Integrin-FAK signaling rapidly and potently promotes mitochondrial function through STAT3
- PMID: 27978828
- PMCID: PMC5159999
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-016-0157-7
Integrin-FAK signaling rapidly and potently promotes mitochondrial function through STAT3
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: Integrin-FAK signaling rapidly and potently promotes mitochondrial function through STAT3.Cell Commun Signal. 2017 Mar 27;15(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12964-017-0167-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2017. PMID: 28347299 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Correction to: Integrin-FAK signaling rapidly and potently promotes mitochondrial function through STAT3.Cell Commun Signal. 2020 Apr 20;18(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s12964-020-00577-y. Cell Commun Signal. 2020. PMID: 32312272 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: STAT3 is increasingly becoming known for its non-transcriptional regulation of mitochondrial bioenergetic function upon activation of its S727 residue (S727-STAT3). Lengthy mitochondrial dysfunction can lead to cell death. We tested whether an integrin-FAK-STAT3 signaling pathway we recently discovered regulates mitochondrial function and cell survival, and treatments thereof.
Methods: Cultured mouse brain bEnd5 endothelial cells were treated with integrin, FAK or STAT3 inhibitors, FAK siRNA, as well as integrin and STAT3 activators. STAT3 null cells were transfected with mutant STAT3 plasmids. Outcome measures included oxygen consumption rate for mitochondrial bioenergetics, Western blotting for protein phosphorylation, mitochondrial membrane potential for mitochondrial integrity, ROS production, and cell counts.
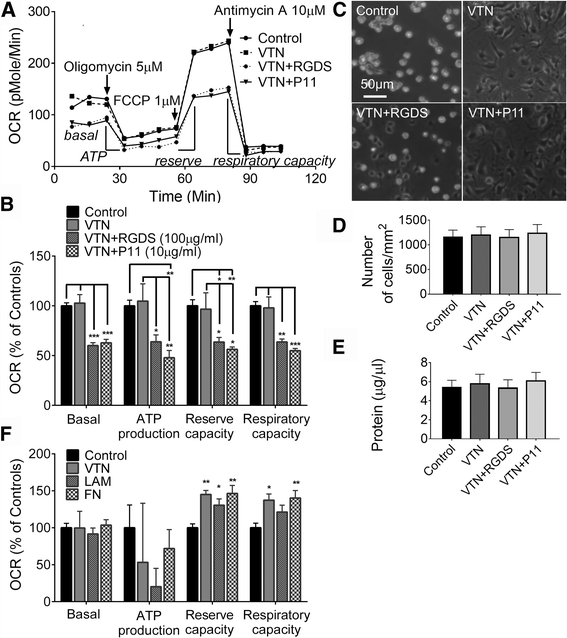
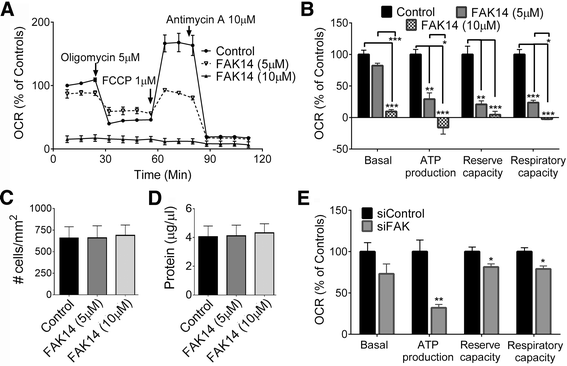
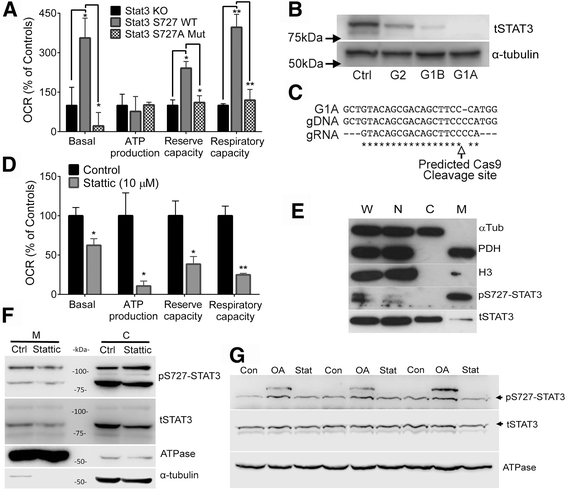
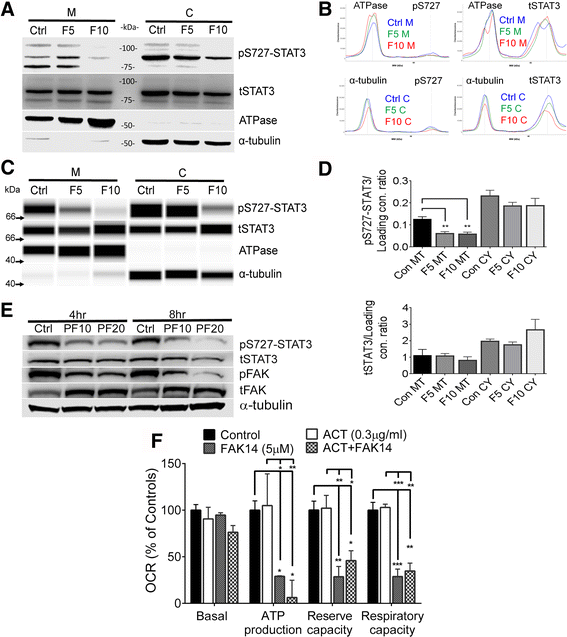
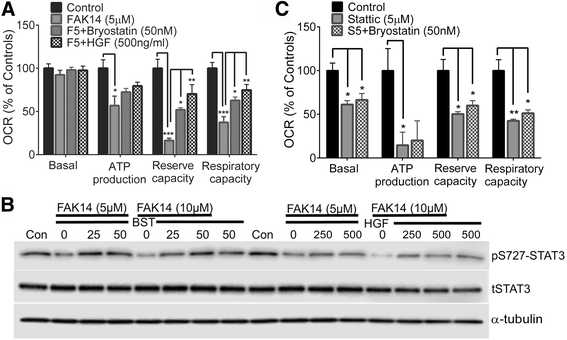
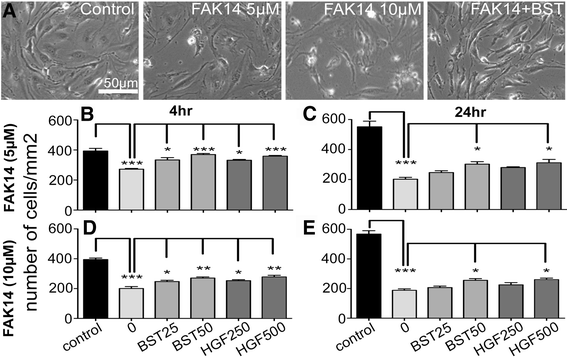
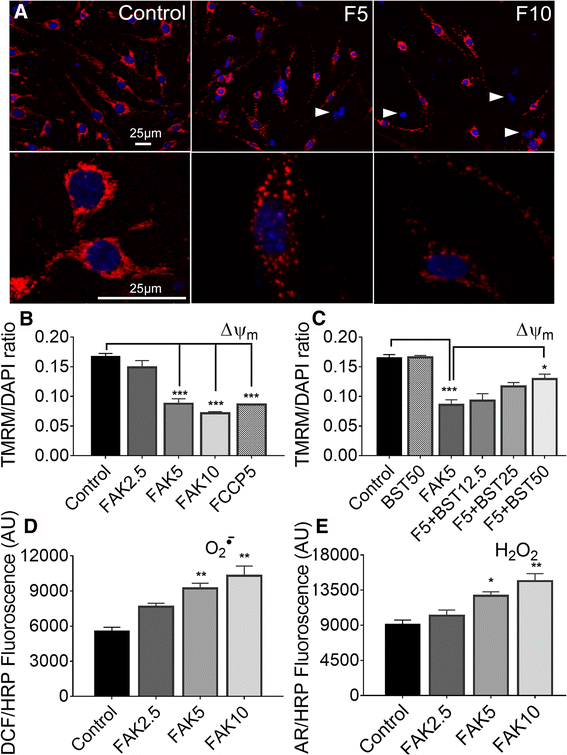
