Voltage-Dependent Anion Channel 1(VDAC1) Participates the Apoptosis of the Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Desminopathy
- PMID: 27941998
- PMCID: PMC5152834
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167908
Voltage-Dependent Anion Channel 1(VDAC1) Participates the Apoptosis of the Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Desminopathy
Abstract
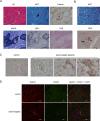
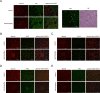
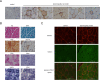
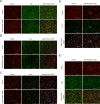
Desminopathies caused by the mutation in the gene coding for desmin are genetically protein aggregation myopathies. Mitochondrial dysfunction is one of pathological changes in the desminopathies at the earliest stage. The molecular mechanisms of mitochondria dysfunction in desminopathies remain exclusive. VDAC1 regulates mitochondrial uptake across the outer membrane and mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP). Relationships between desminopathies and Voltage-dependent anion channel 1 (VDAC1) remain unclear. Here we successfully constructed the desminopathy rat model, evaluated with conventional stains, containing hematoxylin and eosin (HE), Gomori Trichrome (MGT), (PAS), red oil (ORO), NADH-TR, SDH staining and immunohistochemistry. Immunofluorescence results showed that VDAC1 was accumulated in the desmin highly stained area of muscle fibers of desminopathy patients or desminopathy rat model compared to the normal ones. Meanwhile apoptosis related proteins bax and ATF2 were involved in desminopathy patients and desminopathy rat model, but not bcl-2, bcl-xl or HK2.VDAC1 and desmin are closely relevant in the tissue splices of deminopathies patients and rats with desminopathy at protein lever. Moreover, apoptotic proteins are also involved in the desminopathies, like bax, ATF2, but not bcl-2, bcl-xl or HK2. This pathological analysis presents the correlation between VDAC1 and desmin, and apoptosis related proteins are correlated in the desminopathy. Furthermore, we provide a rat model of desminopathy for the investigation of desmin related myopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
VDAC1 deacetylation is involved in the protective effects of resveratrol against mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in cardiomyocytes subjected to anoxia/reoxygenation injury.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Nov;95:77-83. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.08.046. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28826100
-
Mouse uterine epithelial apoptosis is associated with expression of mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channels, release of cytochrome C from mitochondria, and the ratio of Bax to Bcl-2 or Bcl-X.Biol Reprod. 2003 Apr;68(4):1178-84. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.102.007997. Epub 2002 Oct 30. Biol Reprod. 2003. PMID: 12606449
-
Differential proteomic analysis of abnormal intramyoplasmic aggregates in desminopathy.J Proteomics. 2013 Sep 2;90:14-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2013.04.026. Epub 2013 Apr 30. J Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 23639843 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channel 1 in tumor cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Oct;1848(10 Pt B):2547-75. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2014.10.040. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25448878 Review.
-
Oligomerization of the mitochondrial protein VDAC1: from structure to function and cancer therapy.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2013;117:303-34. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386931-9.00011-8. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2013. PMID: 23663973 Review.
Cited by
-
VDAC1 is essential for neurite maintenance and the inhibition of its oligomerization protects spinal cord from demyelination and facilitates locomotor function recovery after spinal cord injury.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 1;9(1):14063. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50506-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31575916 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial quality control in health and cardiovascular diseases.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Nov 6;11:1290046. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1290046. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 38020895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skeletal Muscle Dysfunction in Experimental Pulmonary Hypertension.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 18;23(18):10912. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810912. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142826 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and signaling proteins in the Z-disk and their role in cardiomyopathies.Front Physiol. 2023 Mar 2;14:1143858. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1143858. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36935760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical contribution of mitochondria in the development of cardiomyopathy linked to desmin mutation.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Jan 2;15(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03619-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38167524 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sugawara M, Kato K, Komatsu M, Wada C, Kawamura K, Shindo PS, et al. A novel de novo mutation in the desmin gene causes desmin myopathy with toxic aggregates. Neurology. 2000;55(7):986–90. Epub 2000/11/04. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

