2001;107(2):149–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