Results: Vitronectin-dependent mitochondrial basal respiration, ATP production, and maximum reserve and respiratory capacities were suppressed within 4 h by RGD and αvβ3 integrin antagonist peptides. Conversely, integrin ligands vitronectin, laminin and fibronectin stimulated mitochondrial function. Pharmacological inhibition of FAK completely abolished mitochondrial function within 4 h while FAK siRNA treatments confirmed the specificity of FAK signaling. WT, but not S727A functionally dead mutant STAT3, rescued bioenergetics in cells made null for STAT3 using CRISPR-Cas9. STAT3 inhibition with stattic in whole cells rapidly reduced mitochondrial function and mitochondrial pS727-STAT3. Stattic treatment of isolated mitochondria did not reduce pS727 whereas more was detected upon phosphatase inhibition. This suggests that S727-STAT3 is activated in the cytoplasm and is short-lived upon translocation to the mitochondria. FAK inhibition reduced pS727-STAT3 within mitochondria and reduced mitochondrial function in a non-transcriptional manner, as shown by co-treatment with actinomycin. Treatment with the small molecule bryostatin-1 or hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which indirectly activate S727-STAT3, preserved mitochondrial function during FAK inhibition, but failed in the presence of the STAT3 inhibitor. FAK inhibition induced loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, which was counteracted by bryostatin, and increased superoxide and hydrogen peroxide production. Bryostatin and HGF reduced the substantial cell death caused by FAK inhibition over a 24 h period.
Conclusion: These data suggest that extracellular matrix molecules promote STAT3-dependent mitochondrial function and cell survival through integrin-FAK signaling. We furthermore show a new treatment strategy for cell survival using S727-STAT3 activators.
Keywords: Bioenergetics; CRISPR; Cell death; ECM; Endothelial cell; Focal adhesion kinase; Integrin; Mitochondria; STAT3; Vitronectin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduced FAK-STAT3 signaling contributes to ER stress-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and death in endothelial cells.Cell Signal. 2017 Aug;36:154-162. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2017.05.007. Epub 2017 May 8. Cell Signal. 2017. PMID: 28495589 Free PMC article.
-
PDIA3 inhibits mitochondrial respiratory function in brain endothelial cells and C. elegans through STAT3 signaling and decreases survival after OGD.Cell Commun Signal. 2021 Dec 18;19(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s12964-021-00794-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2021. PMID: 34922569 Free PMC article.
