Regulatory module involving FGF13, miR-504, and p53 regulates ribosomal biogenesis and supports cancer cell survival
- PMID: 27994142
- PMCID: PMC5278483
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1614876114
Regulatory module involving FGF13, miR-504, and p53 regulates ribosomal biogenesis and supports cancer cell survival
Abstract
The microRNA miR-504 targets TP53 mRNA encoding the p53 tumor suppressor. miR-504 resides within the fibroblast growth factor 13 (FGF13) gene, which is overexpressed in various cancers. We report that the FGF13 locus, comprising FGF13 and miR-504, is transcriptionally repressed by p53, defining an additional negative feedback loop in the p53 network. Furthermore, we show that FGF13 1A is a nucleolar protein that represses ribosomal RNA transcription and attenuates protein synthesis. Importantly, in cancer cells expressing high levels of FGF13, the depletion of FGF13 elicits increased proteostasis stress, associated with the accumulation of reactive oxygen species and apoptosis. Notably, stepwise neoplastic transformation is accompanied by a gradual increase in FGF13 expression and increased dependence on FGF13 for survival ("nononcogene addiction"). Moreover, FGF13 overexpression enables cells to cope more effectively with the stress elicited by oncogenic Ras protein. We propose that, in cells in which activated oncogenes drive excessive protein synthesis, FGF13 may favor survival by maintaining translation rates at a level compatible with the protein quality-control capacity of the cell. Thus, FGF13 may serve as an enabler, allowing cancer cells to evade proteostasis stress triggered by oncogene activation.
Keywords: FGF13; miR-504; p53; proteostasis; ribosomal biogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
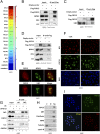
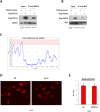
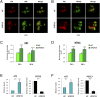
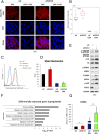
Comment in
-
Tumor suppression by p53 involves inhibiting an enabler, FGF13.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jan 24;114(4):632-633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1619815114. Epub 2017 Jan 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28082725 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
CRKL oncogene is downregulated by p53 through miR-200s.Cancer Sci. 2015 Aug;106(8):1033-40. doi: 10.1111/cas.12713. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Cancer Sci. 2015. PMID: 26079153 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-1827 represses MDM2 to positively regulate tumor suppressor p53 and suppress tumorigenesis.Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 23;7(8):8783-96. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7088. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26840028 Free PMC article.
-
The PTTG1-targeting miRNAs miR-329, miR-300, miR-381, and miR-655 inhibit pituitary tumor cell tumorigenesis and are involved in a p53/PTTG1 regulation feedback loop.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 6;6(30):29413-27. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5003. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26320179 Free PMC article.
-
The nucleolus as a fundamental regulator of the p53 response and a new target for cancer therapy.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jul;1849(7):821-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.10.007. Epub 2014 Nov 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25464032 Review.
-
The miR-34 family in cancer and apoptosis.Cell Death Differ. 2010 Feb;17(2):193-9. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2009.56. Epub 2009 May 22. Cell Death Differ. 2010. PMID: 19461653 Review.
Cited by
-
Crosstalk between noncoding RNAs and ferroptosis: new dawn for overcoming cancer progression.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jul 24;11(7):580. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02772-8. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32709863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FGF13 interaction with SHCBP1 activates AKT-GSK3α/β signaling and promotes the proliferation of A549 cells.Cancer Biol Ther. 2020 Nov 1;21(11):1014-1024. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2020.1824512. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Cancer Biol Ther. 2020. PMID: 33064958 Free PMC article.
-
Interneuron FGF13 regulates seizure susceptibility via a sodium channel-independent mechanism.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 19:2024.04.18.590019. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.18.590019. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Elife. 2025 Jan 08;13:RP98661. doi: 10.7554/eLife.98661 PMID: 38659789 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Prognostic Implication of a Cuproptosis-Related miRNA Signature in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Sep 13;2022:4694323. doi: 10.1155/2022/4694323. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. PMID: 36147869 Free PMC article.
-
A spatially resolved brain region- and cell type-specific isoform atlas of the postnatal mouse brain.Nat Commun. 2021 Jan 19;12(1):463. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20343-5. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33469025 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116(2):281–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

