Degradation of Mrc1 promotes recombination-mediated restart of stalled replication forks
- PMID: 27956499
- PMCID: PMC5389566
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw1249
Degradation of Mrc1 promotes recombination-mediated restart of stalled replication forks
Abstract
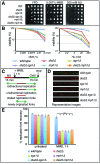
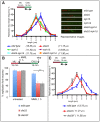
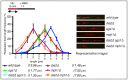
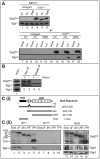
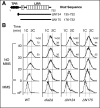
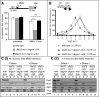
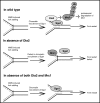
The DNA replication or S-phase checkpoint monitors the integrity of DNA synthesis. Replication stress or DNA damage triggers fork stalling and checkpoint signaling to activate repair pathways. Recovery from checkpoint activation is critical for cell survival following DNA damage. Recovery from the S-phase checkpoint includes inactivation of checkpoint signaling and restart of stalled replication forks. Previous studies demonstrated that degradation of Mrc1, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae ortholog of human Claspin, is facilitated by the SCFDia2 ubiquitin ligase and is important for cell cycle re-entry after DNA damage-induced S-phase checkpoint activation. Here, we show that degradation of Mrc1 facilitated by the SCFDia2 complex is critical to restart stalled replication forks during checkpoint recovery. Using DNA fiber analysis, we showed that Dia2 functions with the Sgs1 and Mph1 helicases (orthologs of human BLM and FANCM, respectively) in the recombination-mediated fork restart pathway. In addition, Dia2 physically interacts with Sgs1 upon checkpoint activation. Importantly, failure to target Mrc1 for degradation during recovery inhibits Sgs1 chromatin association, but this can be alleviated by induced proteolysis of Mrc1 after checkpoint activation. Together, these studies provide new mechanistic insights into how cells recover from activation of the S-phase checkpoint.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genetic Evidence for Roles of Yeast Mitotic Cyclins at Single-Stranded Gaps Created by DNA Replication.G3 (Bethesda). 2018 Feb 2;8(2):737-752. doi: 10.1534/g3.117.300537. G3 (Bethesda). 2018. PMID: 29279302 Free PMC article.
-
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae F-box protein Dia2 is a mediator of S-phase checkpoint recovery from DNA damage.Genetics. 2013 Feb;193(2):483-99. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.146373. Epub 2012 Nov 19. Genetics. 2013. PMID: 23172854 Free PMC article.
-
Mrc1 and DNA polymerase epsilon function together in linking DNA replication and the S phase checkpoint.Mol Cell. 2008 Oct 10;32(1):106-17. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.08.020. Mol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18851837 Free PMC article.
-
Recovery from the DNA Replication Checkpoint.Genes (Basel). 2016 Oct 28;7(11):94. doi: 10.3390/genes7110094. Genes (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27801838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RecQ helicases: guardian angels of the DNA replication fork.Chromosoma. 2008 Jun;117(3):219-33. doi: 10.1007/s00412-007-0142-4. Epub 2008 Jan 11. Chromosoma. 2008. PMID: 18188578 Review.
Cited by
-
Homologous Recombination: To Fork and Beyond.Genes (Basel). 2018 Dec 4;9(12):603. doi: 10.3390/genes9120603. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30518053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network in mural granulosa cells of patients with polycystic ovary syndrome: an analysis of Gene Expression Omnibus data.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Jul;9(14):1156. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-2696. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34430597 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Structure-Specific Endonucleases in Replication Stress.Genes (Basel). 2018 Dec 14;9(12):634. doi: 10.3390/genes9120634. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30558228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fanconi anemia and mTOR pathways functionally interact during stalled replication fork recovery.FEBS Lett. 2021 Mar;595(5):595-603. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14035. Epub 2021 Jan 28. FEBS Lett. 2021. PMID: 33423298 Free PMC article.
-
Maintenance of Yeast Genome Integrity by RecQ Family DNA Helicases.Genes (Basel). 2020 Feb 18;11(2):205. doi: 10.3390/genes11020205. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32085395 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boddy M.N., Russell P.. DNA replication checkpoint. Curr. Biol. 2001; 11:R953–R956. - PubMed
-
- Tercero J.A., Diffley J.F.. Regulation of DNA replication fork progression through damaged DNA by the Mec1/Rad53 checkpoint. Nature. 2001; 412:553–557. - PubMed
-
- Nyberg K.A., Michelson R.J., Putnam C.W., Weinert T.A.. Toward maintaining the genome: DNA damage and replication checkpoints. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2002; 36:617–656. - PubMed
-
- Branzei D., Foiani M.. The DNA damage response during DNA replication. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2005; 17:568–575. - PubMed
-
- Kondo T., Wakayama T., Naiki T., Matsumoto K., Sugimoto K.. Recruitment of Mec1 and Ddc1 checkpoint proteins to double-strand breaks through distinct mechanisms. Science. 2001; 294:867–870. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