-
Blood vitronectin is a major activator of LIF and IL-6 in the brain through integrin-FAK and uPAR signaling.J Cell Sci. 2018 Feb 2;131(3):jcs202580. doi: 10.1242/jcs.202580. J Cell Sci. 2018. PMID: 29222114 Free PMC article.
-
Role of focal adhesion kinase in integrin signaling.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1997 Aug-Sep;29(8-9):1085-96. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(97)00051-4. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9416004 Review.
-
Endosomes: Emerging Platforms for Integrin-Mediated FAK Signalling.Trends Cell Biol. 2016 Jun;26(6):391-398. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2016.02.001. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Trends Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26944773 Review.
Cited by
-
NRF2 regulates the sensitivity of human NSCLC cells to cystine deprivation-induced ferroptosis via FOCAD-FAK signaling pathway.Redox Biol. 2020 Oct;37:101702. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101702. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Redox Biol. 2020. PMID: 32898818 Free PMC article.
-
Osteopontin-Enhanced Autophagy Attenuates Early Brain Injury via FAK-ERK Pathway and Improves Long-Term Outcome after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats.Cells. 2019 Aug 27;8(9):980. doi: 10.3390/cells8090980. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31461955 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Effect of CeO2@PAA-LXW7 Against H2O2-Induced Cytotoxicity in NGF-Differentiated PC12 Cells.Neurochem Res. 2018 Jul;43(7):1439-1453. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2559-y. Epub 2018 Jun 7. Neurochem Res. 2018. PMID: 29882125
-
Loss of the matrix metalloproteinase-10 causes premature features of aging in satellite cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 May 9;11:1128534. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1128534. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37228645 Free PMC article.
-
Edaravone alleviates cell apoptosis and mitochondrial injury in ischemia-reperfusion-induced kidney injury via the JAK/STAT pathway.Biol Res. 2020 Jul 3;53(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s40659-020-00297-0. Biol Res. 2020. PMID: 32620154 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

